Notable given names
- Jimeno of Pamplona (9th century) nobleman and possible sub-king, founder of Jiménez dynasty
- Jimeno Garcés of Pamplona, king of Pamplona, 925-932
Jimeno (also Gimeno, Ximeno, Chemene, Exemeno) is a given name derived from Ximen, [1] [2] a variant of the medieval Basque given name Semen, the origins of which arose in the Basque regions, then its use spread west across northern Spain into Castile and Galicia, then followed the Reconquista south during medieval times. It was frequently recorded in Latin using forms similar to those used for Simon, but this is probably not indicative of shared derivation.
Someone named "Seguin" was attested in Frankish chronicles when referring to the Count of Bordeaux and Duke of Vasconia (778, 814 and 816). The name is also recorded in Medieval Latin as Sihiminus, perhaps a misspelling of Ximinus, may have been a local Basque whose family later fled south over the Pyrenees and helped Enneco Arista take over in Pamplona.
Another character is identified in 778 as "Jimeno, the strong", from Arab sources in Al-Andalus, where it calls him "Mothmin al-Akra", a Basque or Hispanic magnate in the upper Ebro territories within the later independent principality of Navarre. This person was possibly related to others near Pamplona in local opposition to both the invading Franks under Charlemagne and the new ruler of the Islamic Iberian realm, Abd al-Rahman I.
Some think the name may be a corruption of the later part of the Latin name Ma-ximinus, as there is late Classic records that various individuals with this name were becoming very active as officials and residents in upper Hispania near the Pyrenees and Tarraconensis during the last century of the Western Roman Empire, and perhaps into the transition from imperial province to independent Kingdom during the Visigothic rule.

Navarre, officially the Chartered Community of Navarre, is a landlocked foral autonomous community and province in northern Spain, bordering the Basque Autonomous Community, La Rioja, and Aragon in Spain and Nouvelle-Aquitaine in France. The capital city is Pamplona. The present-day province makes up the majority of the territory of the medieval Kingdom of Navarre, a long-standing Pyrenean kingdom that occupied lands on both sides of the western Pyrenees, with its northernmost part, Lower Navarre, located in the southwest corner of France.

Pamplona is the capital city of the Chartered Community of Navarre, in Spain.
Spanish names are the traditional way of identifying, and the official way of registering, a person in Spain. They are composed of a given name and two surnames. Traditionally, the first surname is the father's first surname, and the second is the mother's first surname. Since 1999, the order of the surnames in a family in Spain is decided when registering the first child, but the traditional order is nearly universally chosen.

The Battle of Roncevaux Pass in 778 saw a large force of Basques ambush a part of Charlemagne's army in Roncevaux Pass, a high mountain pass in the Pyrenees on the present border between France and Spain, after his invasion of the Iberian Peninsula.

The Kingdom of Navarre, originally the Kingdom of Pamplona, was a Basque kingdom that occupied lands on both sides of the western Pyrenees, with its northernmost areas originally reaching the Atlantic Ocean, between present-day Spain and France.
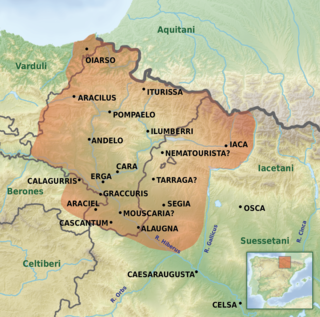
The Vascones were a pre-Roman tribe who, on the arrival of the Romans in the 1st century, inhabited a territory that spanned between the upper course of the Ebro river and the southern basin of the western Pyrenees, a region that coincides with present-day Navarre, western Aragon and northeastern La Rioja, in the Iberian Peninsula. The Vascones are often considered ancestors of the present-day Basques to whom they left their name.
Íñigo Arista was a Basque chieftain and the first king of Pamplona. He is thought to have risen to prominence after the defeat of local Frankish partisans at the Battle of Pancorbo in 816, and his rule is usually dated from shortly after the defeat of a Carolingian army in 824.

The Aquitanian language was the language of the ancient Aquitani, spoken on both sides of the western Pyrenees in ancient Aquitaine and in the areas south of the Pyrenees in the valleys of the Basque Country before the Roman conquest. It probably survived in Aquitania north of the Pyrenees until the Early Middle Ages.
García Íñiguez I, also known as García I was the second king of Pamplona from 851–2 until his death. He was the son of Íñigo Arista, the first king of Pamplona. Educated in Cordoba, he was a successful military leader who led the military campaigns of the kingdom during the last years of his father's life.
Jiménez is a patronymic surname of Iberian origin, first appearing in the Basque lands.
Jimeno Garcés, sometimes Jimeno II, was the King of Pamplona from 925 until his death. He was the brother of King Sancho I Garcés and son of García Jiménez by his second wife, Dadildis of Pallars. When his brother died, Sancho's only son, García Sánchez, was still a child and Jimeno succeeded his brother, becoming the second ruler of the Jiménez dynasty.
Seguin I Lupo was Duke of Gascony from 812 until 816, when Louis the Pious deposed him "because of his boundless arrogance and wicked ways", according to the contemporary Frankish chroniclers. The "Basques across the Garonne and around the Pyrenees" rebelled against the removal of their duke, but the Frankish king received the submission of the rebels in Dax. The emperor crossed the Pyrenees and "settled matters" in Pamplona. This could imply that the Gascony of Seguin's day was trans-Pyrenean, i.e., comprised lands on both sides of the mountains.

The Jiménez dynasty, alternatively called the Jimena, the Sancha, the Banu Sancho, the Abarca or the Banu Abarca, was a medieval ruling family which, beginning in the 9th century, eventually grew to control the royal houses of several kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula during the 11th and 12th centuries, namely the Kingdoms of Navarre, Aragon, Castile, León and Galicia as well as of other territories in the South of France. The family played a major role in the Reconquista, expanding the territory under the direct control of the Christian states as well as subjecting neighboring Muslim taifas to vassalage. Each of the Jiménez royal lines ultimately went extinct in the male line in the 12th or 13th century.

The Duchy of Gascony or Duchy of Vasconia was a duchy located in present-day southwestern France and northeastern Spain, an area encompassing the modern region of Gascony. The Duchy of Gascony, then known as Wasconia, was originally a Frankish march formed to hold sway over the Basques. However, the duchy went through different periods, from its early years with its distinctively Basque element to the merger in personal union with the Duchy of Aquitaine to the later period as a dependency of the Plantagenet kings of England.
Semyon /ʂemen/ or Xemen /ʃemen/ is a medieval Basque given name of the Vasconic area. It is based on the Basque root seme < senbe 'son' as found in the ancient Aquitanian name Sembetten, attested form "sehi" as 'child', hypothetical ancient root *seni. The explanation by the Biblical name Šim’ōn (Simon) is less convincing. Some think the name may be a corruption of the later part of the Latin name Ma-ximinus, as there are late Classic records that various individuals with this name were becoming very active as officials and residents in upper Hispania near the Pyrenees and Tarraconensis during the last century of the Western Roman Empire, and perhaps into the period of transition from imperial province to independent Kingdom during Visigothic rule.
Inigo derives from the Castilian rendering (Íñigo) of the medieval Basque name Eneko. Ultimately, the name means "my little (man)". While mostly seen among the Iberian diaspora, it also gained a limited popularity in the United Kingdom.

Basque surnames are surnames with Basque-language origins or a long, identifiable tradition in the Basque Country. They can be divided into two main types, patronymic and non-patronymic.

Navarro-Aragonese was a Romance language once spoken in a large part of the Ebro River basin, south of the middle Pyrenees; the dialects of the modern Aragonese language, spoken in a small portion of that territory, and the Navarrese dialect can be seen as its last remaining forms. The areas where Navarro-Aragonese was spoken might have included most of Aragon, southern Navarre, and La Rioja. It was also spoken across several towns of central Navarre in a multilingual environment with Occitan, where Basque was the native language.

Wiliesind was a bishop of Pamplona. His episcopate falls in a very obscure period in Pamplonan history. His predecessor, Opilano, is the first bishop mentioned in source after 693, and no successor of his is known before Jimeno in the 880s. Wiliesind's name is Gothic in origin, although the diocese of Pamplona was predominantly Basque at the time. It probably indicates that Pamplona still looked to Toledo as its spiritual guide, rather than across the Pyrenees.