
The Internet is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a network of networks that consists of private, public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope, linked by a broad array of electronic, wireless, and optical networking technologies. The Internet carries a vast range of information resources and services, such as the inter-linked hypertext documents and applications of the World Wide Web (WWW), electronic mail, telephony, and file sharing.
An Internet Protocol address is a numerical label such as 192.0.2.1 that is connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. An IP address serves two main functions: network interface identification and location addressing.

Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) is the fourth version of the Internet Protocol (IP). It is one of the core protocols of standards-based internetworking methods in the Internet and other packet-switched networks. IPv4 was the first version deployed for production on SATNET in 1982 and on the ARPANET in January 1983. It is still used to route most Internet traffic today, even with the ongoing deployment of Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6), its successor.

Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) is the most recent version of the Internet Protocol (IP), the communications protocol that provides an identification and location system for computers on networks and routes traffic across the Internet. IPv6 was developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) to deal with the long-anticipated problem of IPv4 address exhaustion, and is intended to replace IPv4. In December 1998, IPv6 became a Draft Standard for the IETF, which subsequently ratified it as an Internet Standard on 14 July 2017.

A router is a networking device that forwards data packets between computer networks. Routers perform the traffic directing functions on the Internet. Data sent through the internet, such as a web page or email, is in the form of data packets. A packet is typically forwarded from one router to another router through the networks that constitute an internetwork until it reaches its destination node.
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is a standardized exterior gateway protocol designed to exchange routing and reachability information among autonomous systems (AS) on the Internet. BGP is classified as a path-vector routing protocol, and it makes routing decisions based on paths, network policies, or rule-sets configured by a network administrator.

The Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways, commonly known as the Interstate Highway System, is a network of controlled-access highways that forms part of the National Highway System in the United States. The system extends throughout the contiguous United States and has routes in Hawaii, Alaska, and Puerto Rico.
The United States Numbered Highway System is an integrated network of roads and highways numbered within a nationwide grid in the contiguous United States. As the designation and numbering of these highways were coordinated among the states, they are sometimes called Federal Highways, but the roadways were built and have always been maintained by state or local governments since their initial designation in 1926.

Network address translation (NAT) is a method of mapping an IP address space into another by modifying network address information in the IP header of packets while they are in transit across a traffic routing device. The technique was originally used to bypass the need to assign a new address to every host when a network was moved, or when the upstream Internet service provider was replaced, but could not route the network's address space. It has become a popular and essential tool in conserving global address space in the face of IPv4 address exhaustion. One Internet-routable IP address of a NAT gateway can be used for an entire private network.

The Silk Road was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers, it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and religious interactions between the East and West. The name "Silk Road", first coined in the late 19th century, has fallen into disuse among some modern historians in favor of Silk Routes, which more accurately describes the intricate web of land and sea routes connecting East and Southeast Asia, the Indian subcontinent, Central Asia, the Middle East, East Africa and Europe.

U.S. Route 66 or U.S. Highway 66 was one of the original highways in the United States Numbered Highway System. US 66 was established on November 11, 1926, with road signs erected the following year. The highway, which became one of the most famous roads in the United States, originally ran from Chicago, Illinois, through Missouri, Kansas, Oklahoma, Texas, New Mexico, and Arizona before terminating in Santa Monica in Los Angeles County, California, covering a total of 2,448 miles (3,940 km).
A virtual private network (VPN) extends a private network across a public network and enables users to send and receive data across shared or public networks as if their computing devices were directly connected to the private network. The benefits of a VPN include increases in functionality, security, and management of the private network. It provides access to resources that are inaccessible on the public network and is typically used for remote workers. Encryption is common, although not an inherent part of a VPN connection.

Northern California is a geographic and cultural region that generally comprises the northern portion of the U.S. state of California. Spanning the state's northernmost 48 counties, its main population centers include the San Francisco Bay Area, the Greater Sacramento area, the Redding, California, area south of the Cascade Range, and the Metropolitan Fresno area. Northern California also contains redwood forests, along with most of the Sierra Nevada, including Yosemite Valley and part of Lake Tahoe, Mount Shasta, and most of the Central Valley, one of the world's most productive agricultural regions.
A state highway, state road, or state route is usually a road that is either numbered or maintained by a sub-national state or province. A road numbered by a state or province falls below numbered national highways in the hierarchy. Roads maintained by a state or province include both nationally numbered highways and un-numbered state highways. Depending on the state, "state highway" may be used for one meaning and "state road" or "state route" for the other.

Mount Kailash, is a mountain in the Ngari Prefecture, Tibet Autonomous Region of China. It has an altitude of 6,714 m (22,028 ft). It lies in the Kailash Range of the Transhimalaya, in the western part of the Tibetan Plateau. Mount Kailash is less than 100 km towards the north from the western trijunction of the borders of China, India, and Nepal.
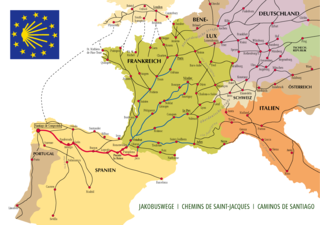
The Camino de Santiago, known in English as the Way of St James, is a network of pilgrims' ways or pilgrimages leading to the shrine of the apostle Saint James the Great in the cathedral of Santiago de Compostela in Galicia in northwestern Spain, where tradition holds that the remains of the apostle are buried.

Greater Boston is the metropolitan region of New England encompassing the municipality of Boston and its surrounding areas. The region forms the northern arc of the Northeast megalopolis, so Greater Boston means both a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) and a combined statistical area (CSA), which is broader. The MSA consists of most of the eastern third of Massachusetts, excluding the South Coast and Cape Cod; the CSA additionally includes the municipalities of Providence, Manchester, Worcester, the South Coast region, and Cape Cod. While the city of Boston covers 48.4 square miles (125 km2) and has 675,647 residents as of the 2020 census, the urbanization has extended well into surrounding areas and the CSA has a more than 8.4 million people, making it one of the most populous such regions in the U.S. The CSA is one of two in Massachusetts, the other being Greater Springfield. Greater Boston is the only CSA in New England that lies in three states ; some definitions extend it into a fourth (Connecticut).

The Lost Coast is a mostly natural and undeveloped area of the California North Coast in Humboldt and Mendocino Counties, which includes the King Range. It was named the "Lost Coast" after the area experienced depopulation in the 1930s. In addition, the steepness and related geotechnical challenges of the coastal mountains made this stretch of coastline too costly for state highway or county road builders to establish routes through the area, leaving it the most undeveloped and remote portion of the California coast. Without any major highways, communities in the Lost Coast region such as Petrolia, Shelter Cove, and Whitethorn are isolated from the rest of California.

A computer network is a set of computers sharing resources located on or provided by network nodes. The computers use common communication protocols over digital interconnections to communicate with each other. These interconnections are made up of telecommunication network technologies, based on physically wired, optical, and wireless radio-frequency methods that may be arranged in a variety of network topologies.














