
In commerce, supply chain management (SCM) is the management of the flow of goods and services including all processes that transform raw materials into final products between businesses and locations. This can include the movement and storage of raw materials, work-in-process inventory, finished goods, and end to end order fulfilment from the point of origin to the point of consumption. Interconnected, interrelated or interlinked networks, channels and node businesses combine in the provision of products and services required by end customers in a supply chain.
Material requirements planning (MRP) is a production planning, scheduling, and inventory control system used to manage manufacturing processes. Most MRP systems are software-based, but it is possible to conduct MRP by hand as well.

Inventory or stock refers to the goods and materials that a business holds for the ultimate goal of resale, production or utilisation.

Lean manufacturing is a production method aimed primarily at reducing times within the production system as well as response times from suppliers and to customers. It is closely related to another concept called just-in-time manufacturing. Just-in-time manufacturing tries to match production to demand by only supplying goods which have been ordered and focuses on efficiency, productivity and reduction of "wastes" for the producer and supplier of goods. Lean manufacturing adopts the just-in-time approach and additionally focuses on reducing cycle, flow and throughput times by further eliminating activities which do not add any value for the customer. Lean manufacturing also involves people who work outside of the manufacturing process, such as in marketing and customer service.
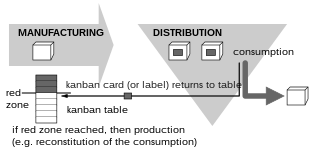
Kanban is a scheduling system for lean manufacturing. Taiichi Ohno, an industrial engineer at Toyota, developed kanban to improve manufacturing efficiency. The system takes its name from the cards that track production within a factory. Kanban is also known as the Toyota nameplate system in the automotive industry.
Vendor-managed inventory (VMI) is an inventory management practice in which a supplier of goods, usually the manufacturer, is responsible for optimizing the inventory held by a distributor.
The beer distribution game is an educational game that is used to experience typical coordination problems of a supply chain process. It reflects a role-play simulation where several participants play with each other. The game represents a supply chain with a non-coordinated process where problems arise due to lack of information sharing. This game outlines the importance of information sharing, supply chain management and collaboration throughout a supply chain process. Due to lack of information, suppliers, manufacturers, sales people and customers often have an incomplete understanding of what the real demand of an order is. The most interesting part of the game is that each group has no control over another part of the supply chain. Therefore, each group has only significant control over their own part of the supply chain. Each group can highly influence the entire supply chain by ordering too much or too little which can lead to a bullwhip effect. Therefore, the order taking of a group also highly depends on decisions of the other groups.
Just In Sequence (JIS) is an inventory strategy that matches just in time (JIT) and complete fit in sequence with variation of assembly line production. Components and parts arrive at a production line right in time as scheduled before they get assembled. Feedback from the manufacturing line is used to coordinate transport to and from the process area. When implemented successfully, JIS improves a company's return on assets (ROA), without loss in flexibility, quality or overall efficiency. JIS is mainly implemented with car manufacture.
Safety stock is a term used by logisticians to describe a level of extra stock that is maintained to mitigate risk of stockouts caused by uncertainties in supply and demand. Adequate safety stock levels permit business operations to proceed according to their plans. Safety stock is held when uncertainty exists in demand, supply, or manufacturing yield, and serves as an insurance against stockouts.
Inventory control or stock control can be broadly defined as "the activity of checking a shop's stock". It is the process of ensuring that the right amount of supply is available within a business. However, a more focused definition takes into account the more science-based, methodical practice of not only verifying a business's inventory but also maximising the amount of profit from the least amount of inventory investment without affecting customer satisfaction. Other facets of inventory control include forecasting future demand, supply chain management, production control, financial flexibility, purchasing data, loss prevention and turnover, and customer satisfaction.
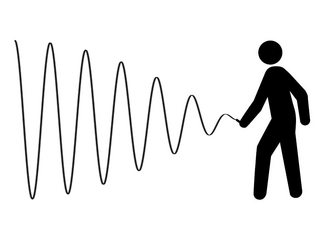
The bullwhip effect is a supply chain phenomenon where orders to suppliers tend to have a larger variability than sales to buyers, which results in an amplified demand variability upstream. In part, this results in increasing swings in inventory in response to shifts in consumer demand as one moves further up the supply chain. The concept first appeared in Jay Forrester's Industrial Dynamics (1961) and thus it is also known as the Forrester effect. It has been described as “the observed propensity for material orders to be more variable than demand signals and for this variability to increase the further upstream a company is in a supply chain”. Science at Stanford University helped incorporate the concept into supply chain vernacular using a story about Volvo. Suffering a glut in green cars, sales and marketing developed a program to sell the excess inventory. While successful in generating the desired market pull, manufacturing did not know about the promotional plans. Instead, they read the increase in sales as an indication of growing demand for green cars and ramped up production.

Demand-chain management (DCM) is the management of relationships between suppliers and customers to deliver the best value to the customer at the least cost to the demand chain as a whole. Demand-chain management is similar to supply-chain management but with special regard to the customers.
Supply-chain optimization (SCO) aims to ensure the optimal operation of a manufacturing and distribution of supply chain. This includes the optimal placement of inventory within the supply chain, minimizing operating costs including manufacturing costs, transportation costs, and distribution costs. Optimization often involves the application of mathematical modelling techniques using computer software. It is often considered to be part of supply chain engineering, although the latter is mainly focused on mathematical modelling approaches, whereas supply chain optimization can also be undertaken using qualitative, management based approaches.
Military supply-chain management is a cross-functional approach to procuring, producing and delivering products and services for military materiel applications. Military supply chain management includes sub-suppliers, suppliers, internal information and funds flow.

Build to Order is a production approach where products are not built until a confirmed order for products is received. Thus, the end consumer determines the time and number of produced products. The ordered product is customized, meeting the design requirements of an individual, organization or business. Such production orders can be generated manually, or through inventory/production management programs. BTO is the oldest style of order fulfillment and is the most appropriate approach used for highly customized or low volume products. Industries with expensive inventory use this production approach. Moreover, "Made to order" products are common in the food service industry, such as at restaurants.

Supply chain risk management (SCRM) is "the implementation of strategies to manage both everyday and exceptional risks along the supply chain based on continuous risk assessment with the objective of reducing vulnerability and ensuring continuity".
Channel coordination aims at improving supply chain performance by aligning the plans and the objectives of individual enterprises. It usually focuses on inventory management and ordering decisions in distributed inter-company settings. Channel coordination models may involve multi-echelon inventory theory, multiple decision makers, asymmetric information, as well as recent paradigms of manufacturing, such as mass customization, short product life-cycles, outsourcing and delayed differentiation. The theoretical foundations of the coordination are based chiefly on the contract theory. The problem of channel coordination was first modeled and analyzed by Anantasubramania Kumar in 1992.
A spare part, spare, service part, repair part, or replacement part, is an interchangeable part that is kept in an inventory and used for the repair or refurbishment of defective equipment/units. Spare parts are an important feature of logistics engineering and supply chain management, often comprising dedicated spare parts management systems.
Inventory management software is a software system for tracking inventory levels, orders, sales and deliveries. It can also be used in the manufacturing industry to create a work order, bill of materials and other production-related documents. Companies use inventory management software to avoid product overstock and outages. It is a tool for organizing inventory data that before was generally stored in hard-copy form or in spreadsheets.
Partner-optimized inventory management, also known as partnerized inventory management or sometimes just the abbreviation PIM is an inventory management technique or model often used in deterministic inventory systems in which a significant portion of the total inventory regularly becomes stochastic in nature, due to slowing and/or low demand such as is typical in heavy machinery and construction equipment where the products themselves are extremely durable and have long lives in the field. Inventory in these cases needs to be maintained for an extended time to allow for repairs and product support perhaps as much as two or more decades after a manufacturer has ceased production.





