The Indian Territory and the Indian Territories are terms that generally described an evolving land area set aside by the United States Government for the relocation of Native Americans who held aboriginal title to their land as a sovereign independent state. In general, the tribes ceded land they occupied in exchange for land grants in 1803. The concept of an Indian Territory was an outcome of the US federal government's 18th- and 19th-century policy of Indian removal. After the American Civil War (1861–1865), the policy of the US government was one of assimilation.

Weakley County is a county located in the northwest of the U.S. state of Tennessee. As of the 2020 census, the population was 32,902. Its county seat is Dresden. Its largest city is Martin, the home of the University of Tennessee at Martin. The county was established by the Tennessee General Assembly on October 21, 1823, and is named for U.S. Congressman Robert Weakley (1764–1845). Weakley County comprises the Martin, TN Micropolitan Statistical Area.

Tipton County is a county located on the western end of the U.S. state of Tennessee, in the Mississippi Delta region. As of the 2020 census, the population was 60,970. Its county seat is Covington. Tipton County, founded in 1823, is part of the Memphis, TN-MS-AR Metropolitan Statistical Area.

The Chickasaw are an indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands. Their traditional territory was in the Southeastern United States of Mississippi, Alabama, and Tennessee as well in southwestern Kentucky. Their language is classified as a member of the Muskogean language family. In the present day, they are organized as the federally recognized Chickasaw Nation.

DeSoto County is a county located on the northwestern border of the U.S. state of Mississippi. As of the 2020 census, the population was 185,314, making it the third-most populous county in Mississippi. Its county seat is Hernando.

The Treaty of Dancing Rabbit Creek was a treaty which was signed on September 27, 1830, and proclaimed on February 24, 1831, between the Choctaw American Indian tribe and the United States Government. This treaty was the first removal treaty which was carried into effect under the Indian Removal Act. The treaty ceded about 11 million acres (45,000 km2) of the Choctaw Nation in what is now Mississippi in exchange for about 15 million acres (61,000 km2) in the Indian territory, now the state of Oklahoma. The principal Choctaw negotiators were Chief Greenwood LeFlore, Mosholatubbee, and Nittucachee; the U.S. negotiators were Colonel John Coffee and Secretary of War John Eaton.
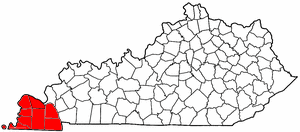
The Jackson Purchase, also known as the Purchase Region or simply the Purchase, is a region in the U.S. state of Kentucky bounded by the Mississippi River to the west, the Ohio River to the north, and the Tennessee River to the east.

West Tennessee is one of the three Grand Divisions of the U.S. state of Tennessee that roughly comprises the western quarter of the state. The region includes 21 counties between the Tennessee and Mississippi rivers, delineated by state law. Its geography consists primarily of flat lands with rich soil and vast floodplain areas of the Mississippi River. Of the three regions, West Tennessee is the most sharply defined geographically, and is the lowest-lying. It is both the least populous and smallest, in land area, of the three Grand Divisions. Its largest city is Memphis, the state's second most populous city.
The Territory South of the River Ohio, more commonly known as the Southwest Territory, was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from May 26, 1790, until June 1, 1796, when it was admitted to the United States as the State of Tennessee. The Southwest Territory was created by the Southwest Ordinance from lands of the Washington District that had been ceded to the U.S. federal government by North Carolina. The territory's lone governor was William Blount.

The territory of the United States and its overseas possessions has evolved over time, from the colonial era to the present day. It includes formally organized territories, proposed and failed states, unrecognized breakaway states, international and interstate purchases, cessions, and land grants, and historical military departments and administrative districts. The last section lists informal regions from American vernacular geography known by popular nicknames and linked by geographical, cultural, or economic similarities, some of which are still in use today.

The Treaty of St. Mary's may refer to one of six treaties concluded in fall of 1818 between the United States and Natives of central Indiana regarding purchase of Native land. The treaties were

The Chickasaw Nation is a federally recognized Native American tribe, with its headquarters located in Ada, Oklahoma in the United States. They are an Indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands, originally from northern Mississippi, northernwestern Alabama, southwestern Kentucky, and western Tennessee. Today, the Chickasaw Nation is the 13th largest tribe in the United States.
Levi Colbert (1759–1834), also known as Itawamba in Chickasaw, was a leader and chief of the Chickasaw nation. Colbert was called Itte-wamba Mingo, meaning bench chief. He and his brother George Colbert were prominent interpreters and negotiators with United States negotiators in the early decades of the 19th century. They were appointed by President Andrew Jackson's administration to gain cession of their lands and arrange for removal of their people to Indian Territory west of the Mississippi River. They were under considerable pressure from the Mississippi state government, white interlopers in their area, and the federal government to cede their lands.
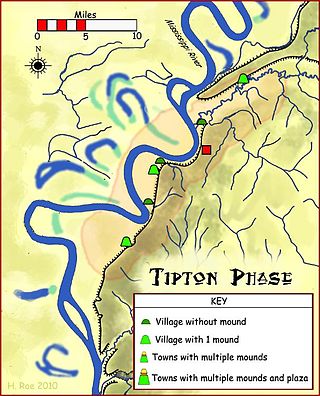
Randolph is an unincorporated rural community in Tipton County, Tennessee, United States, located on the banks of the Mississippi River. The lands of the Mississippi River Basin were inhabited by Paleo-Indians and later Native American tribes of the Mississippian culture for thousands of years. The Tipton phase people and the Chickasaw Indian tribe populated the Mississippi River valley near Randolph during the Mississippian period. In 1541, Spanish explorer Hernando de Soto crossed the Mississippi River at or near Randolph. French explorer Cavelier de La Salle built the first French fortification at or near Randolph on his 1682 canoe expedition of the Mississippi River.
The Cherokee have participated in over forty treaties in the past three hundred years.
Chief George Colbert, also known as Tootemastubbe in Chickasaw, was a leader and war chief of the Chickasaw people in the early 19th century, then occupying territory in what are now the jurisdictions of Alabama and Mississippi. During the Creek War of 1813–1814, he commanded 350 Chickasaw auxiliary troops, whom he had recruited, as a militia captain under Andrew Jackson. Later he joined the US Army under Jackson for the remainder of the War of 1812.
John Gordon, was an American pioneer, Indian trader, planter, and militia captain in several Indian wars. Part of the post-Revolutionary War settlement of the trans-Appalachian frontier, Gordon was an early settler in the Nashville, Tennessee area. He gained notability and rank in the Tennessee Militia, fighting against the Creeks and Seminoles for Andrew Jackson, during the War of 1812. Jackson referred to him as his "Captain of the Spies."

The Treaty of Pontotoc Creek was a treaty signed on October 20, 1832 by representatives of the United States and the Chiefs of the Chickasaw Nation assembled at the National Council House on Pontotoc Creek in Pontotoc, Mississippi. The treaty ceded the 6,283,804 million acres of the remaining Chickasaw homeland in Mississippi in return for Chickasaw relocation on an equal amount of land west of the Mississippi River.
Cyrus H. Harris, a mixed-blood Chickasaw born in Mississippi, was elected the first Governor of the Chickasaw Nation, and served five non-consecutive two-year terms. Although his formal schooling was limited at an elementary level, he became fluent in both the English and Chickasaw languages. He and his family relocated to Indian Territory in 1837, where he was employed in business and also served as an interpreter and developed a keen interest in Chickasaw politics. In 1856, he was elected to his first term as governor of the newly established Chickasaw Nation His accomplishments included organizing a national government after the Chickasaw Nation and Choctaw Nation formally separated into two distinct entities. He also executed a formal alliance between his nation and the Confederate States of America after the outbreak of the American Civil War. After the cessation of hostilities, he played a major role in the recovery of the nation from its devastated condition. He retired from politics in 1874, after serving his fifth term as governor. He died in 1887 at his home in Mill Valley, and was buried at the cemetery in Mill Valley.

The Treaty of Tuscaloosa was signed in October 1818, and ratified by congress in January 1819. endorsed by President James Monroe. It was one of a series of treaties made between the Chickasaw Indians and the United States that year. The Treaty of Tuscaloosa was represented by Senator Andrew Jackson and ex-governor Isaac Shelby to the Chickasaw. It resulted in the acquisition of the Jackson Purchase.













