Cognitive psychology is the scientific study of mental processes such as attention, language use, memory, perception, problem solving, creativity, and reasoning.

Developmental psychology is the scientific study of how and why humans grow, change, and adapt across the course of their lives. Originally concerned with infants and children, the field has expanded to include adolescence, adult development, aging, and the entire lifespan. Developmental psychologists aim to explain how thinking, feeling, and behaviors change throughout life. This field examines change across three major dimensions, which are physical development, cognitive development, and social emotional development. Within these three dimensions are a broad range of topics including motor skills, executive functions, moral understanding, language acquisition, social change, personality, emotional development, self-concept, and identity formation.
Educational psychology is the branch of psychology concerned with the scientific study of human learning. The study of learning processes, from both cognitive and behavioral perspectives, allows researchers to understand individual differences in intelligence, cognitive development, affect, motivation, self-regulation, and self-concept, as well as their role in learning. The field of educational psychology relies heavily on quantitative methods, including testing and measurement, to enhance educational activities related to instructional design, classroom management, and assessment, which serve to facilitate learning processes in various educational settings across the lifespan.
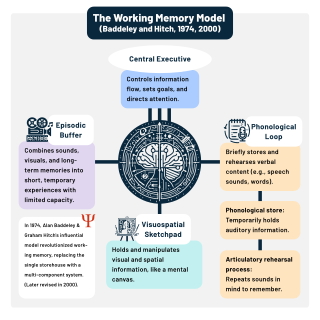
Working memory is a cognitive system with a limited capacity that can hold information temporarily. It is important for reasoning and the guidance of decision-making and behavior. Working memory is often used synonymously with short-term memory, but some theorists consider the two forms of memory distinct, assuming that working memory allows for the manipulation of stored information, whereas short-term memory only refers to the short-term storage of information. Working memory is a theoretical concept central to cognitive psychology, neuropsychology, and neuroscience.

Jean William Fritz Piaget was a Swiss psychologist known for his work on child development. Piaget's theory of cognitive development and epistemological view are together called genetic epistemology.

Cognition is the "mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses". It encompasses all aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as: perception, attention, thought, imagination, intelligence, the formation of knowledge, memory and working memory, judgment and evaluation, reasoning and computation, problem-solving and decision-making, comprehension and production of language. Cognitive processes use existing knowledge to discover new knowledge.
Psychology is an academic and applied discipline involving the scientific study of human mental functions and behavior. Occasionally, in addition or opposition to employing the scientific method, it also relies on symbolic interpretation and critical analysis, although these traditions have tended to be less pronounced than in other social sciences, such as sociology. Psychologists study phenomena such as perception, cognition, emotion, personality, behavior, and interpersonal relationships. Some, especially depth psychologists, also study the unconscious mind.
In psychology, cognitivism is a theoretical framework for understanding the mind that gained credence in the 1950s. The movement was a response to behaviorism, which cognitivists said neglected to explain cognition. Cognitive psychology derived its name from the Latin cognoscere, referring to knowing and information, thus cognitive psychology is an information-processing psychology derived in part from earlier traditions of the investigation of thought and problem solving.
The concepts of fluid intelligence (gf) and crystallized intelligence (gc) were introduced in 1963 by the psychologist Raymond Cattell. According to Cattell's psychometrically-based theory, general intelligence (g) is subdivided into gf and gc. Fluid intelligence is the ability to solve novel reasoning problems and is correlated with a number of important skills such as comprehension, problem-solving, and learning. Crystallized intelligence, on the other hand, involves the ability to deduce secondary relational abstractions by applying previously learned primary relational abstractions.

Piaget's theory of cognitive development, or his genetic epistemology, is a comprehensive theory about the nature and development of human intelligence. It was originated by the Swiss developmental psychologist Jean Piaget (1896–1980). The theory deals with the nature of knowledge itself and how humans gradually come to acquire, construct, and use it. Piaget's theory is mainly known as a developmental stage theory.
In psychology, developmental stage theories are theories that divide psychological development into distinct stages which are characterized by qualitative differences in behavior.
Cognitive development is a field of study in neuroscience and psychology focusing on a child's development in terms of information processing, conceptual resources, perceptual skill, language learning, and other aspects of the developed adult brain and cognitive psychology. Qualitative differences between how a child processes their waking experience and how an adult processes their waking experience are acknowledged. Cognitive development is defined as the emergence of the ability to consciously cognize, understand, and articulate their understanding in adult terms. Cognitive development is how a person perceives, thinks, and gains understanding of their world through the relations of genetic and learning factors. There are four stages to cognitive information development. They are, reasoning, intelligence, language, and memory. These stages start when the baby is about 18 months old, they play with toys, listen to their parents speak, they watch TV, anything that catches their attention helps build their cognitive development.
Information processing theory is the approach to the study of cognitive development evolved out of the American experimental tradition in psychology. Developmental psychologists who adopt the information processing perspective account for mental development in terms of maturational changes in basic components of a child's mind. The theory is based on the idea that humans process the information they receive, rather than merely responding to stimuli. This perspective uses an analogy to consider how the mind works like a computer. In this way, the mind functions like a biological computer responsible for analyzing information from the environment. According to the standard information-processing model for mental development, the mind's machinery includes attention mechanisms for bringing information in, working memory for actively manipulating information, and long-term memory for passively holding information so that it can be used in the future. This theory addresses how as children grow, their brains likewise mature, leading to advances in their ability to process and respond to the information they received through their senses. The theory emphasizes a continuous pattern of development, in contrast with cognitive-developmental theorists such as Jean Piaget's theory of cognitive development that thought development occurs in stages at a time.
Domain-general learning theories of development suggest that humans are born with mechanisms in the brain that exist to support and guide learning on a broad level, regardless of the type of information being learned. Domain-general learning theories also recognize that although learning different types of new information may be processed in the same way and in the same areas of the brain, different domains also function interdependently. Because these generalized domains work together, skills developed from one learned activity may translate into benefits with skills not yet learned. Another facet of domain-general learning theories is that knowledge within domains is cumulative, and builds under these domains over time to contribute to our greater knowledge structure. Psychologists whose theories align with domain-general framework include developmental psychologist Jean Piaget, who theorized that people develop a global knowledge structure which contains cohesive, whole knowledge internalized from experience, and psychologist Charles Spearman, whose work led to a theory on the existence of a single factor accounting for all general cognitive ability.
Nelson Cowan is the Curators' Distinguished Professor of Psychological Sciences at the University of Missouri. He specializes in working memory, the small amount of information held in mind and used for language processing and various kinds of problem solving. To overcome conceptual difficulties that arise for models of information processing in which different functions occur in separate boxes, Cowan proposed a more organically organized "embedded processes" model. Within it, representations held in working memory comprise an activated subset of the representations held in long-term memory, with a smaller subset held in a more integrated form in the current focus of attention. Other work has been on the developmental growth of working memory capacity and the scientific method. His work, funded by the National Institutes of Health since 1984, has been cited over 41,000 times according to Google Scholar. The work has resulted in over 250 peer-reviewed articles, over 60 book chapters, 2 sole-authored books, and 4 edited volumes.
Some of the research that is conducted in the field of psychology is more "fundamental" than the research conducted in the applied psychological disciplines, and does not necessarily have a direct application. The subdisciplines within psychology that can be thought to reflect a basic-science orientation include biological psychology, cognitive psychology, neuropsychology, and so on. Research in these subdisciplines is characterized by methodological rigor. The concern of psychology as a basic science is in understanding the laws and processes that underlie behavior, cognition, and emotion. Psychology as a basic science provides a foundation for applied psychology. Applied psychology, by contrast, involves the application of psychological principles and theories yielded up by the basic psychological sciences; these applications are aimed at overcoming problems or promoting well-being in areas such as mental and physical health and education.
Neo-Piagetian theories of cognitive development criticize and build upon Jean Piaget's theory of cognitive development.

Andreas Demetriou is a Greek Cypriot developmental psychologist and former Minister of Education and Culture of Cyprus. He is a founding fellow and president of The Cyprus Academy of Sciences, Letters and Arts.

Childhood memory refers to memories formed during childhood. Among its other roles, memory functions to guide present behaviour and to predict future outcomes. Memory in childhood is qualitatively and quantitatively different from the memories formed and retrieved in late adolescence and the adult years. Childhood memory research is relatively recent in relation to the study of other types of cognitive processes underpinning behaviour. Understanding the mechanisms by which memories in childhood are encoded and later retrieved has important implications in many areas. Research into childhood memory includes topics such as childhood memory formation and retrieval mechanisms in relation to those in adults, controversies surrounding infantile amnesia and the fact that adults have relatively poor memories of early childhood, the ways in which school environment and family environment influence memory, and the ways in which memory can be improved in childhood to improve overall cognition, performance in school, and well-being, both in childhood and in adulthood.

Attentional control, colloquially referred to as concentration, refers to an individual's capacity to choose what they pay attention to and what they ignore. It is also known as endogenous attention or executive attention. In lay terms, attentional control can be described as an individual's ability to concentrate. Primarily mediated by the frontal areas of the brain including the anterior cingulate cortex, attentional control and attentional shifting are thought to be closely related to other executive functions such as working memory.








