Altamira is one of one hundred and forty-four municipalities in the state of Pará, in northern Brazil. It has an area of 159,533.73 square kilometres or 61,596.32 square miles, making it the largest municipality by area both in Pará state and Brazil, and until 2009 it was the world's largest municipal subdivision. It occupies 12.8% of the state's territory, 1.8% of Brazil's territory and 0.8% of South America. It also covers a more extensive area than 104 countries, and is comparable to the US states of Missouri and Florida.
The Jutaí-Solimões Ecological Station is an ecological station in the state of Amazonas, Brazil. It protects an area of flooded and terra firme forest in the Amazon biome.
Rio Acre Ecological Station is an ecological station in the state of Acre, Brazil.
Serra das Araras Ecological Station is an ecological station in Mato Grosso, Brazil. It contains a sample of the Cerrado biome.
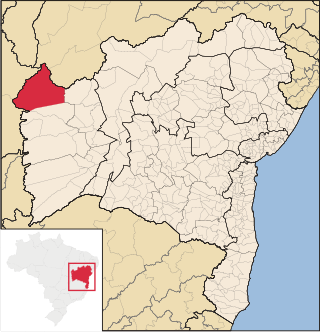
Formosa do Rio Preto is the westernmost and largest city in the Brazilian state of Bahia. It is also the largest in all Northeastern Brazil.

Oriximiná is the westernmost and second-largest municipality in the Brazilian state of Pará. It is also the fourth-largest in the country.

Mateiros is the easternmost city in the state of Tocantins. It is the only city in Tocantins to border the state of Piauí.
The Curuaés River is a river of Pará state in north-central Brazil. It is a right tributary of the Curuá River in the Xingu River basin.

The Curuá River is a tributary of the Iriri River in Pará state in north-central Brazil. The river flows through the Tapajós-Xingu moist forests ecoregion. The river rises in the 342,192 hectares Nascentes da Serra do Cachimbo Biological Reserve, a strictly protected conservation unit established in 2005. It is one of the headwaters of the Xingu River.
The Ipiranga River is a tributary of the Iriri River in Pará state in north-central Brazil.

The Cristalino River is a river of the states of Pará and Mato Grosso in western Brazil. It is a tributary of the Teles Pires.

The Macacu River is a river of Rio de Janeiro state in southeastern Brazil.

São Félix do Xingu is a municipality in the state of Pará in the Northern region of Brazil.

Novo Progresso is a municipality in the state of Pará in the Northern region of Brazil.
Serra do Cachimbo is a low mountain range in the southern part of the state of Pará, Brazil. It is located mostly in the municipalities of Altamira, Itaituba, Jacareacanga, and Novo Progresso.
Cuniã Ecological Station is a strictly protected ecological station in the states of Amazonas and Rondônia, Brazil. It preserves an area of savannah parkland on the border of the Amazon rainforest. The conservation unit is rich in lakes and ponds, and serves as a nursery for various species of fish.
The Nascentes da Serra do Cachimbo Biological Reserve is a biological reserve in the state of Pará, Brazil. The reserve protects an area in the transition between the Cerrado and Amazon biomes, supporting highly diverse flora and fauna including many endemic species. It is accessible via the BR-163 highway, and is among the federal conservation units in the Amazon Legal that has suffered most from deforestation.

Rio Novo National Park is a national park in the state of Pará, Brazil.

Terra do Meio Ecological Station is an ecological station (ESEC) in the state of Pará, Brazil.
Altamira National Forest is a national forest in the state of Pará, Brazil.