
The United Nations Economic Commission for Europe is one of the five regional commissions under the jurisdiction of the United Nations Economic and Social Council. It was established in order to promote economic cooperation and integration among its member states.
UN/CEFACT is the United Nations Centre for Trade Facilitation and Electronic Business. It was established as an intergovernmental body of the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) in 1996 and evolved from UNECE's long tradition of work in trade facilitation which began in 1957.

The International Chamber of Commerce is the largest, most representative business organization in the world. Its over 45 million members in over 100 countries have interests spanning every sector of private enterprise.
The UNECE Convention on Access to Information, Public Participation in Decision-making and Access to Justice in Environmental Matters, usually known as the Aarhus Convention, was signed on 25 June 1998 in the Danish city of Aarhus. It entered into force on 30 October 2001. As of March 2014, it had 47 parties—46 states and the European Union. All of the ratifying states are in Europe and Central Asia. The EU has begun applying Aarhus-type principles in its legislation, notably the Water Framework Directive. Liechtenstein and Monaco have signed the convention but have not ratified it.

Dangerous goods (DG), are substances that when transported are a risk to health, safety, property or the environment. Certain dangerous goods that pose risks even when not being transported are known as hazardous materials. An example for dangerous goods is hazardous waste which is waste that has substantial or potential threats to public health or the environment.

The CMR Convention is a United Nations convention that was signed in Geneva on 19 May 1956. It relates to various legal issues concerning transportation of cargo by road. It has been ratified by the majority of European states. As of January 2022, it has been ratified by 58 states.
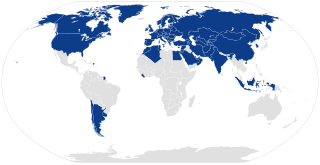
The Convention on International Transport of Goods Under Cover of TIR Carnets is a multilateral treaty that was concluded at Geneva on 14 November 1975 to simplify and harmonise the administrative formalities of international road transport. The 1975 convention replaced the TIR Convention of 1959, which itself replaced the 1949 TIR Agreement between a number of European countries. The conventions were adopted under the auspices of the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE). As of December 2020, there are 77 parties to the Convention, including 76 states and the European Union.
Type approval or certificate of conformity is granted to a product that meets a minimum set of regulatory, technical and safety requirements. Generally, type approval is required before a product is allowed to be sold in a particular country, so the requirements for a given product will vary around the world. Processes and certifications known as type approval in English are often called homologation, or some cognate expression, in other European languages.
The International Organization of Motor Vehicle Manufacturers, founded 1919 in Paris, is an international trade association whose members are 39 national automotive industry trade associations. OICA facilitates communication among its member national automotive industry trade associations and advocates for policies and position of mutual interest to its members at the international level and to the general public.

The World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations is a working party (WP.29) of the Inland Transport Committee (ITC) of the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE). Its responsibility is to manage the multilateral Agreements signed in 1958, 1997 and 1998 concerning the technical prescriptions for the construction, approval of wheeled vehicles as well as their Periodic Technical Inspection and, to operate within the framework of these three Agreements to develop and amend UN Regulations, UN Global Technical Regulations and UN Rules, kind of vehicle regulation.
UN/CEFACT TBG5 is the entity responsible for financial services under the United Nations Centre for Trade facilitation and Electronic Business, (UN/CEFACT) under the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE).

The European Environmental Bureau (EEB) is a network of around 180 environmental citizens' organisations based in more than 40 countries. The EEB is a democratic federation, representing local, national, European and international groups in European Union Member States, plus some accession and neighbouring countries. It plays a prominent role in defending and promoting environmental interests and legislation at the different EU institutions.

An International Certificate of Competence (ICC) is a certificate that may be issued to anyone who has successfully completed certain national boating licenses or has passed an examination to prove the necessary competence for pleasure craft operation. ICC is the only sailing license approved by United Nations as a legitimate recreational sailing license.

TRACECA is an international transport programme involving the European Union and 12 member states of the Eastern European, Caucasus, and Central Asian region. The programme aim is to strengthen economic relations, trade, and transport in the regions of the Black Sea basin, South Caucasus, and Central Asia. It has a permanent Secretariat, originally financed by the European Commission, in Baku, Azerbaijan, and a regional office in Odesa, Ukraine. Since 2009, the organization has been entirely financed by member countries.
Vehicle regulations are requirements that automobiles must satisfy in order to be approved for sale or use in a particular country or region. They are usually mandated by legislation, and administered by a government body. The regulations concern aspects such as lighting, controls, crashworthiness, environment protection and theft protection, and might include safety belts or automated features.
Government regulation in the automotive industry directly affects the way cars look, how their components are designed, the safety features that are included, and the overall performance of any given vehicle. As a result, these regulations also have a significant effect on the automotive business by generally increasing production costs while also placing limitations on how cars are sold and marketed. Automotive regulations are designed to benefit the consumer and protect the environment, and automakers can face stiff fines and other penalties if they are not followed.

The South African Bureau of Standards (SABS) is a South African statutory body that was established in terms of the Standards Act and continues to operate in terms of the latest edition of the Standards Act, 2008 as the national institution for the promotion and maintenance of standardization and quality in connection with commodities and the rendering of services.

The UNECE Environmental Performance Review (EPR) is an assessment process to evaluate the progress made by individual countries in improving their environmental policies. The EPRs are carried out under the auspices of the Committee on Environmental Policy of the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE).
Regulation of self-driving cars, autonomous vehicles and automated driving system is an increasingly relevant topic in the automotive industry strongly related to the success of the actual technology. Multiple countries have passed local legislation and agreed on standards for the introduction of autonomous cars.









