
Biogas is a gaseous renewable energy source produced from raw materials such as agricultural waste, manure, municipal waste, plant material, sewage, green waste, wastewater, and food waste. Biogas is produced by anaerobic digestion with anaerobic organisms or methanogens inside an anaerobic digester, biodigester or a bioreactor. The gas composition is primarily methane and carbon dioxide and may have small amounts of hydrogen sulfide, moisture and siloxanes. The methane can be combusted or oxidized with oxygen. This energy release allows biogas to be used as a fuel; it can be used in fuel cells and for heating purpose, such as in cooking. It can also be used in a gas engine to convert the energy in the gas into electricity and heat.
Alternative technology is a term used to refer to technologies that are more environmentally friendly than the functionally equivalent technologies dominant in current practice. The term was coined by Peter Harper, one of the founders of the Centre for Alternative Technology, North Wales, in Undercurrents (magazine) in the 1970s. Alternative Technologies are created to be safer, cleaner, and overall more efficient. The goals of alternative technology are to decrease demand for critical elements by ensuring a secure supply of technology that is environmentally friendly, increased efficiency with lower costs, and with more common materials to avoid potential future materials crises. Alternative technologies use renewable energy sources such as solar power and wind energy. Some alternative technologies have in the past or may in the future become widely adopted, after which they might no longer be considered "alternative." For example, the use of wind turbines to produce electricity.

Cogeneration or combined heat and power (CHP) is the use of a heat engine or power station to generate electricity and useful heat at the same time.
The Renewables Obligation (RO) is a market support mechanism designed to encourage generation of electricity from eligible renewable sources in the United Kingdom. There are three related schemes for the three legal jurisdictions of the UK. In April 2022 the Renewables Obligation was introduced in England and Wales, and in Scotland as the Renewables Obligation (Scotland). The RO was later introduced in Northern Ireland in April 2005. In all cases, the RO replaced the Non-Fossil Fuel Obligation which operated from 1990.

Anaerobic digestion is a sequence of processes by which microorganisms break down biodegradable material in the absence of oxygen. The process is used for industrial or domestic purposes to manage waste or to produce fuels. Much of the fermentation used industrially to produce food and drink products, as well as home fermentation, uses anaerobic digestion.

District heating is a system for distributing heat generated in a centralized location through a system of insulated pipes for residential and commercial heating requirements such as space heating and water heating. The heat is often obtained from a cogeneration plant burning fossil fuels or biomass, but heat-only boiler stations, geothermal heating, heat pumps and central solar heating are also used, as well as heat waste from factories and nuclear power electricity generation. District heating plants can provide higher efficiencies and better pollution control than localized boilers. According to some research, district heating with combined heat and power (CHPDH) is the cheapest method of cutting carbon emissions, and has one of the lowest carbon footprints of all fossil generation plants.
Renewable natural gas (RNG), also known as biomethane, is a renewable fuel and biogas which has been upgraded to a quality similar to fossil natural gas and has a methane concentration of 90% or greater. By removing CO2 and other impurities from biogas, and increasing the concentration of methane to a level similar to fossil natural gas, it becomes possible to distribute RNG via existing gas pipeline infrastructure. RNG can be used in existing appliances, including vehicles with natural gas burning engines (natural gas vehicles).

Waste-to-energy (WtE) or energy-from-waste (EfW) refers to a series of processes designed to convert waste materials into usable forms of energy, typically electricity or heat. As a form of energy recovery, WtE plays a crucial role in both waste management and sustainable energy production by reducing the volume of waste in landfills and providing an alternative energy source.
A mechanical biological treatment (MBT) system is a type of waste processing facility that combines a sorting facility with a form of biological treatment such as composting or anaerobic digestion. MBT plants are designed to process mixed household waste as well as commercial and industrial wastes.
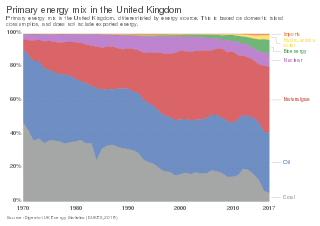
The energy policy of the United Kingdom refers to the United Kingdom's efforts towards reducing energy intensity, reducing energy poverty, and maintaining energy supply reliability. The United Kingdom has had success in this, though energy intensity remains high. There is an ambitious goal to reduce carbon dioxide emissions in future years, but it is unclear whether the programmes in place are sufficient to achieve this objective. Regarding energy self-sufficiency, UK policy does not address this issue, other than to concede historic energy security is currently ceasing to exist.

The bioconversion of biomass to mixed alcohol fuels can be accomplished using the MixAlco process. Through bioconversion of biomass to a mixed alcohol fuel, more energy from the biomass will end up as liquid fuels than in converting biomass to ethanol by yeast fermentation.

The production of renewable energy in Scotland is a topic that came to the fore in technical, economic, and political terms during the opening years of the 21st century. The natural resource base for renewable energy is high by European, and even global standards, with the most important potential sources being wind, wave, and tide. Renewables generate almost all of Scotland's electricity, mostly from the country's wind power.
The Directive on the promotion of cogeneration based on a useful heat demand in the internal energy market and amending Directive 92/42/EEC, officially Directive 2004/8/EC, is a European Union directive for promoting the use of cogeneration, popularly better known as the 'Combined Heat and Power (CHP) Directive'.

The energy policy of Malaysia is determined by the Malaysian Government, which address issues of energy production, distribution, and consumption. The Department of Electricity and Gas Supply acts as the regulator while other players in the energy sector include energy supply and service companies, research and development institutions and consumers. Government-linked companies Petronas and Tenaga Nasional Berhad are major players in Malaysia's energy sector.
A feed-in tariff (FIT) is paid by energy suppliers in the United Kingdom if a property or organisation generates their own electricity using technology such as solar panels or wind turbines and feeds any surplus back to the grid. The FIT scheme was imposed on suppliers by the UK government, and applied to installations completed between July 2009 and March 2019.

The Association for Renewable Energy and Clean Technology, previously known as Renewable Energy Association (REA), is a renewable energy and clean technology trade association in the UK encompassing all of renewables industry in the United Kingdom. REA covers renewable power & flexibility, heat and cooling, circular bioresources and transport. The REA is a not-for-profit company.

The Clean Energy Finance Corporation (CEFC) is an Australian Government-owned green bank that invests in clean energy, to help achieve Australia's national goal of net zero emissions by 2050. The CEFC invests billions of dollars on behalf of the Australian Government in economy-wide decarbonisation opportunities. It aims to help transform the Australian energy grid, as well as supporting sustainable housing initiatives, and climate tech innovators. It was established by and operates under the Clean Energy Finance Corporation Act 2012, along with other subsidiary legislation. As of March 2024 Steven Skala is CEFC chair and Ian Learmonth is CEFC Chief Executive Officer.

Harvest Power, Inc. was a privately held organics management company headquartered in Waltham, Massachusetts, United States that specializes in converting food waste and yard waste into biofuel, compost, mulch and fertilizer. In 2014 Fast Company named it one of the most innovative companies in the world. In August of 2020 Harvest Power Orlando ceased operations for unknown reasons and all assets were put up for sale; the company was dissolved in April 2021.
Biogen (UK) Ltd is a leading UK owner and operator of anaerobic digestion and composting plants based in Bedfordshire. It is responsible for the construction of 22 plants to date and currently operates Nineteen anaerobic digestion plants in England, Scotland and Wales.
Octopus Energy Group is a British renewable energy group. It was founded in 2015 with the backing of Octopus Group, a British asset management company. Headquartered in London, the company has operations in the United Kingdom, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, Australia, Japan, New Zealand and the United States. Octopus is the UK's largest supplier of electricity to domestic customers, and the second largest in domestic gas.










