Related Research Articles

Nuclear warfare, also known as atomic warfare, is a military conflict or prepared political strategy that deploys nuclear weaponry. Nuclear weapons are weapons of mass destruction; in contrast to conventional warfare, nuclear warfare can produce destruction in a much shorter time and can have a long-lasting radiological result. A major nuclear exchange would likely have long-term effects, primarily from the fallout released, and could also lead to secondary effects, such as "nuclear winter", nuclear famine, and societal collapse. A global thermonuclear war with Cold War-era stockpiles, or even with the current smaller stockpiles, may lead to various scenarios including the extinction of the human species.

World War III, WWIII, or WW3, or the Third World War are the names given to the hypothetical global conflict subsequent to World War I and World War II. The term has been in use since as early as 1941. Some apply it loosely to limited or more minor conflicts such as the Cold War or the war on terror. In contrast, others assume that such a conflict would surpass prior world wars in both scope and destructive impact.

Nuclear artillery is a subset of limited-yield tactical nuclear weapons, in particular those weapons that are launched from the ground at battlefield targets. Nuclear artillery is commonly associated with shells delivered by a cannon, but in a technical sense short-range artillery rockets or tactical ballistic missiles are also included.

The M-28 or M-29 Davy Crockett Weapon System was a tactical nuclear recoilless smoothbore gun for firing the M388 nuclear projectile, armed with the W54 nuclear warhead, that was deployed by the United States during the Cold War. It was the first project assigned to the United States Army Weapon Command in Rock Island, Illinois. It remains one of the smallest nuclear weapon systems ever built, with a yield of 20 tonnes of TNT (84 GJ). It is named after American folk hero, soldier, and congressman Davy Crockett.

The Sum of All Fears is a political thriller novel, written by Tom Clancy and released on August 14, 1991, as the sequel to Clear and Present Danger (1989). Main character Jack Ryan, who is now the Deputy Director of Central Intelligence, tries to stop a crisis concerning the Middle East peace process wherein Palestinian and former East German terrorists conspire to bring the United States and Soviet Union into nuclear war. It debuted at number one on the New York Times bestseller list. A film adaptation, which is a reboot of the Jack Ryan film series and starring Ben Affleck as the younger iteration of the CIA analyst, was released on May 31, 2002.

The United States is known to have possessed three types of weapons of mass destruction: nuclear weapons, chemical weapons, and biological weapons. The U.S. is the only country to have used nuclear weapons on another country, when it detonated two atomic bombs over two Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki during World War II. It had secretly developed the earliest form of the atomic weapon during the 1940s under the title "Manhattan Project". The United States pioneered the development of both the nuclear fission and hydrogen bombs. It was the world's first and only nuclear power for four years, from 1945 until 1949, when the Soviet Union produced its own nuclear weapon. The United States has the second-largest number of nuclear weapons in the world, after the Russian Federation.

Canada has not officially maintained and possessed weapons of mass destruction since 1984 and, as of 1998, has signed treaties repudiating possession of them. Canada ratified the Geneva Protocol in 1930 and the Nuclear Non-proliferation Treaty in 1970.
Blue Water was a British battlefield nuclear missile of the early 1960s, intended to replace the MGM-5 Corporal, which was becoming obsolete. With roughly the same role and range as Corporal, the solid-fuel Blue Water was far simpler to use and would be significantly easier to support in the field. It was seen as a replacement for Corporal both in the UK as well as other NATO operators, notably Germany and possibly Turkey.
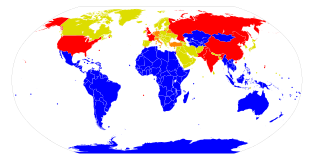
Nuclear sharing is a concept in NATO's policy of nuclear deterrence, which allows member countries without nuclear weapons of their own to participate in the planning for the use of nuclear weapons by NATO. In particular, it provides for the armed forces of those countries to be involved in delivering nuclear weapons in the event of their use.

Although Germany has the technical capability to produce weapons of mass destruction (WMD), since World War II it has refrained from producing those weapons. However, Germany participates in the NATO nuclear weapons sharing arrangements and trains for delivering United States nuclear weapons. Officially, 20 US-nuclear weapons are stationed in Büchel, Germany. It could be more or fewer, but the exact number of the weapons is a state secret.

The Ground Launched Cruise Missile, or GLCM, was a ground-launched cruise missile developed by the United States Air Force in the last decade of the Cold War and disarmed under the INF Treaty.
The Göttingen Manifesto was a declaration of 18 leading nuclear scientists of West Germany against arming the West German army with tactical nuclear weapons in the 1950s, the early part of the Cold War, as the West German government under chancellor Adenauer had suggested.

A tactical nuclear weapon (TNW) or non-strategic nuclear weapon (NSNW) is a nuclear weapon that is designed to be used on a battlefield in military situations, mostly with friendly forces in proximity and perhaps even on contested friendly territory. Generally smaller in explosive power, they are defined in contrast to strategic nuclear weapons, which are designed mostly to be targeted at the enemy interior far away from the war front against military bases, cities, towns, arms industries, and other hardened or larger-area targets to damage the enemy's ability to wage war. As of 2023, tactical nuclear weapons have never been used.

The NATO Double-Track Decision was the decision by NATO from December 12, 1979, to offer the Warsaw Pact a mutual limitation of medium-range ballistic missiles and intermediate-range ballistic missiles. It was combined with a threat by NATO to deploy more medium-range nuclear weapons in Western Europe after the Euromissile Crisis.

The UUM-44 SUBROC was a type of submarine-launched rocket deployed by the United States Navy as an anti-submarine weapon. It carried a 250 kiloton thermonuclear warhead configured as a nuclear depth bomb.

Atomic demolition munitions (ADMs), colloquially known as nuclear land mines, are small nuclear explosive devices. ADMs were developed for both military and civilian purposes. As weapons, they were designed to be exploded in the forward battle area, in order to block or channel enemy forces. Non-militarily, they were designed for demolition, mining or earthmoving. However, apart from testing they have never been used for either purpose.

Büchel Air Base is a military air base of the Luftwaffe in Büchel (Germany), near the city of Cochem and at about 70 km from Spangdahlem Air Base. It is home to the Taktisches Luftwaffengeschwader 33 of the German Air Force (Luftwaffe) and the 702 Munitions Support Squadron of the United States Air Force (USAF). Since 1985, tactical Air Force Wing 33 has been operating German Panavia Tornado airplanes, which can deliver twenty B61 nuclear bombs, the only remaining nuclear weapons in Germany.

The Italian nuclear weapons program was an effort by Italy to develop nuclear weapons in the late 1960s and early 1970s. Italian scientists such as Enrico Fermi and Edoardo Amaldi had been at the forefront of the development of the technology behind nuclear weapons, but the country was banned from developing the technology at the end of the Second World War. After abortive proposals to establish a multilateral program with NATO Allies in the 1950s and 1960s, Italy launched a national nuclear weapons program. The country converted the light cruiser Giuseppe Garibaldi and developed and tested a ballistic missile called Alfa. The program ended in 1975 upon Italy's accession to the Non-Proliferation Treaty. Currently, Italy does not produce or possess nuclear weapons but takes part in the NATO nuclear sharing program, hosting B61 nuclear bombs at the Aviano and Ghedi Air Bases.
During the Russian invasion of Ukraine, several senior Russian politicians, including president Vladimir Putin, former president and prime minister Dmitry Medvedev, and foreign minister Sergey Lavrov, have made a number of statements widely seen as threatening the use of nuclear weapons. The possibility of Russia using tactical nuclear weapons, and the risk of broader nuclear escalation, has been widely discussed by commentators and in the media. Additionally, the Russian occupation of the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant has led to a crisis over the safety of the plant and the risk of a nuclear disaster.