Icos Corporation was an American biotechnology company and the largest biotechnology company in the U.S. state of Washington, before it was sold to Eli Lilly and Company in 2007. It was founded in 1989 by David Blech, Isaac Blech, Robert Nowinski, and George Rathmann, a pioneer in the industry and chief executive officer (CEO) and co-founder of Amgen. Icos focused on the development of drugs to treat inflammatory disorders. During its 17-year history, the company conducted clinical trials of twelve drugs, three of which reached the last phase of clinical trials. Icos also manufactured antibodies for other biotechnology companies.

Human Genome Sciences (HGS) was a biopharmaceutical corporation founded in 1992 by Craig Venter, Alan Walton and Wally Steinberg. It uses the human DNA sequence to develop protein and antibody drugs. It had drugs under development to treat such diseases as hepatitis C, systemic lupus erythmatosis, anthrax, and cancer. It collaborated with other biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies for development partnerships and licensing.
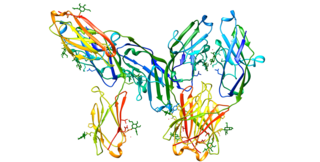
CD33 or Siglec-3 is a transmembrane receptor expressed on cells of myeloid lineage. It is usually considered myeloid-specific, but it can also be found on some lymphoid cells.
Genmab A/S is a Danish biotechnology company, founded in February 1999 by Florian Schönharting, at the time managing director of BankInvest Biomedical venture fund. The company is based in Copenhagen, Denmark – internationally, it operates through the subsidiaries Genmab B.V. in Utrecht, The Netherlands, Genmab U.S., Inc. in Princeton, USA, and Genmab K.K. in Tokyo, Japan. Genmab is a dual-listed company with shares traded on both the Copenhagen Stock Exchange in Denmark and the NASDAQ Global Select Market in the US.
Nuvelo Inc. was a biopharmaceutical company engaged in the discovery, development and commercialization of drugs for acute cardiovascular disease, cancer and other debilitating medical conditions. On January 27, 2009, the company was acquired by ARCA Biopharma, Inc. in a reverse takeover transaction.
Sequenom, Inc. is an American company based in San Diego, California. It develops enabling molecular technologies, and highly sensitive laboratory genetic tests for NIPT. Sequenom's wholly owned subsidiary, Sequenom Center for Molecular Medicine (SCMM), offers multiple clinical molecular genetics tests to patients, including MaterniT21, plus a noninvasive prenatal test for trisomy 21, trisomy 18, and trisomy 13, and the SensiGene RHD Fetal RHD genotyping test.

Cambridge Antibody Technology Group Plc, was a biotechnology company headquartered in Cambridge, England, United Kingdom. Its core focus was on antibody therapeutics, primarily using Phage Display and Ribosome Display technology.
Melior Discovery, Inc. is a private biopharmaceutical company based in Exton, Pennsylvania, USA.
Life Sciences Foundation (LSF) was a San Francisco-based nonprofit organization that was established in 2011 to collect, preserve, interpret, and promote the history of biotechnology. LSF conducted historical research, maintained archives and published historically relevant materials and information.

CompugenLtd. is a clinical-stage publicly traded predictive drug discovery and development company headquartered in Israel, with shares traded on the NASDAQ Capital Market and on the Tel Aviv Stock Exchange. Compugen was established as computational drug discovery service provider in 1993. Compugen originally acted as service provider for pharma companies, supplying its software and computational services to predict different types of biological phenomena. It had arrangements with big companies such as Novartis AG, Abbot Laboratories and Pfizer Inc. Subsequently, Compugen made a decision to become a drug development company with its own internal pipeline, and in 2010, decided to a focus on oncology and immunology. OncoMed Pharmaceuticals and Five Prime Therapeutics are among Compugen's competitors.

Moderna, Inc. is an American pharmaceutical and biotechnology company based in Cambridge, Massachusetts, that focuses on RNA therapeutics, primarily mRNA vaccines. These vaccines use a copy of a molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA) to carry instructions for proteins to produce an immune response. The company's name is derived from the terms "modified", "RNA", and "modern".
Seagen Inc. is an American biotechnology company focused on developing and commercializing innovative, empowered monoclonal antibody-based therapies for the treatment of cancer. The company, headquartered in Bothell, Washington, is the industry leader in antibody-drug conjugates or ADCs, a technology designed to harness the targeting ability of monoclonal antibodies to deliver cell-killing agents directly to cancer cells. Antibody-drug conjugates are intended to spare non-targeted cells and thus reduce many of the toxic effects of traditional chemotherapy, while potentially enhancing antitumor activity.

Sutro Biopharma, Inc. is a publicly traded biotechnology company headquartered in South San Francisco, California focused on clinical-stage drug discovery, development and manufacturing. Using a proprietary cell-free protein synthesis platform, Sutro is working on oncology therapeutics using protein engineering and rational design. Founded in 2003 under the name Fundamental Applied Biology, the company name changed to Sutro Biopharma in 2009. William Newell, CEO as of 2024, joined Sutro in January 2009.
ImmunoGen, Inc. was a biotechnology company focused on the development of antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) therapeutics for the treatment of cancer. ImmunoGen was founded in 1981 and was headquartered in Waltham, Massachusetts.

Samsung Biologics Co., Ltd. is a global contract development and manufacturing organization headquartered in Songdo, Incheon, South Korea. The biotech division of Samsung Group, its core services range from late discovery to large-scale commercial manufacturing. The company focuses on monoclonal antibodies, bispecific antibodies, antibody-drug conjugates, and mRNA vaccines.
Rinat Neuroscience Corporation was a privately held biotechnology company that discovered and developed antibody-based drugs, including:

Kevin Donald Lustig is an American scientist and entrepreneur and founder of three life science companies: the pharmaceutical company Kalypsys in 2001; the online research marketplace Scientist.com in 2007; and the non-profit lab incubator Bio, Tech and Beyond in 2013.
Roivant Sciences Ltd. is a healthcare company focused on applying technology to drug development and building subsidiary biotech and healthcare technology companies. It was founded in 2014 by Vivek Ramaswamy.

Alexandria Real Estate Equities, Inc. is a real estate investment trust based in Pasadena, California that invests in office buildings and laboratories leased to tenants in the life science and technology industries.

BioNTech SE is a German biotechnology company based in Mainz that develops and manufactures active immunotherapies for patient-specific approaches to the treatment of diseases. It develops pharmaceutical candidates based on messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) for use as individualized cancer immunotherapies, as vaccines against infectious diseases and as protein replacement therapies for rare diseases, and also engineered cell therapy, novel antibodies and small molecule immunomodulators as treatment options for cancer.










