
The VB-6 Felix was a precision-guided munition developed by the United States during World War II. It used an infrared seeker to attack targets like blast furnaces or the metal roofs of large factories. The war ended before it could be used operationally.

The LBD-1 Gargoyle was an American air-to-surface missile developed during World War II by McDonnell Aircraft for the United States Navy. One of the precursors of modern anti-ship missiles,it was extensively used as a test vehicle during the late 1940s.

The NOTS-EV-2 Caleb,also known as NOTS-500,Hi-Hoe and SIP was an expendable launch system,which was later used as a sounding rocket and prototype anti-satellite weapon. It was developed by the United States Navy's Naval Ordnance Test Station (NOTS) as a follow-up to the NOTS-EV-1 Pilot,which had been abandoned following ten launches officially classified as failed missions. Two were launched in July and October 1960,before the cancellation of the project. Following cancellation,two leftover Calebs were used in the Satellite Interceptor Program (SIP),while three more were used as sounding rockets,under the designation Hi-Hoe. These derivatives flew until July 1962,when the Hi-Hoe made its final flight.

The Bold Orion missile,also known as Weapons System 199B (WS-199B),was a prototype air-launched ballistic missile (ALBM) developed by Martin Aircraft during the 1950s. Developed in both one- and two-stage designs,the missile was moderately successful in testing,and helped pave the way for development of the GAM-87 Skybolt ALBM. In addition,the Bold Orion was used in early anti-satellite weapons testing,performing the first interception of a satellite by a missile.

The Hopi was an air-to-surface missile developed by the United States Navy's Naval Ordnance Test Station. Intended to provide a medium-range nuclear capability for carrier aircraft,the missile reached the flight test stage during 1958,but the project was cancelled following testing and no production was undertaken.
The Diamondback was a proposed nuclear-armed air-to-air missile studied by the United States Navy's Naval Ordnance Test Station during the 1950s. Intended as an enlarged,nuclear-armed version of the successful Sidewinder missile,Diamondback did not progress beyond the study stage.

The JB-4,also known as MX-607,was an early American air-to-surface missile developed by the United States Army Air Forces during World War II. Using television/radio-command guidance,the JB-4 reached the flight-testing stage before being cancelled at the end of the war.
The ASM-N-5 Gorgon V was an unpowered air-to-surface missile,developed by the Glenn L. Martin Company during the early 1950s for use by the United States Navy as a chemical weapon delivery vehicle. Developed from the earlier PTV-N-2 Gorgon IV test vehicle,the program was cancelled without any Gorgon Vs seeing service.

The 4.5-Inch Beach Barrage Rocket,also known as "Old Faithful",was a 4.5-inch (110 mm) rocket developed and used by the United States Navy during World War II. Originally developed from the "Mousetrap" anti-submarine rocket,it saw widespread use during the war,being replaced by more powerful rockets toward the end of the conflict.

The AAM-N-5 Meteor was an early American air-to-air missile,developed by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Bell Aircraft for the United States Navy. Initially,both air-launched and ship-launched versions were considered. Versions designed for launch from carrier-based aircraft proceeded to the flight testing stage before the project was cancelled.
The Cherokee was an experimental rocket built by the Cook Electric Co. for use by the United States Air Force during the 1950s for the testing of ejection seats.
The Anti-Aircraft Target Rocket M2 was a 3.25-inch (83 mm) rocket developed and used by the United States Army during World War II. It was designed to serve as a training target for anti-aircraft guns,capable of simulating attacks by low-flying aircraft. The nosecone of the rocket was ogival,and it was fitted with oversized fins to aid in tracking of the rocket by trainees.

The KA2N Gorgon IIA –also designated KU2N,CTV-4,and CTV-N-4 –was an air-to-air missile developed by the United States Navy near the end of World War II. Proving a failure in its designed role,it was repurposed as an experimental testbed for missile technology.

The XSSM-A-23 Dart was an anti-tank guided missile developed for the United States Army in the 1950s. After protracted development,the missile,similar in design to the French SS.10,was cancelled in favor of purchasing the SS.11 missile.

Skokie was a family of research vehicles developed by the Cook Electric Co. for the United States Air Force during the mid to late 1950s. Launched from a B-29 bomber,Skokie 1 was an unpowered,ballistic vehicle,while Skokie 2 was rocket-propelled;both were used for evaluating and testing high-speed parachute recovery systems.
The Republic SD-4 Swallow was an early high-speed reconnaissance drone developed by Republic Aviation for the United States Army. Intended for use by the U.S. Army Signal Corps to target tactical ballistic missiles,it was cancelled before the first prototype could be completed,and did not see operational service.

The Fairchild SD-5 Osprey was an early high-speed reconnaissance drone developed by Fairchild Aircraft for the United States Army. Intended for use by the U.S. Army Signal Corps to target tactical ballistic missiles,it was cancelled before the first prototype could be completed,and did not see operational service.
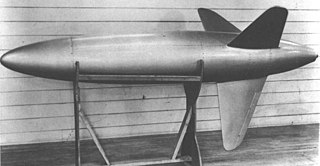
The JB-3 Tiamat,also designated MX-570,was an early air-to-air missile developed by Hughes Aircraft for the United States Army Air Forces during World War II. Regarded as a purely experimental vehicle,test launches took place for several years before the program was terminated.

The TDU-12/B Skydart was an unguided target rocket built by Curtiss-Wright for use by the United States Air Force. It was used operationally from the late 1950s to the mid 1960s.
Dervish was an unguided air-to-air and air-to-surface rocket developed by the Northrop Corporation for use by the United States Navy and United States Army during the early 1950s. Originally intended as an air-to-air rocket to replace the Mighty Mouse rocket,it was later expanded in role to also operate in an air-to-surface capacity. Spin-stabilized,2.75 inches (70 mm) in diameter,and powered by a Thiokol TRX-126B solid fuel rocket,in 1958 development of Dervish was resumed as a solely Army project,but no production ever emerged.














