Bisht is a surname found in the country of Nepal and the Indian state of Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh. Bisht was a title given by kings to nobles, derived from the Sanskrit vishisht ("distinguished").The term "Bisht" originally referred to someone who held a land grant from the government. The Bisht families in Uttarakhand were chiefly Thokdars(Zamindars) of Thuljat origin. In Uttrakhand, Bishts are generally Kshatriya Rajputs. In Nepal, Bisht was adopted as a surname by Raute and Raji people. Bishta, as Bista, was also used as a surname used by Khas people, group under the caste Chhetri.
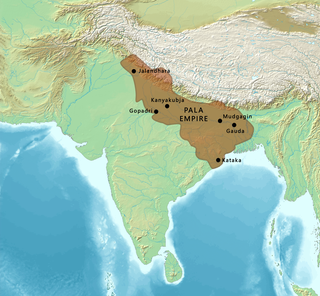
The Pāla Empire was an imperial power during the post-classical period in the Indian subcontinent, which originated in the region of Bengal. It is named after its ruling dynasty, whose rulers bore names ending with the suffix Pāla. The empire was founded with the election of Gopāla as the emperor of Gauda in late eighth century CE. The Pala stronghold was located in Bengal and eastern Bihar, which included the major cities of Gauḍa, Vikramapura, Pāṭaliputra, Monghyr, Somapura, Ramavati (Varendra), Tāmralipta and Jagaddala.

Khas peoples or Khas Tribes, popularly known as Khashya are an Indo-Aryan ethno-linguistic group native to the Himalayan region of the Indian subcontinent, in what is now the South Asian country of Nepal, as well as the Indian states of Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, West Bengal, Assam and Sikkim. Khas consists of many subtribes like Kshetri, Thakuri, Bahun, khas dalit and Sanyasis and all spread across the Himalayas.

Khasas were an ancient Indo-Aryan tribe and a late Janapada kingdom from Himalayan regions of northern Indian subcontinent mentioned in the various historical Indian inscriptions and ancient Indian Hindu and Tibetan literature. European sources described the Khasa tribe living in the Northwest Himalayas and the Roman geographer Pliny The Elder specifically described them as "Indian people". They were reported to have lived around Gandhara, Trigarta and Madra Kingdom as per the Mahabharata.

Doti District, part of Sudurpashchim Province, is one of the 77 districts of Nepal. This district, with Silgadhi as its headquarters, covers an area of 2,025 square kilometres (782 sq mi) with a population of 207,066 in 2001 and increasing marginally to 211,746 in 2011.

Jumla District, is one of the ten districts of the Karnali province of Nepal. This district has Jumla as its headquarters, an area of 2,531 square kilometres (977 sq mi); it had populations of 89,427 and 108,921, respectively, in the national censuses of 2001 and 2011. Its territory lies between longitudes 81⁰ 28' and 82⁰ 18' East, and between latitudes 28⁰ 58' and 29⁰ 30' North.

Doti, also known as Dotigarh (डोटीगढ़) or the Far-Western Development Region was a development region of Nepal situated between River Kali bordering Kumaon division of Uttarakhand, India in the west and the Karnali river on the east. Doti was one of eight different princely states of the Katyuri Kingdom.

The Malla dynasty also known as the Malla confederacy, was the ruling dynasty of the Kathmandu Valley in Nepal from 1201 to 1779. This dynasty was founded by Arideva Malla. Though the latter Mallas were regarded as belonging to the Raghuvamsha dynasty, they were also seen as continuations and descendants of the Licchavi dynasty. Later Malla kings also traced one section of their lineage from Nanyadeva, the founder of the Karnat dynasty of Mithila. The term malla means wrestler in Sanskrit. The first use of the word malla in the Kathmandu Valley began in 1201.
Karki (Devanagari:कार्की) is a Chhetri surname from Nepal and a Kumaoni Rajput clan in Uttarakhand.

Thapa (pronunciation:[t̪ʰapa]) is an Indo-Aryan surname belonging to the Chhetri/Rajput caste (Kshatriya) in Nepal and parts of Northern India.[2][3] It is also used by the Magar tribes, a Sino-Tibetan speaking ethnicity.

Baise Rajya were sovereign and intermittently allied petty kingdoms on the Indian subcontinent, ruled by Khasas from medieval Nepal, located around the Karnali-Bheri river basin of modern-day Nepal. The Baise were annexed during the unification of Nepal from 1744 to 1810. The Gorkha kingdom's founder Prithvi Narayan Shah did not live to see this, but his son and grandson annexed the entire collection by the end of the 18th century.

The Far-Western Development Region was one of Nepal's five development regions. It was located at the western end of the country and had its headquarters in Dipayal.

Khasa-Malla kingdom, popularly known as Khasa Kingdom and Yatse in Tibetan, was a medieval kingdom established around the 11th century in regions that are presently in far-western Nepal and parts of Uttarakhand state in India.
Mahat (Nepali: महत) is an Ekthariya chhetri surname among Nepalese, of Khasa heritage. The name may have originated when one of the Jumli Malla kings in medieval times made his younger brother, Dharma Malla, chief of staff in the army. This granted Dharma Malla the title of Mahat (Kshatriya) (meaning The Great One), and as a result, his descendants started using 'Mahat' as their surnames.
The Thakuri is a Royal caste forming the core of the ruling class in Nepal. This term is a Nepali adaptation of the Indian title Thakur, which translates to 'master of the estate'. The term denotes the royal descendants of kings of Khasa Kingdom, Gandaki kingdom and the Kingdom of Nepal.
Ranajit Kunwar was a Nepalese governor and military personnel in the Kingdom of Nepal. He was a son of Ramakrishna Kunwar of Kunwar family. He served as governor of Jumla, Pyuthan and sub-ordinate administrator under Amar Singh Thapa at Srinagar of Garhwal province. He suppressed the rebellion of Jumla as a governor. He fought at the battle of Khadbuda where he killed King Pradyumna Shah of Garhwal. He was the grandfather of Jang Bahadur Kunwar Ranaji who later became the Maharaja of Kaski & Lamjung and Prime Minister of Nepal.
Rajputs of Nepal or anciently Rajputras are Rajput Kshatriya community of Nepal.
The Kingdom of Lalitpur, also known as Patan, was a kingdom ruled by the Malla dynasty of Nepal. It was established in 1482 after King Yaksha Malla's death. His sons divided the kingdom into four parts: Bhaktapur, Kantipur, Lalitpur, and Banepa.










