
Neuropil is any area in the nervous system composed of mostly unmyelinated axons, dendrites and glial cell processes that forms a synaptically dense region containing a relatively low number of cell bodies. The most prevalent anatomical region of neuropil is the brain which, although not completely composed of neuropil, does have the largest and highest synaptically concentrated areas of neuropil in the body. For example, the neocortex and olfactory bulb both contain neuropil.
The development of the nervous system, or neural development (neurodevelopment), refers to the processes that generate, shape, and reshape the nervous system of animals, from the earliest stages of embryonic development to adulthood. The field of neural development draws on both neuroscience and developmental biology to describe and provide insight into the cellular and molecular mechanisms by which complex nervous systems develop, from nematodes and fruit flies to mammals.

In neuroscience, long-term potentiation (LTP) is a persistent strengthening of synapses based on recent patterns of activity. These are patterns of synaptic activity that produce a long-lasting increase in signal transmission between two neurons. The opposite of LTP is long-term depression, which produces a long-lasting decrease in synaptic strength.

The α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor (also known as AMPA receptor, AMPAR, or quisqualate receptor) is an ionotropic transmembrane receptor for glutamate (iGluR) and predominantly Na+ ion channel that mediates fast synaptic transmission in the central nervous system (CNS). It has been traditionally classified as a non-NMDA-type receptor, along with the kainate receptor. Its name is derived from its ability to be activated by the artificial glutamate analog AMPA. The receptor was first named the "quisqualate receptor" by Watkins and colleagues after a naturally occurring agonist quisqualate and was only later given the label "AMPA receptor" after the selective agonist developed by Tage Honore and colleagues at the Royal Danish School of Pharmacy in Copenhagen. The GRIA2-encoded AMPA receptor ligand binding core (GluA2 LBD) was the first glutamate receptor ion channel domain to be crystallized.
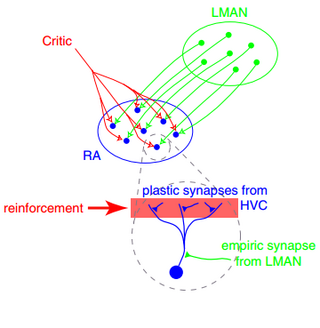
In neuroscience, synaptic plasticity is the ability of synapses to strengthen or weaken over time, in response to increases or decreases in their activity. Since memories are postulated to be represented by vastly interconnected neural circuits in the brain, synaptic plasticity is one of the important neurochemical foundations of learning and memory.

An electrical synapse is a mechanical and electrically conductive synapse, a functional junction between two neighboring neurons. The synapse is formed at a narrow gap between the pre- and postsynaptic neurons known as a gap junction. At gap junctions, such cells approach within about 3.8 nm of each other, a much shorter distance than the 20- to 40-nanometer distance that separates cells at a chemical synapse. In many animals, electrical synapse-based systems co-exist with chemical synapses.
In neuroscience, a silent synapse is an excitatory glutamatergic synapse whose postsynaptic membrane contains NMDA-type glutamate receptors but no AMPA-type glutamate receptors. These synapses are named "silent" because normal AMPA receptor-mediated signaling is not present, rendering the synapse inactive under typical conditions. Silent synapses are typically considered to be immature glutamatergic synapses. As the brain matures, the relative number of silent synapses decreases. However, recent research on hippocampal silent synapses shows that while they may indeed be a developmental landmark in the formation of a synapse, that synapses can be "silenced" by activity, even once they have acquired AMPA receptors. Thus, silence may be a state that synapses can visit many times during their lifetimes.

Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), or abrineurin, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the BDNF gene. BDNF is a member of the neurotrophin family of growth factors, which are related to the canonical nerve growth factor (NGF), a family which also includes NT-3 and NT-4/NT-5. Neurotrophic factors are found in the brain and the periphery. BDNF was first isolated from a pig brain in 1982 by Yves-Alain Barde and Hans Thoenen.
Spike-timing-dependent plasticity (STDP) is a biological process that adjusts the strength of connections between neurons in the brain. The process adjusts the connection strengths based on the relative timing of a particular neuron's output and input action potentials. The STDP process partially explains the activity-dependent development of nervous systems, especially with regard to long-term potentiation and long-term depression.
Coincidence detection is a neuronal process in which a neural circuit encodes information by detecting the occurrence of temporally close but spatially distributed input signals. Coincidence detectors influence neuronal information processing by reducing temporal jitter and spontaneous activity, allowing the creation of variable associations between separate neural events in memory. The study of coincidence detectors has been crucial in neuroscience with regards to understanding the formation of computational maps in the brain.

Homer protein homolog 1 or Homer1 is a neuronal protein that in humans is encoded by the HOMER1 gene. Other names are Vesl and PSD-Zip45.

Glutamate receptor, ionotropic, delta 2, also known as GluD2, GluRδ2, or δ2, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GRID2 gene. This protein together with GluD1 belongs to the delta receptor subtype of ionotropic glutamate receptors. They possess 14–24% sequence homology with AMPA, kainate, and NMDA subunits, but, despite their name, do not actually bind glutamate or various other glutamate agonists.

Nonsynaptic plasticity is a form of neuroplasticity that involves modification of ion channel function in the axon, dendrites, and cell body that results in specific changes in the integration of excitatory postsynaptic potentials and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials. Nonsynaptic plasticity is a modification of the intrinsic excitability of the neuron. It interacts with synaptic plasticity, but it is considered a separate entity from synaptic plasticity. Intrinsic modification of the electrical properties of neurons plays a role in many aspects of plasticity from homeostatic plasticity to learning and memory itself. Nonsynaptic plasticity affects synaptic integration, subthreshold propagation, spike generation, and other fundamental mechanisms of neurons at the cellular level. These individual neuronal alterations can result in changes in higher brain function, especially learning and memory. However, as an emerging field in neuroscience, much of the knowledge about nonsynaptic plasticity is uncertain and still requires further investigation to better define its role in brain function and behavior.
Developmental plasticity is a general term referring to changes in neural connections during development as a result of environmental interactions as well as neural changes induced by learning. Much like neuroplasticity, or brain plasticity, developmental plasticity is specific to the change in neurons and synaptic connections as a consequence of developmental processes. A child creates most of these connections from birth to early childhood. There are three primary methods by which this may occur as the brain develops, but critical periods determine when lasting changes may form. Developmental plasticity may also be used in place of the term phenotypic plasticity when an organism in an embryonic or larval stage can alter its phenotype based on environmental factors. However, a main difference between the two is that phenotypic plasticity experienced during adulthood can be reversible, whereas traits that are considered developmentally plastic set foundations during early development that remain throughout the life of the organism.
Long-term potentiation (LTP), thought to be the cellular basis for learning and memory, involves a specific signal transmission process that underlies synaptic plasticity. Among the many mechanisms responsible for the maintenance of synaptic plasticity is the cadherin–catenin complex. By forming complexes with intracellular catenin proteins, neural cadherins (N-cadherins) serve as a link between synaptic activity and synaptic plasticity, and play important roles in the processes of learning and memory.

Michael A. Häusser FRS FMedSci is professor of Neuroscience, based in the Wolfson Institute for Biomedical Research at University College London (UCL).
Extrasynaptic NMDA receptors are glutamate-gated neurotransmitter receptors that are localized to non-synaptic sites on the neuronal cell surface. In contrast to synaptic NMDA receptors that promote acquired neuroprotection and synaptic plasticity, extrasynaptic NMDA receptors are coupled to activation of death-signaling pathways. Extrasynaptic NMDA receptors are responsible for initiating excitotoxicity and have been implicated in the etiology of neurodegenerative diseases, including stroke, Huntington’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).

Panayiota Poirazi is a neuroscientist known for her work in modelling dendritic computations. She is an elected member of the European Molecular Biology Organization (EMBO).
Hey-Kyoung Lee is a neuroscience professor at Johns Hopkins University. She studies cross-modal plasticity between visual and auditory systems.

Yukiko Goda is a Japanese molecular biologist who is a professor and group leader at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology. Her research considers neural communication through synapses. She was elected a Member of the European Molecular Biology Organization in 2023.











