A performance appraisal, also referred to as a performance review, performance evaluation, (career) development discussion, or employee appraisal, sometimes shortened to "PA", is a periodic and systematic process whereby the job performance of an employee is documented and evaluated. This is done after employees are trained about work and settle into their jobs. Performance appraisals are a part of career development and consist of regular reviews of employee performance within organizations.
A Physician Assistant or Physician Associate (PA) is a type of non-doctor health care provider. While this job title is used internationally, there is significant variation in scope of practice across different juristictions.
Parental alienation syndrome (PAS) is a term introduced by child psychiatrist Richard Gardner in 1985 to describe signs and symptoms he believed to be exhibited by children who have been alienated from one parent through manipulation by the other parent. Proposed symptoms included extreme but unwarranted fear, and disrespect or hostility towards a parent. Gardner believed that a set of behaviors that he observed in some families involved in child custody litigation could be used to diagnose psychological manipulation or undue influence of a child by a parent, typically by the other parent who may be attempting to prevent an ongoing relationship between a child and other family members after family separation or divorce. Use of the term "syndrome" has not been accepted by either the medical or legal communities and Gardner's research has been broadly criticized by legal and mental health scholars for lacking scientific validity and reliability.

Onychomycosis, also known as tinea unguium, is a fungal infection of the nail. Symptoms may include white or yellow nail discoloration, thickening of the nail, and separation of the nail from the nail bed. Toenails or fingernails may be affected, but it is more common for toenails. Complications may include cellulitis of the lower leg. A number of different types of fungus can cause onychomycosis, including dermatophytes and Fusarium. Risk factors include athlete's foot, other nail diseases, exposure to someone with the condition, peripheral vascular disease, and poor immune function. The diagnosis is generally suspected based on the appearance and confirmed by laboratory testing.
Richard Alan Gardner was an American child psychiatrist known for his work in psychotherapy with children, parental alienation and child custody evaluations. Based on his clinical work with children and families, Gardner introduced the term Parental alienation syndrome (PAS), which is now "largely rejected by most credible professionals." He wrote 41 books and more than 200 journal articles and book chapters, although most of his work was self-published, non-peer-reviewed, and anecdotal. He developed child play therapy and test materials which he published through his company Creative Therapeutics. Gardner was an expert witness in child custody cases.

Periodic acid–Schiff (PAS) is a staining method used to detect polysaccharides such as glycogen, and mucosubstances such as glycoproteins, glycolipids and mucins in tissues. The reaction of periodic acid oxidizes the vicinal diols in these sugars, usually breaking up the bond between two adjacent carbons not involved in the glycosidic linkage or ring closure in the ring of the monosaccharide units that are parts of the long polysaccharides, and creating a pair of aldehydes at the two free tips of each broken monosaccharide ring. The oxidation condition has to be sufficiently regulated so as to not oxidize the aldehydes further. These aldehydes then react with the Schiff reagent to give a purple-magenta color. A suitable basic stain is often used as a counterstain.

Pas Tehran Football Club was an Iranian football club based in Tehran, Iran. Pas F.C. was the football club of the multisport Pas Cultural and Sports Club. The club has a long and rich history and has always been associated with Iranian police, receiving most of its funding from that branch. In recent years the football club had shown itself to be a contender, thanks to increased funding and support from the team board. The team played its matches in Shahid Dastgerdi Stadium. On 9 June 2007, Pas Tehran was officially dissolved. Their right to participate in the Persian Gulf Cup was given to a newly formed team called Pas Hamedan.

The aryl hydrocarbon receptor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AHR gene. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor is a transcription factor that regulates gene expression. It was originally thought to function primarily as a sensor of xenobiotic chemicals and also as the regulator of enzymes such as cytochrome P450s that metabolize these chemicals. The most notable of these xenobiotic chemicals are aromatic (aryl) hydrocarbons from which the receptor derives its name.
Paquita is a ballet in two acts and three scenes originally choreographed by Joseph Mazilier to music by Édouard Deldevez and Ludwig Minkus. Paul Foucher received royalties as librettist.

The Pakistan Academy of Sciences, is a learned society of sciences, which described itself as "a repository of the highest scientific talent available in the country."

Marilyn Buferd was an American film and television actress as well as the winner of both the Miss California and Miss America pageants of 1946. During the latter half of the 1940s and throughout the 1950s, she performed in nearly two dozen American, Italian, and French films, including Touchez pas au grisbi opposite Jean Gabin (1954). Buford also appears in several television series originally broadcast in the 1950s, such as The Millionaire, Highway Patrol, Schlitz Playhouse, The Ford Television Theatre, and Orient Express.

NPAS3 or Neuronal PAS domain protein 3 is a brain-enriched transcription factor belonging to the bHLH-PAS superfamily of transcription factors, the members of which carry out diverse functions, including circadian oscillations, neurogenesis, toxin metabolism, hypoxia, and tracheal development. NPAS3 contains basic helix-loop-helix structural motif and PAS domain, like the other proteins in the superfamily.

The University of Artois is a public university situated in the Nord and Pas-de-Calais departments of northern France.

The University of the Littoral Opal Coast is a public university located in the Nord and Pas-de-Calais departments of northern France. Its namesake is the Opal Coast region, of which it is a part.

Neuronal PAS domain protein 2 (NPAS2) also known as member of PAS protein 4 (MOP4) is a transcription factor protein that in humans is encoded by the NPAS2 gene. NPAS2 is paralogous to CLOCK, and both are key proteins involved in the maintenance of circadian rhythms in mammals. In the brain, NPAS2 functions as a generator and maintainer of mammalian circadian rhythms. More specifically, NPAS2 is an activator of transcription and translation of core clock and clock-controlled genes through its role in a negative feedback loop in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), the brain region responsible for the control of circadian rhythms.
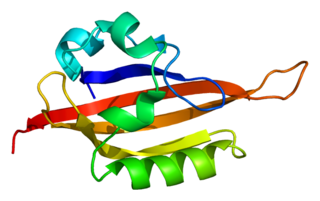
Endothelial PAS domain-containing protein 1 is a protein that is encoded by the EPAS1 gene in mammals. It is a type of hypoxia-inducible factor, a group of transcription factors involved in the physiological response to oxygen concentration. The gene is active under hypoxic conditions. It is also important in the development of the heart, and for maintaining the catecholamine balance required for protection of the heart. Mutation often leads to neuroendocrine tumors.

Aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like protein 1 (ARNTL) or brain and muscle ARNT-Like 1 (BMAL1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ARNTL gene on chromosome 11, region p15.3. It's also known as BMAL1, MOP3, and, less commonly, bHLHe5, BMAL, BMAL1C, JAP3, PASD3, and TIC.

A Per-Arnt-Sim (PAS) domain is a protein domain found in all kingdoms of life. Generally, the PAS domain acts as a molecular sensor, whereby small molecules and other proteins associate via binding of the PAS domain. Due to this sensing capability, the PAS domain has been shown as the key structural motif involved in protein-protein interactions of the circadian clock, and it is also a common motif found in signaling proteins, where it functions as a signaling sensor.
Murray Spivack was an American sound engineer best known as the sound designer for the 1933 film King Kong. He won an Oscar for Sound Recording and was nominated for another in the same category. He was also a drum teacher whose students included Louie Bellson, Remo Belli, David Garibaldi, William Kraft, Alan Maitland, Jim Banks, Chad Wackerman and Joe Morello.












