Titan is the largest moon of Saturn and the second-largest in the Solar System. It is the only moon known to have an atmosphere denser than the Earth's and is the only known object in space—other than Earth—on which there is clear evidence that stable bodies of liquid exist. Titan is one of seven gravitationally rounded moons of Saturn and the second-most distant among them. Frequently described as a planet-like moon, Titan is 50% larger in diameter than Earth's Moon and 80% more massive. It is the second-largest moon in the Solar System after Jupiter's Ganymede and is larger than Mercury; yet Titan is only 40% as massive as Mercury, because Mercury is mainly iron and rock while much of Titan is ice, which is less dense.

Xanadu is a highly reflective area on the leading hemisphere of Saturn's moon Titan. Its name comes from an alternate transcription of Shangdu, the summer capital of the Yuan dynasty established by Kublai Khan and made famous by Samuel Taylor Coleridge.

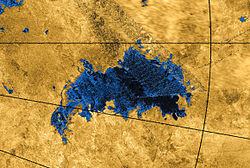
Ontario Lacus is a lake composed of methane, ethane and propane near the south pole of Saturn's moon Titan. Its character as a hydrocarbon lake was confirmed by observations from the Cassini spacecraft, published in the 31 July 2008 edition of Nature. Ontario Lacus has a surface area of about 15,000 square kilometers (5,800 sq mi), about 20% smaller than its terrestrial namesake, Lake Ontario in North America. In April 2012, it was announced that it may be more like a mudflat or salt pan.

Lakes of liquid ethane and methane exist on the surface of Titan, Saturn's largest moon. This was confirmed by the Cassini–Huygens space probe, as had been suspected since the 1980s. The large bodies of liquid are known as maria (seas) and the small ones as lacūs (lakes).

The climate of Titan, the largest moon of Saturn, is similar in many respects to that of Earth, despite having a far lower surface temperature. Its thick atmosphere, methane rain, and possible cryovolcanism create an analogue, though with different materials, to the climatic changes undergone by Earth during the far shorter year of Earth.
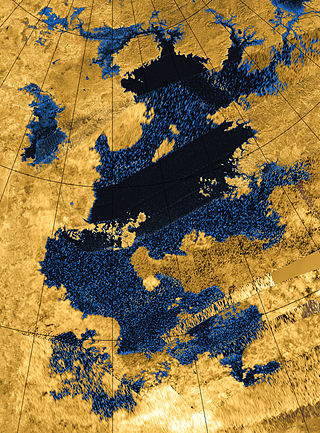
Kraken Mare is the largest known hydrocarbon sea on the surface of Saturn's moon Titan. It was discovered by the space probe Cassini in 2006, and was named in 2008 after the Kraken, a legendary sea monster. It covers an area slightly bigger than the Caspian Sea on Earth, making it the largest known lake in the Solar System.

Ligeia Mare is a lake in the north polar region of Titan, the planet Saturn's largest moon. It is the second largest body of liquid on the surface of Titan, after Kraken Mare. Larger than Lake Superior on Earth, it is mostly composed of liquid methane, with unknown but lesser components of dissolved nitrogen and ethane, as well as other organic compounds. It is located at 78° N, 249° W, and has been fully imaged by the Cassini spacecraft. Measuring roughly 420 km (260 mi) by 350 km (217 mi) across, it has a surface area of about 126,000 km2, and a shoreline over 2,000 km (1,240 mi) in length. The lake may be hydrologically connected to the larger Kraken Mare. Its namesake is Ligeia, one of the sirens in Greek mythology.

Sun glitter is a bright, sparkling light formed when sunlight reflects from water waves. The waves may be caused by natural movement of the water, or by the movement of birds or animals in the water. Even a ripple from a thrown rock will create a momentary glitter.

Sotra Patera is a prominent depression on Titan, the largest moon of Saturn. It was formerly known as Sotra Facula; the current name was approved on 19 December 2012. It is a possible cryovolcanic caldera 30 km (19 mi) across and 1.7 km (1.1 mi) deep, and is immediately to the east of the largest putative cryovolcanic mountain on Titan, the 1.45 km (0.90 mi) high Doom Mons. Sotra Patera is the deepest known pit on Titan.

Punga Mare is a lake in the north polar region of Titan, the planet Saturn's largest moon. After Kraken Mare and Ligeia Mare, it is the third largest known body of liquid on Titan. It is composed of liquid hydrocarbons. Located almost adjacent to the north pole at 85.1° N, 339.7° W, it measures roughly 380 km (236 mi) across, greater than the length of Lake Victoria on Earth. Its surface area is ~61,000 km2. Its namesake is Punga, in Māori mythology ancestor of sharks, rays and lizards and a son of Tangaroa, the god of the sea.

Bolsena Lacus is one of a number of hydrocarbon lakes found on Saturn's largest moon, Titan.

Sotonera Lacus is one of a number of hydrocarbon lakes found on Saturn's largest moon, Titan.

Hammar Lacus is one of a number of hydrocarbon seas and lakes found on Saturn's largest moon, Titan.

Feia Lacus is one of a number of hydrocarbon seas and lakes found on Saturn's largest moon, Titan. It was named in 2007 on the basis of data taken by the space probe Cassini.

Müggel Lacus is one of a number of hydrocarbon seas and lakes found on Saturn's largest moon, Titan.

Ladoga Lacus is a geographical feature on Saturn's largest moon, Titan, named after Lake Ladoga, Russia. It is one of a number of "methane lakes" found in Titan's north polar region.
Vid Flumina is a river system of liquid methane and ethane on Saturn's moon Titan. It is more than 400 km (249 mi) long and flows into Titan's second largest hydrocarbon sea, Ligeia Mare. The surface of Titan is mostly water ice, so Vid Flumina is a river of methane and ethane flowing across and cutting canyons into ice as though it were bedrock. NASA scientists think that it likely has rapids, whirlpools and falls, just like rivers on Earth.

Mayda Insula is an island in the Kraken Mare, a body of liquid composed primarily of methane, on Saturn's largest moon Titan. Mayda Insula is the first island (insula) to be named on a planet or moon other than Earth.

The geology of Titan encompasses the geological characteristics of Titan, the largest moon of Saturn. Titan's density of 1.881 g/cm3 indicates that it is roughly 40–60% rock by mass, with the rest being water ice and other materials. It is differentiated into a rocky core, liquid water ocean, and an icy shell; the core and ocean may be partitioned by a layer of exotic high-pressure ices, and the icy shell may have a chemically distinct surface crust.