The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) maintained a number of airfields in Nebraska from 1939-1945. They were training centers for pilots and aircrews of fighters and bombers during World War II. Nebraska was a favored location because it has excellent, year-round flying conditions. The sparsely populated land made ideal locations for gunnery, bombing, and training ranges.
During World War II, Kansas was a major United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) training center for pilots and aircrews of USAAF fighters and bombers. Kansas was favored because it has excellent, year-round flying conditions. The sparsely populated land made ideal locations for gunnery, bombing, and training ranges.

During World War II, the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) established numerous airfields in Alabama for antisubmarine defense in the Gulf of Mexico and for training pilots and aircrews of AAF fighters and bombers.
During World War II, the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) established numerous air facilities in Louisiana for antisubmarine defense in the Gulf of Mexico and for training pilots and aircrews of USAAF fighters and bombers. The larger facilities were Army Air Bases (AAB) while the Army Air Fields ( AAFld) were lesser facilities. The map below shows both types as AAB and AAF.
During World War II, the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) established numerous airfields in Tennessee for training pilots and aircrews of USAAF fighters and bombers.
During World War II, the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) established numerous airfields in North Dakota for training pilots and aircrews of USAAF fighters and bombers.
During World War II, the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) established numerous airfields in Maryland for training pilots and aircrews of USAAF fighters and bombers.
During World War II, the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) established numerous airfields in Michigan for training pilots and aircrews of USAAF fighters and bombers.
During World War II, the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) established numerous airfields in Minnesota for training pilots and aircrews of USAAF fighters and bombers.
During World War II, the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) established numerous airfields in Missouri for training pilots and aircrews of USAAF fighters and bombers.
During World War II, the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) established numerous airfields in New York for training pilots and aircrews of USAAF fighters and bombers.
During World War II, the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) established numerous airfields in Pennsylvania for training pilots and aircrews of USAAF fighters and bombers.

During World War II, the United States Army Air Forces engaged in combat against the air, ground and naval forces of the Empire of Japan in the South West Pacific Theatre.

During World War II, the United States Army Air Forces engaged in combat against the Empire of Japan in the South Pacific Area. As defined by the War Department, this consisted of the Pacific Ocean areas which lay south of the Equator between longitude 159° East and 110° West. It included New Zealand, New Caledonia, New Hebrides, Fiji, and most of the Solomon Islands.
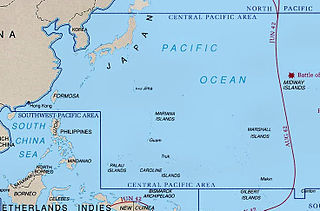
During World War II, the United States Army Air Forces fought the Empire of Japan in the Central Pacific Area. As defined by the War Department, this consisted of most of the Pacific Ocean and its islands, excluding the Philippines, Australia, the Netherlands East Indies, the Territory of New Guinea the Solomon Islands and areas to the south and east of the Solomons.

Cross City Air Force Station is a former United States Air Force facility, located 1.6 miles (2.6 km) east of Cross City, Florida.

Stuttgart Army Airfield is a former World War II military airfield, located 7 miles north of Stuttgart, Arkansas. It operated as an advanced pilot training school for the United States Army Air Forces from 1942 until 1945.

The San Francisco Air Defense Sector (SFADS) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with the 28th Air Division, being stationed at Beale Air Force Base, California.

The Sioux City Air Defense Sector (SCADS) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with the Air Defense Command 29th Air Division, being stationed at Sioux City Air Force Station, Iowa.
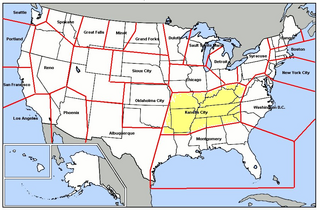
The Kansas City Air Defense Sector (KCADS) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with the Air Defense Command 29th Air Division, being stationed at Richards-Gebaur Air Force Base, Missouri. It was inactivated on 1 January 1962.