A dentist, also known as a dental surgeon, is a health care professional who specializes in dentistry, the branch of medicine focused on the teeth, gums, and mouth. The dentist's supporting team aids in providing oral health services. The dental team includes dental assistants, dental hygienists, dental technicians, and sometimes dental therapists.
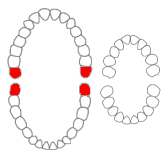
The third molar, commonly called wisdom tooth, is the most posterior of the three molars in each quadrant of the human dentition. The age at which wisdom teeth come through (erupt) is variable, but this generally occurs between late teens and early twenties. Most adults have four wisdom teeth, one in each of the four quadrants, but it is possible to have none, fewer, or more, in which case the extras are called supernumerary teeth. Wisdom teeth may become stuck (impacted) against other teeth if there is not enough space for them to come through normally. Impacted wisdom teeth are still sometimes removed for orthodontic treatment, believing that they move the other teeth and cause crowding, though this is not held anymore as true.
Oral and maxillofacial surgery is a surgical specialty focusing on reconstructive surgery of the face, facial trauma surgery, the oral cavity, head and neck, mouth, and jaws, as well as facial cosmetic surgery/facial plastic surgery including cleft lip and cleft palate surgery.

Cementoblastoma, or benign cementoblastoma, is a relatively rare benign neoplasm of the cementum of the teeth. It is derived from ectomesenchyme of odontogenic origin. Cementoblastomas represent less than 0.69–8% of all odontogenic tumors.
The American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons (AAOMS) is the non-profit professional association serving the specialty of oral and maxillofacial surgery, the surgical arm of dentistry. Its headquarters are in Rosemont, Illinois.
Epulis fissuratum is a benign hyperplasia of fibrous connective tissue which develops as a reactive lesion to chronic mechanical irritation produced by the flange of a poorly fitting denture. More simply, epulis fissuratum is where excess folds of firm tissue form inside the mouth, as a result of rubbing on the edge of dentures that do not fit well. It is a harmless condition and does not represent oral cancer. Treatment is by simple surgical removal of the lesion, and also by adjustment of the denture or provision of a new denture.
An oral medicine or stomatology doctor/dentist has received additional specialized training and experience in the diagnosis and management of oral mucosal abnormalities including oral cancer, salivary gland disorders, temporomandibular disorders and facial pain, taste and smell disorders; and recognition of the oral manifestations of systemic and infectious diseases. It lies at the interface between medicine and dentistry. An oral medicine doctor is trained to diagnose and manage patients with disorders of the orofacial region, essentially as a "physician of the mouth".
Stomatitis nicotina is a diffuse white patch on the hard palate, usually caused by tobacco smoking, usually pipe or cigar smoking. It is painless, and it is caused by a response of the palatal oral mucosa to chronic heat. A more pronounced appearance can occur with reverse smoking, sometimes distinguished from stomatitis nicotina by the term reverse smoker's stomatitis. While stomatitis nicotina that is caused by heat is not a premalignant condition, the condition that is caused by reverse smoking is premalignant.

A glandular odontogenic cyst (GOC) is a rare and usually benign odontogenic cyst developed at the odontogenic epithelium of the mandible or maxilla. Originally, the cyst was labeled as "sialo-odontogenic cyst" in 1987. However, the World Health Organization (WHO) decided to adopt the medical expression "glandular odontogenic cyst". Following the initial classification, only 60 medically documented cases were present in the population by 2003. GOC was established as its own biological growth after differentiation from other jaw cysts such as the "central mucoepidermoid carcinoma (MEC)", a popular type of neoplasm at the salivary glands. GOC is usually misdiagnosed with other lesions developed at the glandular and salivary gland due to the shared clinical signs. The presence of osteodentin supports the concept of an odontogenic pathway. This odontogenic cyst is commonly described to be a slow and aggressive development. The inclination of GOC to be large and multilocular is associated with a greater chance of remission. GOC is an infrequent manifestation with a 0.2% diagnosis in jaw lesion cases. Reported cases show that GOC mainly impacts the mandible and male individuals. The presentation of GOC at the maxilla has a very low rate of incidence. The GOC development is more common in adults in their fifth and sixth decades.

The Faculty of Dentistry at the University of the Western Cape (UWC) is the largest dental school in Africa. Located in Belville, near Cape Town the UWC Faculty of Dentistry offers the BChD (DDS) Degree, degree in dental hygiene, and post-graduate MChD, MSc(Dent) degrees.
Oral and maxillofacial pathology refers to the diseases of the mouth, jaws and related structures such as salivary glands, temporomandibular joints, facial muscles and perioral skin. The mouth is an important organ with many different functions. It is also prone to a variety of medical and dental disorders.
The Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery is a peer-reviewed medical journal that publishes original research in oral and maxillofacial surgery, oral pathology, and other related topics. It is published monthly by Elsevier on behalf of the American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons. The current editor-in-chief is James R. Hupp and associate editor is Thomas Dodson.

The International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery is a peer-reviewed medical journal covering oral and maxillofacial surgery, oral pathology, and related topics. It is published monthly by Elsevier for the International Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons.
Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, and Oral Radiology is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal that covers research in oral surgery, medicine, pathology, radiology, and endodontics published by Mosby. It was originally established as Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, and Oral Pathology in 1948, changing its name to Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology, and Endodontology in 1995, and acquiring its current name in 2012. It is an official journal of the American College of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, American Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, American Academy of Oral Medicine, and the American Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology. According to the Journal Citation Reports, the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 2.589.
In the United States and Canada, there are twelve recognized dental specialties in which some dentists choose to train and practice, in addition to or instead of general dentistry. In the United Kingdom and Australia, there are thirteen.
Christoffel Nortje is a South African dentist who is emeritus professor of oral and maxillofacial radiology at the Department of Diagnostics and Radiology at the University of the Western Cape, Faculty of Dentistry in Cape Town, South Africa. He was in private practice prior to joining the Department of Diagnostics and Radiology at Stellenbosch University, where he headed the department until 2005.

Tooth pathology is any condition of the teeth that can be congenital or acquired. Sometimes a congenital tooth diseases are called tooth abnormalities. These are among the most common diseases in humans The prevention, diagnosis, treatment and rehabilitation of these diseases are the base to the dentistry profession, in which are dentists and dental hygienists, and its sub-specialties, such as oral medicine, oral and maxillofacial surgery, and endodontics. Tooth pathology is usually separated from other types of dental issues, including enamel hypoplasia and tooth wear.





