
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic, was a country that existed from 1949 to 1990, when the eastern portion of Germany was part of the Eastern Bloc during the Cold War. It described itself as a socialist "workers' and peasants' state", and the territory was administered and occupied by Soviet forces at the end of World War II — the Soviet Occupation Zone of the Potsdam Agreement, bounded on the east by the Oder–Neisse line. The Soviet zone surrounded West Berlin but did not include it; as a result, West Berlin remained outside the jurisdiction of the GDR.
The Democratic-Republican Party was an American political party formed by Thomas Jefferson and James Madison around 1792 to oppose the centralizing policies of the new Federalist Party run by Alexander Hamilton, who was Secretary of the Treasury and chief architect of George Washington's administration. From 1801 to 1825, the new party controlled the presidency and Congress as well as most states during the First Party System. It began in 1791 as one faction in Congress and included many politicians who had been opposed to the new constitution. They called themselves Republicans after their political philosophy, republicanism. They distrusted the Federalist tendency to centralize and loosely interpret the Constitution, believing these policies were signs of monarchism and anti-republican values. The party splintered in 1824, with the faction loyal to Andrew Jackson coalescing into the Jacksonian movement, the faction led by John Quincy Adams and Henry Clay forming the National Republican Party and some other groups going on to form the Anti-Masonic Party. The National Republicans, Anti-Masons, and other opponents of Andrew Jackson later formed themselves into the Whig Party.
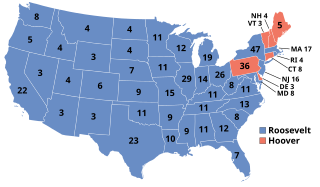
The United States presidential election of 1932 was the thirty-seventh quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 8, 1932. The election took place against the backdrop of the Great Depression. Incumbent Republican President Herbert Hoover was defeated in a landslide by Democrat Franklin D. Roosevelt, the Governor of New York. The election marked the effective end of the Fourth Party System, which had been dominated by Republicans.

The Social Democratic Party of Germany, or SPD, is a social-democratic political party in Germany.

The Minnesota Democratic–Farmer–Labor Party (DFL) is a center-left political party in the U.S. state of Minnesota. It is affiliated with the U.S. Democratic Party. Formed by a merger of the Minnesota Democratic Party and the left-wing Minnesota Farmer–Labor Party in 1944, the DFL is one of only two state Democratic party affiliates of a different name.

The Democratic Republic of the Congo, also known as DR Congo, the DRC, DROC, Congo-Kinshasa, or simply the Congo, is a country located in Central Africa. It is sometimes anachronistically referred to by its former name of Zaire, which was its official name between 1971 and 1997. It is, by area, the largest country in Sub-Saharan Africa, the second-largest in all of Africa, and the 11th-largest in the world. With a population of over 78 million, the Democratic Republic of the Congo is the most populated officially Francophone country, the fourth-most-populated country in Africa, and the 16th-most-populated country in the world. Currently, eastern DR Congo is the scene of ongoing military conflict in Kivu, since 2015.

The Democratic National Committee (DNC) is the formal governing body for the United States Democratic Party. The committee coordinates strategy to support Democratic Party candidates throughout the country for local, state, and national office. It organizes the Democratic National Convention held every four years to nominate and confirm a candidate for president, and to formulate the party platform. While it provides support for party candidates, it does not have direct authority over elected officials.
Christian democracy is a political ideology that emerged in nineteenth-century Europe under the influence of Catholic social teaching, as well as Neo-Calvinism. Christian democratic political ideology advocates for a commitment to social market principles and qualified interventionism. It was conceived as a combination of modern democratic ideas and traditional Christian values, incorporating the social teachings espoused by the Catholic, Lutheran, Reformed, and Pentecostal traditions in various parts of the world. After World War II, the Protestant and Catholic movements of the Social Gospel and Neo-Thomism, respectively, played a role in shaping Christian democracy. Christian democracy continues to be influential in Europe and Latin America, although it is also present in other parts of the world.

Bernard Sanders is an American politician who has served as the junior United States Senator from Vermont since 2007. The longest-serving Independent in congressional history, he was elected to the U.S. House of Representatives in 1990 and caucuses with the Democratic Party, enabling his appointment to congressional committees and at times giving Democrats a majority.

Pro-Europeanism, sometimes called European Unionism, is a political position that favours European integration and membership of the European Union (EU). It includes the more radical European federalists, who seek to create a single superstate known informally as a United States of Europe. A related term is "Europhile".

The Cook Partisan Voting Index, often abbreviated as CPVI or simply PVI, is a measurement of how strongly a United States congressional district or state leans toward the Democratic or Republican Party, compared to the nation as a whole. The index is updated after each election cycle. The Cook Political Report introduced the PVI in August 1997 to better gauge the competitiveness of each district using the 1992 and 1996 presidential elections as a baseline. The index is based on analysis by the Center for Voting and Democracy for its July 1997 Monopoly Politics report.

The New York State Senate is the upper house of the New York State Legislature. There are 63 seats in the Senate, and its members are elected to two-year terms. There are no term limits.

The Democratic Party is one of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Republican Party. Tracing its heritage back to Thomas Jefferson and James Madison's Democratic-Republican Party, the modern-day Democratic Party was founded around 1828 by supporters of Andrew Jackson, making it the world's oldest active political party.
Social democracy is a political, social and economic ideology that supports economic and social interventions to promote social justice within the framework of a liberal democratic polity and a capitalist economy. The protocols and norms used to accomplish this involve a commitment to representative and participatory democracy, measures for income redistribution and regulation of the economy in the general interest and welfare state provisions. Social democracy thus aims to create the conditions for capitalism to lead to greater democratic, egalitarian and solidaristic outcomes. Due to longstanding governance by social democratic parties and their influence on socioeconomic policy development in the Nordic countries, in policy circles social democracy has become associated with the Nordic model in the latter part of the 20th century.

The 2016 Democratic Party presidential primaries and caucuses were a series of electoral contests organized by the Democratic Party to select the 4,051 delegates to the Democratic National Convention held July 25–28 and determine the nominee for President of the United States in the 2016 U.S. presidential election. The elections took place within all fifty U.S. states, the District of Columbia, and five U.S. territories and occurred between February 1 and June 14, 2016.
Democratic socialism is a political philosophy that advocates political democracy alongside social ownership of the means of production, with an emphasis on self-management and democratic management of economic institutions within a market or some form of decentralized planned socialist economy. Democratic socialists espouse that capitalism is inherently incompatible with what they hold to be the democratic values of liberty, equality and solidarity; and that these ideals can only be achieved through the realization of a socialist society. Democratic socialism can be supportive of either revolutionary or reformist politics as a means to establish socialism.

The Democratic Socialists of America (DSA) is an organization of democratic socialist, social democratic and labor-oriented members in the United States.
Democratic centralism is a democratic practice in which political decisions reached by voting processes are binding upon all members of the party.
The 2020 Democratic Party presidential primaries and caucuses will be a series of electoral contests organized by the Democratic Party to select at least 3,768 delegates to the Democratic National Convention and determine the Democratic nominee for President of the United States in the 2020 U.S. presidential election. The elections will take place within all fifty U.S. states, the District of Columbia, and five U.S. territories. An extra 764 unpledged delegates or superdelegates, including party leaders and elected officials, will be appointed by the party leadership independently of the primary's electoral process. The convention will also approve the party's platform and vice-presidential nominee.

Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez, also known by her initials, AOC, is an American politician and member of the Democratic Party. Since January 3, 2019, she has been the U.S. Representative for New York's 14th congressional district, which includes the eastern part of The Bronx and portions of north-central Queens in New York City.















