Related Research Articles

Bettiah is a city and the administrative headquarters of West Champaran district - (Tirhut). It is near the Indo-Nepal border, 225 kilometres (140 mi) northwest of Patna, in the state of Bihar, India.

Samastipur is one of the thirty-eight districts of Bihar in India. The district headquarters are located at Samastipur. The district occupies an area of 2904 km² and has a population of 4,261,566.
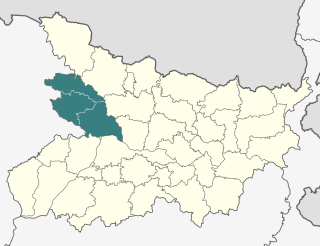
Saran division is an administrative geographical unit of Bihar state of India. Chhapra is the administrative headquarters of the division. Currently (2005), the division consists of Saran district, also called Chhapra District, Siwan district, Gopalganj district.

Bihari Muslims are adherents of Islam who identify linguistically, culturally, and genealogically as Biharis. They are geographically native to the region comprising the Bihar state of India, although there are significantly large communities of Bihari Muslims living elsewhere in the subcontinent due to the Partition of British India in 1947, which prompted the community to migrate en masse from Bihar to the dominion of Pakistan.
The Darbhanga Raj, also known as Raj Darbhanga and the Khandwala dynasty, was a Maithil Brahmin dynasty and the rulers of territories, not all contiguous, that were part of the Mithila region, now divided between India and Nepal.
Bhumihar, also locally called Bhuinhar and Babhan, is a Hindu caste mainly found in Bihar, the Purvanchal region of Uttar Pradesh, Jharkhand, the Bundelkhand region of Madhya Pradesh, and Nepal.

The Bettiah Raj was the second-largest zamindari in the Bettiah region of Bihar, India. It generated annual land revenue rentals of more than 2 million rupees.
Hathuwa Raj was a chieftaincy belonging to Baghochia dynasty of Bhumihars. It encompassed 1,365 villages, was inhabited by more than 391,000 people, and produced an annual rental of almost a million rupees. It was located in the Saran Division of Bihar. Earlier seats of the Raj included Huseypur, Kalyanpur, Balchowra and Baghoch. The Kalyanpur chieftaincy was subjugated by the Mughal Emperor Akbar during late 16th century.

The Tekari Raj was a zamindari estate of the Bhumihar community in South Bihar. They controlled 2,046 villages on their estate, which covered a 7,500 square kilometres (2,900 sq mi) area, near to the town of Gaya.

Saran district is one of the thirty-eight districts of Indian state of Bihar. The district, part of Saran Division, is also known as Chhapra district after the headquarters of the district, Chhapra. It is considered as one of the richest Zamindari of Bihar after Raj Darbhanga, Hathwa Raj, Bettiah Raj and Raj Najarganj, Saran Raj.
Maharaja Harendra Kishore Public Library is a depository library in Bettiah in West Champaran district in the Indian state of Bihar. It was established in 1905 as Victoria Memorial Library and was renamed to its present name, Maharaja Harendra Kishore Public Library on Maharaja Sir Harendra Kishore Singh's birthday in 1955.
Maharaja Fateh Bahadur Shahi was 99th Raja of Huseypur or Hathwa Raj situated in today's Gopalganj district of Bihar in India. He relentlessly pursued his objective of driving them out for nearly three decades while waging a guerilla war against the British. The British used all of their might and resources to oppose him.

Government Medical College and Hospital, Bettiah is a government medical college situated at Bettiah, in the West Champaran district of the Indian state of Bihar.This college came into existence into year 2008.
Rajputs in Bihar are members of the Rajput community living in the eastern Indian state of Bihar. They traditionally formed part of the feudal elite in Bihari society. Rajputs were pressed with the Zamindari abolition and Bhoodan movement in post-independence India; along with other Forward Castes, they lost their significant position in Bihar's agrarian society, leading to the rise of Other Backward Classes (OBCs).
Kinwar is a clan whose members belong to the Kshatriya, Kurmi and Bhumihar Brahmin caste. the Kshatriya members principally reside in the states of Bihar and Eastern Uttar Pradesh. A particularly large population of Kinwar Bhumihars can be found in Ghazipur district.

The Zamindars of Bihar were the autonomous and semi-autonomous rulers and administrators of the Mughal subah of Bihar and later during British rule. The zamindars of Bihar were numerous and could be divided into small, medium and large depending on how much land they controlled. Within Bihar, the zamindars had both economic and military power. Each zamindari would have their own standing army which was typically composed of their own clansmen.
The 1781 revolt in Bihar was an uprising by certain Zamindars and chieftains against the British East India Company in the Indian state of Bihar. The majority of the rebel zamindars were from South Bihar and were likely pushed to revolt due to the recurring droughts which hampered their revenue collections.
The House of Baghoch commonly known as Baghochia was the ruling dynasty of Hathwa Raj until 1947 when the state was abolished and merged into the newly formed Union of India. The House takes its name from Baghoch and Bharhichowra, the ancient seats of the rulers of Hathwa Raj. The name Baghauch also may have been associated with the clan from totemistic stage as the name makes reference to Bagh (Tiger) as the clans totem. Based on the totem the name of the first capital was Baghauch. They are a sub-group of the Vats gotra Bhumihar Brahmin. The founder of the dynasty was Raja Bir Sen who played an instrumental role in the invasion of the Sakyas by the Kosla Maharaj Virudhaka in 6th century BCE, and it is in the aftermath that Raja Bir Sen got part of the newly invaded country as his Raj. This makes the Baghochia dynasty one of the oldest and the longest ruling dynasty in the world and also a clan with one of the deepest genealogy.

The Bettiah Christians, also known as Betiawi Christians, are the northern Indian subcontinent's oldest Christian community, which emerged in the 18th century. The origins of the Bettiah Christian community lie in Champaran in what is now the Indian state of Bihar, in which the king of the Bettiah Raj, Maharaja Dhurup Singh, invited Roman Catholic missionaries of the Order of Friars Minor Capuchin to establish the Bettiah Christian Mission there.
References
- ↑ Kumar, Maltinandan. Chalein Such Ki Aur (in Hindi). Notion Press. ISBN 978-93-5206-582-0.
- ↑ Pouchepadass, Jacques (2000-07-27). Land, Power and Market: A Bihar District Under Colonial Rule, 1860-1947. SAGE Publications. ISBN 978-0-7619-9402-2.