
In biology, histones are highly basic proteins abundant in lysine and arginine residues that are found in eukaryotic cell nuclei. They act as spools around which DNA winds to create structural units called nucleosomes. Nucleosomes in turn are wrapped into 30-nanometer fibers that form tightly packed chromatin. Histones prevent DNA from becoming tangled and protect it from DNA damage. In addition, histones play important roles in gene regulation and DNA replication. Without histones, unwound DNA in chromosomes would be very long. For example, each human cell has about 1.8 meters of DNA if completely stretched out; however, when wound about histones, this length is reduced to about 90 micrometers (0.09 mm) of 30 nm diameter chromatin fibers.

Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH+
3 form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a side chain lysyl ((CH2)4NH2), classifying it as a basic, charged (at physiological pH), aliphatic amino acid. It is encoded by the codons AAA and AAG. Like almost all other amino acids, the α-carbon is chiral and lysine may refer to either enantiomer or a racemic mixture of both. For the purpose of this article, lysine will refer to the biologically active enantiomer L-lysine, where the α-carbon is in the S configuration.

Histone acetyltransferases (HATs) are enzymes that acetylate conserved lysine amino acids on histone proteins by transferring an acetyl group from acetyl-CoA to form ε-N-acetyllysine. DNA is wrapped around histones, and, by transferring an acetyl group to the histones, genes can be turned on and off. In general, histone acetylation increases gene expression.

Elastin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ELN gene. Elastin is a key component of the extracellular matrix in gnathostomes. It is highly elastic and present in connective tissue allowing many tissues in the body to resume their shape after stretching or contracting. Elastin helps skin to return to its original position when it is poked or pinched. Elastin is also an important load-bearing tissue in the bodies of vertebrates and used in places where mechanical energy is required to be stored.

Elastic cartilage, fibroelastic cartilage or yellow fibrocartilage is a type of cartilage present in the pinnae (auricles) of the ear giving it shape, provides shape for the lateral region of the external auditory meatus, medial part of the auditory canal Eustachian tube, corniculate and cuneiform laryneal cartilages, and the epiglottis. It contains elastic fiber networks and collagen type II fibers. The principal protein is elastin.
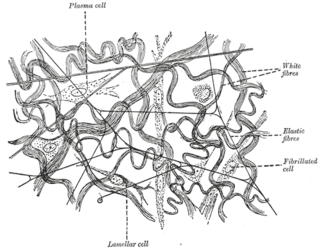
Elastic fibers are an essential component of the extracellular matrix composed of bundles of proteins (elastin) which are produced by a number of different cell types including fibroblasts, endothelial, smooth muscle, and airway epithelial cells. These fibers are able to stretch many times their length, and snap back to their original length when relaxed without loss of energy. Elastic fibers include elastin, elaunin and oxytalan.

Histone H3 is one of the five main histones involved in the structure of chromatin in eukaryotic cells. Featuring a main globular domain and a long N-terminal tail, H3 is involved with the structure of the nucleosomes of the 'beads on a string' structure. Histone proteins are highly post-translationally modified however Histone H3 is the most extensively modified of the five histones. The term "Histone H3" alone is purposely ambiguous in that it does not distinguish between sequence variants or modification state. Histone H3 is an important protein in the emerging field of epigenetics, where its sequence variants and variable modification states are thought to play a role in the dynamic and long term regulation of genes.
Lysyl oxidase (LOX), also known as protein-lysine 6-oxidase, is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the LOX gene. It catalyzes the conversion of lysine residues into its aldehyde derivative allysine. Allysine form cross-links in extracellular matrix proteins. Inhibition of lysyl oxidase can cause osteolathyrism, but, at the same time, its upregulation by tumor cells may promote metastasis of the existing tumor, causing it to become malignant and cancerous.

Desmosine is an amino acid found uniquely in elastin, a protein found in connective tissue such as skin, lungs, and elastic arteries.
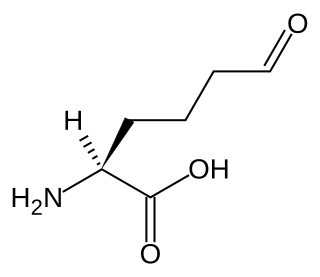
Allysine is a derivative of lysine that features a formyl group in place of the terminal amine. The free amino acid does not exist, but the allysine residue does. It is produced by aerobic oxidation of lysine residues by the enzyme lysyl oxidase. The transformation is an example of a post-translational modification. The semi-aldehyde form exists in equilibrium with a cyclic derivative.
In molecular biology, the protein domain Saccharopine dehydrogenase (SDH), also named Saccharopine reductase, is an enzyme involved in the metabolism of the amino acid lysine, via an intermediate substance called saccharopine. The Saccharopine dehydrogenase enzyme can be classified under EC 1.5.1.7, EC 1.5.1.8, EC 1.5.1.9, and EC 1.5.1.10. It has an important function in lysine metabolism and catalyses a reaction in the alpha-Aminoadipic acid pathway. This pathway is unique to fungal organisms therefore, this molecule could be useful in the search for new antibiotics. This protein family also includes saccharopine dehydrogenase and homospermidine synthase. It is found in prokaryotes, eukaryotes and archaea.
The enzyme Lysine decarboxylase converts lysine to cadaverine.

Galactosidase, beta 1, also known as GLB1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the GLB1 gene.
In enzymology, a lysine carbamoyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a lysine—tRNA ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Rombo syndrome is a very rare genetic disorder characterized mainly by atrophoderma vermiculatum of the face, multiple milia, telangiectases, acral erythema, peripheral vasodilation with cyanosis, and a propensity to develop basal cell carcinomas.

Copper peptide GHK-Cu is a naturally occurring copper complex of the tripeptide glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine. The tripeptide has strong affinity for copper(II) and was first isolated from human plasma. It can be found also in saliva and urine.

In molecular biology, the trappin protein transglutaminase binding domain or cementoin is a protein domain found at the N-terminus of Whey Acidic Protein (WAP) domain-containing protease inhibitors such as trappin-2. This N-terminal domain enables it to become cross-linked to extracellular matrix proteins by transglutaminase. This domain contains several repeated motifs with the consensus sequence Gly-Gln-Asp-Pro-Val-Lys, and these together can anchor the whole molecule to extracellular matrix proteins, such as laminin, fibronectin, beta-crystallin, collagen IV, fibrinogen, and elastin, by transglutaminase-catalysed cross-links. The whole domain is rich in glutamine and lysine, thus allowing transglutaminase(s) to catalyse the formation of an intermolecular epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl)lysine isopeptide bond.

Abductin is a naturally occurring elastomeric protein found in the hinge ligament of bivalve mollusks. It is unique as it is the only natural elastomer with compressible elasticity, as compared to resilin, spider silk, and elastin. Its name was proposed from the fact that it functions as the abductor of the valves of bivalve mollusks.
Elastin-like polypeptides (ELPs) are synthetic biopolymers with potential applications in the fields of cancer therapy, tissue scaffolding, metal recovery, and protein purification. For cancer therapy, the addition of functional groups to ELPs can enable them to conjugate with cytotoxic drugs. Also, ELPs may be able to function as polymeric scaffolds, which promote tissue regeneration. This capacity of ELPs has been studied particularly in the context of bone growth. ELPs can also be engineered to recognize specific proteins in solution. The ability of ELPs to undergo morphological changes at certain temperatures enables specific proteins that are bound to the ELPs to be separated out from the rest of the solution via experimental techniques such as centrifugation.
















