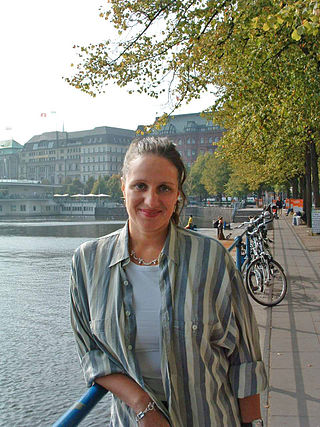Alliance 90/The Greens, often simply referred to as Greens, is a green political party in Germany. It was formed in 1993 by the merger of the Greens and Alliance 90. The Greens had itself merged with the East German Green Party after German reunification in 1990.

Ulrike Marie Meinhof was a German left-wing journalist and founding member of the Red Army Faction (RAF) in West Germany, commonly referred to in the press as the "Baader-Meinhof gang". She is the reputed author of The Urban Guerilla Concept (1971). The manifesto acknowledges the RAF's "roots in the history of the student movement"; condemns "reformism" as "a brake on the anti-capitalist struggle"; and invokes Mao Zedong to define "armed struggle" as "the highest form of Marxism-Leninism".

Gudrun Ensslin was a German far-left terrorist and founder of the West German far-left militant group Red Army Faction.

Joseph Martin "Joschka" Fischer is a German former politician of the Alliance 90/The Greens party. He served as the foreign minister and as the vice chancellor of Germany in the cabinet of Gerhard Schröder from 1998 to 2005. Fischer has been a leading figure in the German Greens since the 1970s, and according to opinion polls, he was the most popular politician in Germany for most of the Schröder government's duration. Following the September 2005 election, in which the Schröder government was defeated, he left office on 22 November 2005. In September 2010, he supported the creation of the Spinelli Group, a Europarliamentarian initiative founded with a view to reinvigorate efforts to federalise the European Union.

Alfred Willi Rudolf "Rudi" Dutschke was a German sociologist and political activist who, until severely injured by an assassin in 1968, was a leading charismatic figure within the Socialist Students Union (SDS) in West Germany, and that country's broader "extra-parliamentary opposition" (APO).
Klaus Rainer Röhl was a German journalist and author, best known as founder, owner, publisher and editor-in-chief of konkret, the most influential magazine on the German political left from the 1960s to the early 1970s. He later became critical of communism and leftist tendencies.

Braunbuch – Kriegs- und Nazi-verbrecher in der Bundesrepublik: Staat – Wirtschaft – Verwaltung – Armee – Justiz – Wissenschaft is a book edited by Albert Norden in 1965. In this book Norden claimed that 1,800 politicians and other prominents in West Germany held prominent positions in Germany prior to 1945.

Katja Lange-Müller is a German writer living in Berlin. Her works include several short stories and novellas, radio dramas, and dramatic works.
The Sozialistische Deutsche Studentenbund — the Socialist German Students' Union or Socialist German Students' League — was founded in 1946 in Hamburg, Germany, as the collegiate branch of the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD). In the 1950s, tensions between the SDS and the main party surfaced, particularly over the party's support of West Germany's rearming, until the SPD expelled all members of the SDS from the party in 1961.

Alice Sophie Schwarzer is a German journalist and prominent feminist. She is founder and publisher of the German feminist journal EMMA. Beginning in France, she became a forerunner of feminist positions against anti-abortion laws, for economic self-sufficiency for women, against pornography, prostitution, female genital mutilation, and for a position on women in Islam. She authored many books, including biographies of Romy Schneider, Marion Dönhoff, and herself.

konkret has been the name of two German magazines.
Hoimar von Ditfurth was a German physician and scientific journalist. He was the father of Christian von Ditfurth, a historian, and Jutta Ditfurth, a writer and journalist.

Werner Kurt Armin Meinhof was a German art historian of the 20th century.

Kiepenheuer & Witsch is a German publishing house, established in 1948 by Joseph C. Witsch and on behalf of Gustav Kiepenheuer. The partners initially held respectively 30% and 40% of the company's share capital. Kiepenheuer died in 1949, after which Witsch took over control and broke the original link with the existing Gustav Kiepenheuer Verlag in Weimar. For the Kiepenheuer & Witsch publishing business several years of major organisational restructuring followed. The first books to be published under the Kiepenheuer & Witsch imprint was the novel Marion by Vicki Baum, which appeared in 1951. In 1953 the firm acquired a new head office incorporating, for the first time, its own onsite publishing facilities, at Cologne-Marienburg.
Putzgruppe was a German left-wing militant group, that emerged from the German student movement and was active in the 1970s. It participated in riots against the police in Frankfurt.

Gerd Koenen is a German historian and former communist politician.

Gerhard Zwerenz was a German writer and politician. From 1994 until 1998 he was a member of the Bundestag for the Party of Democratic Socialism (PDS).

Kathrin Schmidt, is a German writer. She is known both for her poetry and prose.
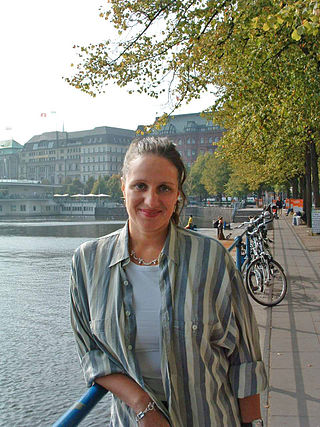
Bettina Röhl is a German journalist and author. She is best known for her writings about student radicalism of the 1960s and the terrorist kidnappings that it spawned in West Germany during the early 1970s. Röhl has written extensively about the former Foreign Minister Joschka Fischer's time as a left-wing militant leader. She has also researched and written at length about her own mother, journalist and Red Army Faction terrorist Ulrike Meinhof. Her assessments of the violence associated with the Red Army Faction in the 1970s are at times intensely critical.

Eva-Ruth Weissweiler is a German writer, musicologist and non fiction writer.