
In computing, a printer is a peripheral machine which makes a persistent representation of graphics or text, usually on paper. While most output is human-readable, bar code printers are an example of an expanded use for printers. Different types of printers include 3D printers, inkjet printers, laser printers, and thermal printers.

Screen printing is a printing technique where a mesh is used to transfer ink onto a substrate, except in areas made impermeable to the ink by a blocking stencil. A blade or squeegee is moved across the screen to fill the open mesh apertures with ink, and a reverse stroke then causes the screen to touch the substrate momentarily along a line of contact. This causes the ink to wet the substrate and be pulled out of the mesh apertures as the screen springs back after the blade has passed. One colour is printed at a time, so several screens can be used to produce a multi-coloured image or design.

Inkjet printing is a type of computer printing that recreates a digital image by propelling droplets of ink onto paper and plastic substrates. Inkjet printers were the most commonly used type of printer in 2008, and range from small inexpensive consumer models to expensive professional machines. By 2019, laser printers outsold inkjet printers by nearly a 2:1 ratio, 9.6% vs 5.1% of all computer peripherals.

Dye-sublimation printing is a term that covers several distinct digital computer printing techniques that involve using heat to transfer dye onto a substrate.

A T-shirt is a style of fabric shirt named after the T shape of its body and sleeves. Traditionally, it has short sleeves and a round neckline, known as a crew neck, which lacks a collar. T-shirts are generally made of stretchy, light, and inexpensive fabric and are easy to clean. The T-shirt evolved from undergarments used in the 19th century and, in the mid-20th century, transitioned from undergarments to general-use casual clothing.
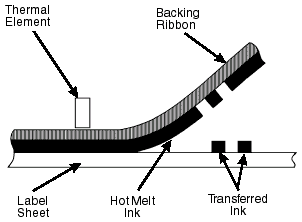
Thermal-transfer printing is a digital printing method in which material is applied to paper by melting a coating of ribbon so that it stays glued to the material on which the print is applied. It contrasts with direct thermal printing, where no ribbon is present in the process.

A label is a piece of paper, plastic film, cloth, metal, or other material affixed to a container or product, on which is written or printed information or symbols about the product or item. Information printed directly on a container or article can also be considered labelling.

Wide format printers are generally accepted to be any computer-controlled printing machines (printers) that support a maximum print roll width of between 18 and 100 inches. Printers with capacities over 100 in wide are considered super-wide or grand format. Wide-format printers are used to print banners, posters, trade show graphics, wallpaper, murals, backlit film (duratrans), vehicle image wraps, electronic circuit schematics, architectural drawings, construction plans, backdrops for theatrical and media sets, and any other large format artwork or signage. Wide-format printers usually employ some variant of inkjet or toner-based technology to produce the printed image; and are more economical than other print methods such as screen printing for most short-run print projects, depending on print size, run length, and the type of substrate or print medium. Wide-format printers are usually designed for printing onto a roll of print media that feeds incrementally during the print process, rather than onto individual sheets.

Textile printing is the process of applying color to fabric in definite patterns or designs. In properly printed fabrics the colour is bonded with the fibre, so as to resist washing and friction. Textile printing is related to dyeing but in dyeing properly the whole fabric is uniformly covered with one colour, whereas in printing one or more colours are applied to it in certain parts only, and in sharply defined patterns.

A laminator is a device which laminates pieces or rolls of paper or card stock.
Inkjet transfer or inkjet photo transfer is a technique to transfer a photograph or graphic, printed with an inkjet printer onto textiles, cups, CDs, glass and other surfaces.

A heat press is a machine engineered to imprint a design or graphic on a substrate, such as a t-shirt, with the application of heat and pressure for a preset period of time. While heat presses are often used to apply designs to fabrics, specially designed presses can also be used to imprint designs on mugs, plates, jigsaw puzzles, caps, and other products.

Thermal paper is a special fine paper that is coated with a material formulated to change color locally when exposed to heat. It is used in thermal printers, particularly in inexpensive devices such as adding machines, cash registers, and credit card terminals and small, lightweight portable printers.

Thermographic printing refers to two types of printing, both of which rely on heat to create the letters or images on a sheet of paper.

Transfer paper is used in textiles and arts and crafts projects. Transfer paper is a thin piece of paper coated with wax and pigment. Often, an ink-jet or other printer is used to print the image on the transfer paper. A heat press can transfer the image onto clothing, canvas, or other surface. Transfer paper is used in creating iron-ons. Transfer papers can also be used for the application of rhinestones to clothing and other arts and crafts projects.
In streetwear fashion, an all over print is a print composed of a design that is repeated across the entire surface of a garment. The image is on both the front and back. Often, such prints are screen printed. Other processes include dye-diffusion of the fabric itself and printed t-shirts. All over printing relies on synthetic fibers as they can best withstand the process. One way to check for all over printing is to be sure the pattern or design can be seen on the seam, hem, and around zippers.
Digital textile printing is described as any ink jet based method of printing colorants onto fabric. Most notably, digital textile printing is referred to when identifying either printing smaller designs onto garments and printing larger designs onto large format rolls of textile. The latter is a growing trend in visual communication, where advertisement and corporate branding is printed onto polyester media. Examples are: flags, banners, signs, retail graphics.

A vinyl cutter is an entry level machine for making signs. Computer designed vector files with patterns and letters are directly cut on the roll of vinyl which is mounted and fed into the vinyl cutter through USB or serial cable. Vinyl cutters are mainly used to make signs, banners and advertisements. Advertisements seen on automobiles and vans are often made with vinyl cut letters. While these machines were designed for cutting vinyl, they can also cut through computer and specialty papers, as well as thicker items like thin sheets of magnet.
Heat transfer vinyl (HTV) is a speciality polyurethane with a heat-activated adhesive that can be used on certain fabrics and materials to apply designs to promotional products, textiles and apparel, such as T-shirts. It comes laminated together with a clear polyester carrier in a roll or sheet form, with an adhesive tacky backing, so it can be cut, weeded, and placed on a substrate for application via a heat press. The design is cut into the material with a cutting plotter in reverse. The excess material is removed with tools such as hooks or tweezers - a manual and dextrous process referred to as "weeding". The tacky adhesive between the carrier and the vinyl holds together complex designs, although the labour naturally increases the more weeding that is required. The clear polyester carrier keeps the design visible to aid positioning on the substrate. For these and other reasons, it is a popular and more robust alternative to transfer paper. Heat transfer vinyl is made in single colors and also has special options such as patterned, glitter, flocked, holographic, glow-in-the-dark, reflective and 3D puff. Heat transfer vinyl also benefits from a high degree of stretch and rebound, achieved by a memory effect, making it suitable for use on apparel and other flexible items including the garments typically used, such as sports jerseys.















