
Anaximander is a lunar impact crater that is located near the northwest limb of the Moon. It is joined at the northern rim by the crater Carpenter, a younger and better-defined formation. To the southeast is the much larger J. Herschel, a formation of the variety known as a walled plain.

Archimedes is a large lunar impact crater on the eastern edges of the Mare Imbrium. Its diameter is 81 km.

Eddington is the lava-flooded remnant of a lunar impact crater, located on the western part of Oceanus Procellarum. The western rim is attached to the wall of the walled plain Struve. To the east-southeast is the smaller but prominent crater Seleucus. South of Eddington is Krafft.

Finsch is a relatively small lunar impact crater in the mid-part of Mare Serenitatis that has been almost completely covered by the mare, forming a ghost crater in the lava plain. It was named after German zoologist Otto Finsch. It is located to the south-southeast of the crater Sarabhai and northeast of Bessel.
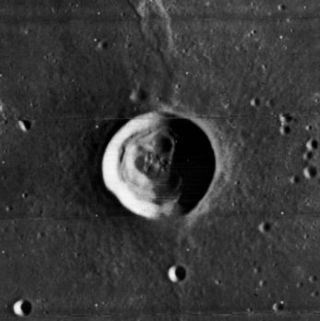
C. Herschel is a small lunar impact crater that lies on the western part of Mare Imbrium. It is named after German astronomer Caroline Herschel. It is a circular, bowl-shaped formation that has not undergone significant erosion. The interior floor has the same low albedo as the surrounding lunar mare. To the south-southwest is the similar crater Heis. C. Herschel lies on a wrinkle ridge of the lunar mare named the Dorsum Heim.

Aristillus is a prominent lunar impact crater that lies in the eastern Mare Imbrium. It was named after Greek astronomer Aristyllus. Directly to the south is the smaller crater Autolycus, while to the southwest is the large Archimedes. To the northeast are the craters Theaetetus and Cassini.

Herschel is a lunar impact crater located just to the north of the walled plain Ptolemaeus. Its diameter is 39 km. It was named after German-born British astronomer William Herschel.

Belʹkovich is a large lunar impact crater of the form termed a walled plain. The formation has been heavily eroded by a history of subsequent impacts, leaving it reshaped, worn, and the features softened and rounded. Belʹkovich is located along the northeastern limb of the Moon, and so its visibility is subject to libration effects. From the Earth this crater is viewed from the side, making it difficult to view it in detail.

De La Rue is the remnant of a lunar impact crater, or possibly several merged craters, creating a formation sometimes called a walled plain. It lies in the northeastern part of the Moon on the near side, and so appears foreshortened due to its location. This formation lies to the north-northwest of the prominent crater Endymion, just beyond the eastern extreme of Mare Frigoris. The crater Strabo intrudes into the northern part of De La Rue's northern rim, and the smaller Thales is attached to the northwestern part of the wall.

Brunner is a lunar impact crater that is located along the eastern limb of the Moon, to the southeast of the Mare Smythii. At this location the crater is viewed from the edge, and so it is not possible to see much detail from the Earth. The visibility of this formation is also affected by libration. The crater lies to the southwest of the walled plain Hirayama, and to the east of the elongated crater Houtermans.

South is a large lunar impact crater that is located in the northwest part of the Moon. Most of the southern wall of this crater is joined to the Sinus Roris bay of the Oceanus Procellarum, with the southeast rim facing Mare Frigoris. Attached to the northwest of the formation is the larger walled plain Babbage. Just to the northeast is the crater Robinson, and farther to the northeast is another walled plain, J. Herschel.

Colombo is a lunar impact crater that lies on the strip of rough continental terrain between Mare Fecunditatis to the east and Mare Nectaris in the west. It is located to the south of the crater Goclenius, and northwest of Cook, and is named for the late 15th and early 16th century Italian explorer Christopher Columbus.

Daubrée is a lunar impact crater that is located to the southwest of the Mare Serenitatis, just to the west-southwest of the crater Menelaus in the Montes Haemus range. The small lunar mare Lacus Hiemalis lies along the southwest rim of Daubrée. The crater was named after French geologist Gabriel A. Daubrée. It was previously designated Menelaus S.

Hall is a lunar impact crater in the southeast part of the Lacus Somniorum, a lunar mare in the northeast part of the Moon. It was named after American astronomer Asaph Hall. This feature can be found to the east of the prominent walled plain Posidonius. Just to the south, and nearly attached to the southern rim of Hall is the smaller crater G. Bond.

Horrebow is a lunar impact crater that is located along the northern shore of Mare Frigoris, just to the south of the walled plain J. Herschel. To the west of Horrebow is the crater Robinson.

Nichollet is a small, isolated lunar impact crater on the Mare Nubium, a lunar mare in the southwest quadrant of the Moon. It was named after French astronomer Joseph Nicollet. This crater is located to the north of the crater Pitatus, about midway between Wolf to the west and Birt to the east.

Robinson is a small lunar impact crater that lies to the southwest of the large walled plain J. Herschel. It is located in the continental terrain to the north of the Mare Frigoris, in the northwestern part of the Moon's near side. To the southwest is another walled plain, South.

Eimmart is a lunar impact crater that is located near the east-northeastern limb of the Moon, to the northeast of the Mare Crisium. The northern and eastern outer rim of this crater borders on the narrow Mare Anguis. To the northwest of Eimmart are the smaller crater Delmotte and the prominent Cleomedes.

Fridman is the remains of a lunar impact crater on the far side of the Moon. It lies due south of the huge walled plain Hertzsprung, and is attached to the northeastern rim of the crater Ioffe.

Mohorovičić is a lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon. It lies to the southwest of the larger crater Doppler and the huge walled plain Korolev. To the southwest of Mohorovičić is a small lunar mare that has been named Lacus Oblivionis. Due south of it is an unnamed mountain that formed during the impact that created the South Pole-Aitken Basin.





















