
The Burgess Shale is a fossil-bearing deposit exposed in the Canadian Rockies of British Columbia, Canada. It is famous for the exceptional preservation of the soft parts of its fossils. At 508 million years old, it is one of the earliest fossil beds containing soft-part imprints.

Marrella is an extinct genus of marrellomorph arthropod known from the middle Cambrian Burgess Shale of British Columbia. It is the most common animal represented in the Burgess Shale, with tens of thousands of specimens collected. Much rarer remains are also known from deposits in China.

Pikaia gracilens is an extinct, primitive chordate animal known from the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale of British Columbia. Described in 1911 by Charles Doolittle Walcott as an annelid, and in 1979 by Harry B. Whittington and Simon Conway Morris as a chordate, it became the "One of the most famous early chordate fossils," or "famously known as relative the earliest" chordates. It is estimated to have lived during the latter period of the Cambrian explosion. Since it initial discovery, more than a hundred specimens have been recovered.

Sidneyia is an extinct arthropod known from fossils found from the Early to the Mid Cambrian of China and the Burgess Shale formation of British Columbia. 144 specimens of Sidneyia are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they comprise 0.27% of the community.

Ottoia is a stem-group archaeopriapulid worm known from Cambrian fossils. Although priapulid-like worms from various Cambrian deposits are often referred to Ottoia on spurious grounds, the only clear Ottoia macrofossils come from the Burgess Shale of British Columbia, which was deposited 508 million years ago. Microfossils extend the record of Ottoia throughout the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin, from the mid- to late- Cambrian. A few fossil finds are also known from China.
Derek Ernest Gilmor Briggs is an Irish palaeontologist and taphonomist based at Yale University. Briggs is one of three palaeontologists, along with Harry Blackmore Whittington and Simon Conway Morris, who were key in the reinterpretation of the fossils of the Burgess Shale. He is the Yale University G. Evelyn Hutchinson Professor of Geology and Geophysics, Curator of Invertebrate Paleontology at Yale's Peabody Museum of Natural History, and former Director of the Peabody Museum.

Dinomischusis a rare fossil animal from the Cambrian period. It reached 20 mm in height, was attached to the sea floor by a stalk, and looked loosely like a flower. The cup-shaped body at the top of the stalk probably fed by filtering the surrounding seawater, and may have created a current to facilitate this. Its mouth and anus sat next to one another.

Odaraia is a genus of bivalved arthropod from the Middle Cambrian. Its fossils, which reach 15 centimetres (5.9 in) in length, have been found in the Burgess Shale in British Columbia, Canada.

Habelia is a genus of extinct arthropod from the Middle Cambrian. Its fossils have been found in the Burgess Shale in British Columbia, Canada. Fifty-four specimens of Habelia are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they comprise 0.1% of the community. While previously enigmatic, a 2017 redescription found that it formed a clade (Habeliida) with Sanctacaris, Utahcaris, Wisangocaris and Messorocaris as a stem-group to Chelicerata. Habelia is thought to have been durophagous, feeding on hard shelled organisms.
A number of assemblages bear fossil assemblages similar in character to that of the Burgess Shale. While many are also preserved in a similar fashion to the Burgess Shale, the term "Burgess Shale-type fauna" covers assemblages based on taxonomic criteria only.

Hurdia is an extinct genus of hurdiid radiodont that lived 505 million years ago during the Cambrian Period. As a radiodont like Peytoia and Anomalocaris, it is part of the ancestral lineage that led to euarthropods.

The Burgess Shale, a series of fossil beds in the Canadian Rockies, was first noticed in 1886 by Richard McConnell of the Geological Survey of Canada (GSC). His and subsequent finds, all from the Mount Stephen area, came to the attention of palaeontologist Charles Doolittle Walcott, who in 1907 found time to reconnoitre the area. He opened a quarry in 1910 and in a series of field trips brought back 65,000 specimens, which he identified as Middle Cambrian in age. Due to the quantity of fossils and the pressures of his other duties at the Smithsonian Institution, Walcott was only able to publish a series of "preliminary" papers, in which he classified the fossils within taxa that were already established. In a series of visits beginning in 1924, Harvard University professor Percy Raymond collected further fossils from Walcott's quarry and higher up on Fossil Ridge, where slightly different fossils were preserved.

Herpetogaster is an extinct cambroernid genus of animal from the Early Cambrian Chengjiang biota of China, Pioche Formation of Nevada and Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale of Canada containing the species Herpetogaster collinsi and Herpetogaster haiyanensis.

Pagetia Walcott, 1916. is a small genus of trilobite, assigned to the Eodiscinid family Pagetiidae and which had global distribution during the Middle Cambrian. The genus contains 55 currently recognized species, each with limited spatial and temporal ranges.

Selkirkia is a genus of predatory, tubicolous priapulid worms known from the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale, Ogygopsis Shale and Puncoviscana Formation. 142 specimens of Selkirkia are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they comprise 0.27% of the community. In the Burgess Shale, 20% of the tapering, organic-walled tubes are preserved with the worm inside them, whereas the other 80% are empty. Whilst alive, the tubes were probably vertical, whereas trilobite-occupied tubes are horizontal.
The Mount Stephen trilobite beds are a series of fossil strata on Mount Stephen, British Columbia that contain exceptionally preserved fossil material. Part of the same stratigraphic unit as the Burgess Shale deposit, many non-mineralized parts are preserved; in addition, a high density of trilobite fossils is present.

Titanokorys is a genus of extinct hurdiid radiodont that existed during the mid Cambrian. It is the largest member of its family from the Cambrian, with a body length of 50 cm (20 in) long, making it one of the largest animals of the time. It bears a resemblance to the related genus Cambroraster. Fossils of T. gainesi were first found within Marble Canyon in 2018. The fossils were not named until 2021 because they were assumed to be giant specimens of Cambroraster.

Collinsovermis is a genus of extinct panarthropod belonging to the group Lobopodia and known from the middle Cambrian Burgess Shale in British Columbia, Canada. It is monotypic having only one species, Collinsovermis monstruosus. After its initial discovery in 1983, Desmond H. Collins popularised it as a unique animal and was subsequently dubbed "Collins' monster" for its unusual super armoured body. The formal scientific description and name were given in 2020.
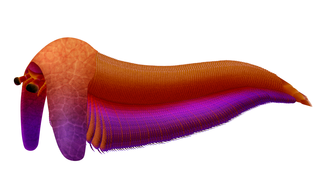
Balhuticaris is a genus of extinct bivalved hymenocarine arthropod that lived in the Cambrian aged Burgess Shale in what is now British Columbia around 506 million years ago. This extremely multisegmented arthropod is the largest member of the group, and it was even one of the largest animals of the Cambrian, with individuals reaching lengths of 245 mm (9 in). Fossils of this animal suggests that gigantism occurred in more groups of Arthropoda than had been previously thought. It also presents the possibility that bivalved arthropods were very diverse, and filled in a lot of ecological niches.
This is a list of the biota of the Burgess Shale, a Cambrian lagerstätte located in Yoho National Park in Canada.
















