
The AES Corporation is a Fortune 500 company that generates and distributes electrical power. AES is headquartered in Arlington, Virginia, and is one of the world's leading power companies, generating and distributing electric power in 15 countries and employing 10,500 people worldwide.

The Nellis Solar Power Plant is a 14-megawatt (MW) photovoltaic power station located within Nellis Air Force Base in Clark County, Nevada, northeast of Las Vegas. The power plant was inaugurated in a ceremony on December 17, 2007, with Nevada Governor Jim Gibbons activating its full operation. On average, it has since generated 32 gigawatt-hours of electricity annually and supplied more than 25% of the power used at the base.
The Cadiz Solar Power Plant is a 132.5 MW solar power plant in Cadiz, Negros Occidental, Philippines. Upon its completion, the facility located in a 176 hectares land in Hacienda Paz, Barangay Tinampaan and is the largest solar power facility in Southeast Asia upon its commissioning.
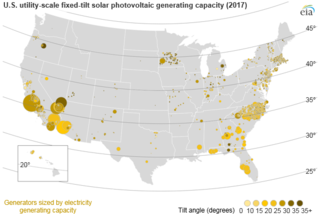
Solar power in the United States includes utility-scale solar power plants as well as local distributed generation, mostly from rooftop photovoltaics. As of the end of 2017, the United States had over 50 gigawatts (GW) of installed photovoltaic capacity. In 2018, utility scale solar power generated 66.6 terawatt-hours (TWh), 1.66% of total U.S. electricity. During the same time period total solar generation, including estimated small scale photovoltaic generation, was 96.1 TWh, 2.30% of total U.S. electricity. In terms of total cumulative installed capacity, by year end 2017 the United States ranked 2nd in the world behind China. In 2016, 39% of all new electricity generation capacity in the country came from solar, more than any other source and ahead of natural gas (29%). By 2015, solar employment had overtaken oil and gas as well as coal employment in the United States. In 2016, more than 260,000 Americans were employed in the solar industry.

Historically, the main applications of solar energy technologies in Canada have been non-electric active solar system applications for space heating, water heating and drying crops and lumber. In 2001, there were more than 12,000 residential solar water heating systems and 300 commercial/ industrial solar hot water systems in use. These systems presently comprise a small fraction of Canada’s energy use, but some government studies suggest they could make up as much as five per cent of the country’s energy needs by the year 2025.
The Windy Point/Windy Flats project, located in Goldendale, Washington, is the largest wind farm Washington State. The 90 square miles (230 km2) wind farm spans 26 miles (42 km) along the Columbia River ridgeline offering upon completion a capacity of 500 megawatts (MW).
Renewable energy in Morocco represented 0.4% of the national energy balance and nearly 10% of electricity production in 2007. Renewable energy is supported by strong hydropower sources and the newly installed wind energy parks. Morocco plans a $13 billion expansion of wind, solar and hydroelectric power generation capacity and associated infrastructure that should see the country get 42% of its electricity from renewable sources by 2020. The Moroccan government is keen on increasing renewable energy production, as Morocco's January–September oil bill reached about USD 1.4 billion in subsidies in 2009, registering a fall of 57.9% compared to 2008.

The Copper Mountain Solar Facility is a 552 megawatt (MWAC) solar photovoltaic power plant in Boulder City, Nevada developed by Sempra Generation. It uses approximately 9 million cadmium telluride modules made by the US thin-film manufacturer First Solar. When the first unit of the facility entered service on December 1, 2010, it was the largest photovoltaic plant in the U.S. at 58 MW. It is co-located with the 64 MW Nevada Solar One, 150 MW Boulder Solar, and 300 MW Techren Solar projects in the Eldorado Valley, thus forming a more than 1 gigawatt (GW) solar generating complex. By comparison, generating capacity at the nearby Hoover Dam is about 2 GW.

The Desert Sunlight Solar Farm is a 550 megawatt (MWAC) photovoltaic power station approximately six miles north of Desert Center, California, in the Mojave Desert. It uses approximately 8.8 million cadmium telluride modules made by the US thin-film manufacturer First Solar. As of Fall 2015, the Solar Farm has the same 550 MW installed capacity as the Topaz Solar Farm in the Carrizo Plain region of Central California, making both of them tied for the second largest completed solar plants by installed capacity.

Solar power in Mexico has the potential to produce vast amounts of energy. 70% of the country has an insolation of greater than 4.5 kWh/m²/day. Using 15% efficient photovoltaics, a square 25 km (16 mi) on each side in the state of Chihuahua or the Sonoran Desert could supply all of Mexico's electricity.

Solar power in Bulgaria has expanded by 100 megawatts (MW) in 2011. A 16.2 MW solar power plant in Zdravetz, Bulgaria was expected to be completed in June 2012. Power will be sold for $0.30/kWh in a fixed rate 20 year power purchase agreement.

Renewable energy in Nepal is a sector that is rapidly developing in Nepal. While Nepal mainly relies on hydroelectricity for its energy needs, solar and wind power is being seen as an important supplement to solve its energy crisis.
In 2018 Chile produced about 7% of its electricity from solar power. As of year end, it had 2137 MW of solar PV capacity.

The San Carlos Solar Energy Inc. (SaCaSol) I is a 22 megawatt (MW) solar photovoltaic power plant in San Carlos, Negros Occidental. It is currently the largest operational solar plant in the Philippines

islaSol I, formerly known as SaCaSol II is a 32-megawatt (MW) photovoltaic power station under construction developed by Bronzeoak Philippines for San Carlos Solar Energy Inc. (SaCaSol), in La Carlota, Negros Occidental.
The Boulder Solar project is a 150 megawatt (MWAC) photovoltaic power station near Boulder City, Nevada. It was built in two phases by SunPower using its Oasis Power Plant system. The project is co-located with several other large solar power projects in the Eldorado Valley.
San Carlos Solar Energy Inc. is a Philippine energy company based in San Carlos, Negros Occidental that generates renewable energy particularly solar energy.
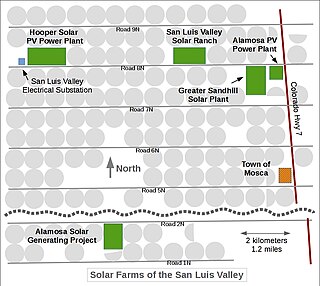
The Hooper Solar PV Power Plant is a 50 megawatt (MWAC) photovoltaic power station in the San Luis Valley, located near the town of Mosca, Colorado. It was the largest solar facility in the state when it came online at the end of 2015. The electricity is being sold to Public Service of Colorado, a subsidiary of Xcel Energy, under a long-term power purchase agreement.

The Comanche Solar Project is a 120 megawatt (MWAC) photovoltaic power station near the city of Pueblo, Colorado. It became the largest solar facility in the state when it came online in late 2016. The electricity is being sold to Public Service of Colorado, a subsidiary of Xcel Energy, under a 25-year power purchase agreement (PPA). Xcel determined through an open bid process that the PPA's terms were competitive with natural gas.

The San Isabel Solar Energy Center is a 30 megawatt (MWAC) photovoltaic power station in Las Animas County, Colorado located about 20 miles north of the city of Trinidad. The electricity is being sold to Tri-State Generation and Transmission under a 25-year power purchase agreement. It is the second solar project, following the Cimarron Solar Facility in year 2010, to be added to the utility cooperative's renewables portfolio.















