Radiology is the medical specialty that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide their treatment, within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography, but today it includes all imaging modalities, including those that use no ionizing electromagnetic radiation, as well as others that do, such as computed tomography (CT), fluoroscopy, and nuclear medicine including positron emission tomography (PET). Interventional radiology is the performance of usually minimally invasive medical procedures with the guidance of imaging technologies such as those mentioned above.
The Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Radiologists (RANZCR) is the leading professional organisation for the promotion of the science and practice of the medical specialties of clinical radiology and radiation oncology in Australia and New Zealand. The college has members throughout the world. RANZCR provides the educational curricula for medical graduates training to enter the specialties.

The Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) is a non-profit organization and an international society of radiologists, medical physicists and other medical imaging professionals representing 31 radiologic subspecialties from 145 countries around the world. Based in Oak Brook, Illinois, it was established in 1915.
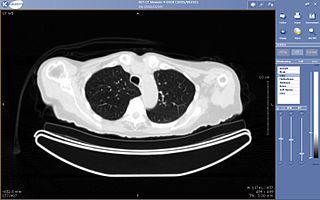
Teleradiology is the transmission of radiological patient images from procedures such as x-rays photographs, Computed tomography (CT), and MRI imaging, from one location to another for the purposes of sharing studies with other radiologists and physicians. Teleradiology allows radiologists to provide services without actually having to be at the location of the patient. This is particularly important when a sub-specialist such as an MRI radiologist, neuroradiologist, pediatric radiologist, or musculoskeletal radiologist is needed, since these professionals are generally only located in large metropolitan areas working during daytime hours. Teleradiology allows for specialists to be available at all times.
Sir Peter James Kerley KCVO CBE (1900–1979) was an Irish radiologist famous for his role in the lung surgery of King George VI and the naming of the radiological sign in heart failure, Kerley lines.
The American College of Radiology (ACR), founded in 1923, is a professional medical society representing nearly 40,000 diagnostic radiologists, radiation oncologists, interventional radiologists, nuclear medicine physicians and medical physicists.

Radiographers, also known as radiologic technologists, diagnostic radiographers and medical radiation technologists are healthcare professionals who specialise in the imaging of human anatomy for the diagnosis and treatment of pathology. Radiographers are infrequently, and almost always erroneously, known as x-ray technicians. In countries that use the title radiologic technologist they are often informally referred to as techs in the clinical environment; this phrase has emerged in popular culture such as television programmes. The term radiographer can also refer to a therapeutic radiographer, also known as a radiation therapist.

The Royal College of Radiologists (RCR) is the professional body responsible for the specialties of clinical oncology and clinical radiology throughout the United Kingdom. Its role is to advance the science and practice of radiology and oncology, further public education, and set appropriate professional standards of practice. The college sets and monitors the educational curriculum for those training to enter the profession, and administers the Fellowship of the Royal College of Radiologists exams. It is a registered charity in the United Kingdom (no. 211540).
Kakarla Subba Rao was an Indian radiologist who served as the first director of Nizam's Institute of Medical Sciences, Hyderabad. For his contributions to the field of medicine, Rao was conferred Padma Shri in 2000, the fourth highest civilian award by the Government of India. He was also the founder and president of the Telugu Association of North America.
Oral and maxillofacial radiology, also known as dental and maxillofacial radiology, or even more common DentoMaxilloFacial Radiology, is the specialty of dentistry concerned with performance and interpretation of diagnostic imaging used for examining the craniofacial, dental and adjacent structures.
Professor Dame Janet Elizabeth Husband is Emeritus Professor of Radiology at the Institute of Cancer Research. She had a career in diagnostic radiology that spanned nearly 40 years, using scanning technology to diagnose, stage, and follow-up cancer. She continues to support medicine and research as a board member and advisor for various organisations.

The Biomedical Imaging and Intervention Journal is a quarterly open access peer-reviewed medical journal established in July 2005. It is financed by donations from regional and international biomedical imaging industry and the University of Malaya Research Imaging Centre. The journal also receives support from many regional associations and societies and in turn has become the official publication of them. As of 2009, it is the official publication of the ASEAN Association of Radiologists, ASEAN Society of Interventional Radiology, Asia-Oceania Federation of Organizations for Medical Physics, Asian Oceania Society of Radiology, College of Radiology, Academy of Medicine Malaysia, Southeast Asian Federation of Organisations of Medical Physics, and the South East Asian Association of Academic Radiologists.
Marvin E. Haskin was a physician and Professor and Chairman of the Department of Diagnostic Radiology at Hahnemann University for a total of 22 years. He was also an author, editor, and researcher in the field of radiological medicine. His work with Dr. J. George Teplick on the medical textbook Roentgenologic Diagnosis is considered to be one of the seminal works on radiological medicine.
The International Day of Radiology (IDoR) is an annual event promoting the role of medical imaging in modern healthcare. It is celebrated on November 8 each year and coincides with the anniversary of the discovery of x-rays. It was first introduced in 2012, as a joint initiative of the European Society of Radiology (ESR), the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA), and the American College of Radiology (ACR). The International Day of Radiology is acknowledged and celebrated by nearly 200 national, sub-speciality, and related societies around the world. 'Radiographers Association of Madhya Pradesh(India)''' has celebrated this day since 1996 and the theme for this day was raised by '''Mr.Shivakant Vajpai''', Secretary of Madhya Pradesh Radiographers Association, also holding a designation of Radiation Safety Officer and Senior Radiographer in government of Madhya Pradesh, India.
Sudarshan Kumar Aggarwal is an Indian medical doctor and radiologist. He was honoured by the Government of India, in 2013, by bestowing on him the Padma Shri, the fourth highest civilian award, for his contributions to the field of medicine.

James Ralston Kennedy "RP" Paterson, was a Scottish medical doctor and scientist specialising in oncology and radiology. Along with Herbert Parker, pioneered the development of the Paterson-Parker rules for the Radium Dosage System, also known as the Manchester system.
Fiona Jane Gilbert is a Scottish radiologist and academic.
Brian Worthington was the first radiologist to be elected a Fellow of the Royal Society and is acknowledged as a pioneer in clinical magnetic resonance imaging. He was born in Oldham, England and was educated at Hulme Grammar School, training at Guy's Hospital after graduating in physiology and medicine. After graduation his career developed rapidly, particularly in the field of MRI research and he was subsequently admitted as a Fellow of the Royal College of Radiologists.
Makhan Singh (Mark) Khangure in an Indian-born radiologist and a pioneer in the field of neuroradiology. He trained in the United Kingdom and Australia, and has been based in Perth, Western Australia, since the 1970s.







