
In theoretical physics, quantum chromodynamics (QCD) is the study of the strong interaction between quarks mediated by gluons. Quarks are fundamental particles that make up composite hadrons such as the proton, neutron and pion. QCD is a type of quantum field theory called a non-abelian gauge theory, with symmetry group SU(3). The QCD analog of electric charge is a property called color. Gluons are the force carriers of the theory, just as photons are for the electromagnetic force in quantum electrodynamics. The theory is an important part of the Standard Model of particle physics. A large body of experimental evidence for QCD has been gathered over the years.

In particle physics, quantum electrodynamics (QED) is the relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved. QED mathematically describes all phenomena involving electrically charged particles interacting by means of exchange of photons and represents the quantum counterpart of classical electromagnetism giving a complete account of matter and light interaction.

In physics, a spin network is a type of diagram which can be used to represent states and interactions between particles and fields in quantum mechanics. From a mathematical perspective, the diagrams are a concise way to represent multilinear functions and functions between representations of matrix groups. The diagrammatic notation can thus greatly simplify calculations.

Renormalization is a collection of techniques in quantum field theory, statistical field theory, and the theory of self-similar geometric structures, that are used to treat infinities arising in calculated quantities by altering values of these quantities to compensate for effects of their self-interactions. But even if no infinities arose in loop diagrams in quantum field theory, it could be shown that it would be necessary to renormalize the mass and fields appearing in the original Lagrangian.
In theoretical physics, the term renormalization group (RG) refers to a formal apparatus that allows systematic investigation of the changes of a physical system as viewed at different scales. In particle physics, it reflects the changes in the underlying force laws as the energy scale at which physical processes occur varies, energy/momentum and resolution distance scales being effectively conjugate under the uncertainty principle.

Leonard Susskind is an American theoretical physicist, Professor of theoretical physics at Stanford University and founding director of the Stanford Institute for Theoretical Physics. His research interests are string theory, quantum field theory, quantum statistical mechanics and quantum cosmology. He is a member of the US National Academy of Sciences, and the American Academy of Arts and Sciences, an associate member of the faculty of Canada's Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics, and a distinguished professor of the Korea Institute for Advanced Study.

In physics, lattice gauge theory is the study of gauge theories on a spacetime that has been discretized into a lattice.
In physics, the Landau pole is the momentum scale at which the coupling constant of a quantum field theory becomes infinite. Such a possibility was pointed out by the physicist Lev Landau and his colleagues in 1954. The fact that couplings depend on the momentum scale is the central idea behind the renormalization group.

Lattice QCD is a well-established non-perturbative approach to solving the quantum chromodynamics (QCD) theory of quarks and gluons. It is a lattice gauge theory formulated on a grid or lattice of points in space and time. When the size of the lattice is taken infinitely large and its sites infinitesimally close to each other, the continuum QCD is recovered.
In lattice field theory, fermion doubling occurs when naively putting fermionic fields on a lattice, resulting in more fermionic states than expected. For the naively discretized Dirac fermions in Euclidean dimensions, each fermionic field results in identical fermion species, referred to as different tastes of the fermion. The fermion doubling problem is intractably linked to chiral invariance by the Nielsen–Ninomiya theorem. Most strategies used to solve the problem require using modified fermions which reduce to the Dirac fermion only in the continuum limit.

In particle physics, the history of quantum field theory starts with its creation by Paul Dirac, when he attempted to quantize the electromagnetic field in the late 1920s. Major advances in the theory were made in the 1940s and 1950s, leading to the introduction of renormalized quantum electrodynamics (QED). The field theory behind QED was so accurate and successful in predictions that efforts were made to apply the same basic concepts for the other forces of nature. Beginning in 1954, the parallel was found by way of gauge theory, leading by the late 1970s, to quantum field models of strong nuclear force and weak nuclear force, united in the modern Standard Model of particle physics.
In lattice field theory, staggered fermions are a fermion discretization that reduces the number of fermion doublers from sixteen to four. They are one of the fastest lattice fermions when it comes to simulations and they also possess some nice features such as a remnant chiral symmetry, making them very popular in lattice QCD calculations. Staggered fermions were first formulated by John Kogut and Leonard Susskind in 1975 and were later found to be equivalent to the discretized version of the Dirac–Kähler fermion.
In physics, Hamiltonian lattice gauge theory is a calculational approach to gauge theory and a special case of lattice gauge theory in which the space is discretized but time is not. The Hamiltonian is then re-expressed as a function of degrees of freedom defined on a d-dimensional lattice.
In particle physics, the parton model is a model of hadrons, such as protons and neutrons, proposed by Richard Feynman. It is useful for interpreting the cascades of radiation produced from quantum chromodynamics (QCD) processes and interactions in high-energy particle collisions.
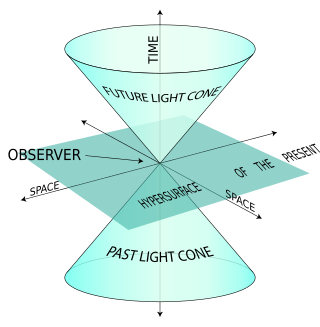
The light-front quantization of quantum field theories provides a useful alternative to ordinary equal-time quantization. In particular, it can lead to a relativistic description of bound systems in terms of quantum-mechanical wave functions. The quantization is based on the choice of light-front coordinates, where plays the role of time and the corresponding spatial coordinate is . Here, is the ordinary time, is one Cartesian coordinate, and is the speed of light. The other two Cartesian coordinates, and , are untouched and often called transverse or perpendicular, denoted by symbols of the type . The choice of the frame of reference where the time and -axis are defined can be left unspecified in an exactly soluble relativistic theory, but in practical calculations some choices may be more suitable than others.

In strong interaction physics, light front holography or light front holographic QCD is an approximate version of the theory of quantum chromodynamics (QCD) which results from mapping the gauge theory of QCD to a higher-dimensional anti-de Sitter space (AdS) inspired by the AdS/CFT correspondence proposed for string theory. This procedure makes it possible to find analytic solutions in situations where strong coupling occurs, improving predictions of the masses of hadrons and their internal structure revealed by high-energy accelerator experiments. The most widely used approach to finding approximate solutions to the QCD equations, lattice QCD, has had many successful applications; however, it is a numerical approach formulated in Euclidean space rather than physical Minkowski space-time.
Davison "Dave" Eugene Soper is an American theoretical physicist specializing in high energy physics.

The light-front quantization of quantum field theories provides a useful alternative to ordinary equal-time quantization. In particular, it can lead to a relativistic description of bound systems in terms of quantum-mechanical wave functions. The quantization is based on the choice of light-front coordinates, where plays the role of time and the corresponding spatial coordinate is . Here, is the ordinary time, is a Cartesian coordinate, and is the speed of light. The other two Cartesian coordinates, and , are untouched and often called transverse or perpendicular, denoted by symbols of the type . The choice of the frame of reference where the time and -axis are defined can be left unspecified in an exactly soluble relativistic theory, but in practical calculations some choices may be more suitable than others. The basic formalism is discussed elsewhere.

The light-front quantization of quantum field theories provides a useful alternative to ordinary equal-time quantization. In particular, it can lead to a relativistic description of bound systems in terms of quantum-mechanical wave functions. The quantization is based on the choice of light-front coordinates, where plays the role of time and the corresponding spatial coordinate is . Here, is the ordinary time, is one Cartesian coordinate, and is the speed of light. The other two Cartesian coordinates, and , are untouched and often called transverse or perpendicular, denoted by symbols of the type . The choice of the frame of reference where the time and -axis are defined can be left unspecified in an exactly soluble relativistic theory, but in practical calculations some choices may be more suitable than others.
Xiangdong Ji is a Chinese theoretical nuclear and elementary particle physicist. He is a Distinguished University Professor at the University of Maryland, College Park.






