Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is a country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and its offshore islands in Melanesia. Its capital, located along its southeastern coast, is Port Moresby. The country is the world's third largest island country with an area of 462,840 km2 (178,700 sq mi).

Melanesia is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from New Guinea in the west to Tonga in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea and a few thousand islands.

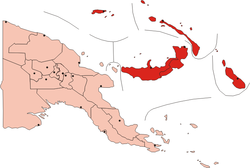
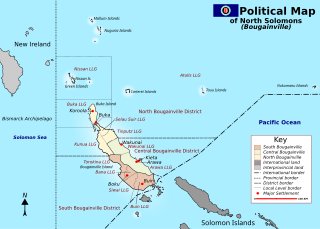
Bougainville, officially the Autonomous Region of Bougainville, is an autonomous region in Papua New Guinea. The largest island is Bougainville Island, while the region also includes Buka Island and a number of outlying islands and atolls. The interim capital is Buka, although this is considered temporary, with the capital likely to move. One potential location is Arawa, the previous capital.

Bougainville Island is the main island of the Autonomous Region of Bougainville, which is part of Papua New Guinea. It was previously the main landmass in the German Empire-associated North Solomons. Its land area is 9,300 km2 (3,600 sq mi). The population of the whole province, including nearby islets such as the Carterets, is approximately 300,000. The highest point is Mount Balbi, on the main island, at 2,715 m (8,907 ft). The much-smaller Buka Island, c. 500 km2 (190 sq mi), lies to the north, across the 400–500 m (1,300–1,600 ft) wide Buka Strait. Even though the strait is narrow, there is no bridge across it, but there is a regular ferry service between the key settlements on either side. The main airport in the north is in the town of Buka.

For administrative purposes, Papua New Guinea is divided into administrative divisions called provinces. There are 22 provincial-level divisions, which include 20 provinces, the Autonomous Region of Bougainville, and the National Capital District of Port Moresby.

Bougainville, an autonomous region of Papua New Guinea (PNG), has been inhabited by humans for at least 29,000 years, according to artefacts found in Kilu Cave on Buka Island. The region is named after Bougainville Island, the largest island of the Solomon Islands archipelago, but also contains a number of smaller islands.
The East Melanesian Islands, also known as the Solomons-Vanuatu-Bismarck moist forests, is a biogeographic region in the Melanesia subregion of Oceania. Biogeographically, the East Melanesian Islands are part of the Australasian realm.

Papua New Guinea is divided into four regions, which are its broadest administrative divisions of Papua New Guinea. While the 22 provincial-level divisions are the primary administrative divisions of PNG, the regions are quite significant in daily life, as they are often the basis for organisation of government services, corporate operations, sporting competitions, and even the machinations of politics.

Papua New Guinea has 326 local-level governments (LLGs) comprising 6,112 wards as of 2018.

Papua New Guinea, a sovereign state in Oceania, is the most linguistically diverse country in the world. According to Ethnologue, there are 839 living languages spoken in the country. In 2006, Papua New Guinea Prime Minister Sir Michael Somare stated that "Papua New Guinea has 832 living languages ." Languages with statutory recognition are Tok Pisin, English, Hiri Motu, and Papua New Guinean Sign Language. Tok Pisin, an English-based creole, is the most widely spoken, serving as the country's lingua franca. Papua New Guinean Sign Language became the fourth officially recognised language in May 2015, and is used by the deaf population throughout the country.

This page is a list of districts of Papua New Guinea.
For administrative purposes, Papua New Guinea (PNG) is divided into administrative divisions called regions and provinces. Papua New Guinea is divided into four regions and 22 province-level divisions: 20 provinces plus the autonomous region (Bougainville) and the National Capital District.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Solomon Islands:

The Republic of the North Solomons was an unrecognised state that purported to exist for about six months in what is now the Autonomous Region of Bougainville, Papua New Guinea (PNG). It involved:
a 'Unilateral Declaration of Independence of the Republic of North Solomons' and a failed bid for self-determination at the UN

The Solomon Islands is an archipelago in the western South Pacific Ocean, located northeast of Australia. The archipelago is in the Melanesia subregion and bioregion of Oceania. It forms the eastern boundary of the Solomon Sea. The archipelago forms much of the territory of Solomon Islands. The main islands are Choiseul, the Shortland Islands, the New Georgia Islands, Santa Isabel, the Russell Islands, the Florida Islands, Tulagi, Malaita, Maramasike, Ulawa, Owaraha, Makira, and Guadalcanal. The largest island, Bougainville Island, is geographically part of the Solomon Islands (archipelago), while politically an autonomous region of Papua New Guinea. The nation state of Solomon Islands covers a subset of the Solomon Islands archipelago and includes isolated low-lying coral atolls and high islands including Sikaiana, Rennell Island, Bellona Island, and the Santa Cruz Islands.

Buin is a town on Bougainville Island, and the capital of the South Bougainville District, in the Autonomous Region of Bougainville, in eastern Papua New Guinea. The island is in the northern Solomon Islands Archipelago of the Melanesia region, in the South Pacific Ocean.

John Momis is a Bougainvillean politician who served as the President of the Autonomous Region of Bougainville in Papua New Guinea between 2010 and 2020.
Noah Musingku, under the name "King David Peii II", is head of the twin "kingdoms" of Papaala and Me’ekamui on Bougainville Island in the North Solomon Islands. Musingku is the creator of U-Vistract which was banned as a pyramid scheme outside of the kingdoms. As of November 2020, his "kingdoms" remain at large, mainly due to fears of destabilising the island and because many of the local authorities have invested in him. Musinku's influence in Bougainville is widely considered one of the chief problems facing President of the Autonomous Region of Bougainville Ishmael Toroama in his attempts to stabilise Bougainville in preparation for its independence.
The Bougainville conflict, also known as the Bougainville Civil War, was a multi-layered armed conflict fought from 1988 to 1998 in the North Solomons Province of Papua New Guinea (PNG) between PNG and the secessionist forces of the Bougainville Revolutionary Army (BRA), and between the BRA and other armed groups on Bougainville. The conflict was described by Bougainvillean President John Momis as the largest conflict in Oceania since the end of World War II in 1945, with an estimated 15,000–20,000 Bougainvilleans dead, although lower estimates place the toll at around 1,000–2,000.

A non-binding independence referendum was held in Bougainville, an autonomous region of Papua New Guinea, between 23 November and 7 December 2019. The referendum question was a choice between greater autonomy within Papua New Guinea and full independence; voters voted overwhelmingly (98.31%) for independence.