
Absolute zero is the lowest limit of the thermodynamic temperature scale, a state at which the enthalpy and entropy of a cooled ideal gas reach their minimum value, taken as zero kelvin. The fundamental particles of nature have minimum vibrational motion, retaining only quantum mechanical, zero-point energy-induced particle motion. The theoretical temperature is determined by extrapolating the ideal gas law; by international agreement, absolute zero is taken as −273.15 degrees on the Celsius scale, which equals −459.67 degrees on the Fahrenheit scale. The corresponding Kelvin and Rankine temperature scales set their zero points at absolute zero by definition.

In physics, cryogenics is the production and behaviour of materials at very low temperatures.

Sir James Dewar was a Scottish chemist and physicist. He is best known for his invention of the vacuum flask, which he used in conjunction with research into the liquefaction of gases. He also studied atomic and molecular spectroscopy, working in these fields for more than 25 years.
The following is a timeline of low-temperature technology and cryogenic technology. It also lists important milestones in thermometry, thermodynamics, statistical physics and calorimetry, that were crucial in development of low temperature systems.

Heike Kamerlingh Onnes was a Dutch physicist and Nobel laureate. He exploited the Hampson–Linde cycle to investigate how materials behave when cooled to nearly absolute zero and later to liquefy helium for the first time, in 1908. He also discovered superconductivity in 1911.

Willem Hendrik Keesom was a Dutch physicist who, in 1926, invented a method to freeze liquid helium. He also developed the first mathematical description of dipole–dipole interactions in 1921. Thus, dipole–dipole interactions are also known as Keesom interactions. He was previously a student of Heike Kamerlingh Onnes, who had discovered superconductivity.
A cryopump or a "cryogenic pump" is a vacuum pump that traps gases and vapours by condensing them on a cold surface, but are only effective on some gases. The effectiveness depends on the freezing and boiling points of the gas relative to the cryopump's temperature. They are sometimes used to block particular contaminants, for example in front of a diffusion pump to trap backstreaming oil, or in front of a McLeod gauge to keep out water. In this function, they are called a cryotrap, waterpump or cold trap, even though the physical mechanism is the same as for a cryopump.

Magnetic refrigeration is a cooling technology based on the magnetocaloric effect. This technique can be used to attain extremely low temperatures, as well as the ranges used in common refrigerators.

Johannes Diderik van der Waals was a Dutch theoretical physicist and thermodynamicist famous for his pioneering work on the equation of state for gases and liquids. Van der Waals started his career as a school teacher. He became the first physics professor of the University of Amsterdam when in 1877 the old Athenaeum was upgraded to Municipal University. Van der Waals won the 1910 Nobel Prize in physics for his work on the equation of state for gases and liquids.

The lowest natural temperature ever directly recorded at ground level on Earth is −89.2 °C at the then-Soviet Vostok Station in Antarctica on 21 July 1983 by ground measurements.

Liquid helium is a physical state of helium at very low temperatures at standard atmospheric pressures. Liquid helium may show superfluidity.

A 3He/4He dilution refrigerator is a cryogenic device that provides continuous cooling to temperatures as low as 2 mK, with no moving parts in the low-temperature region. The cooling power is provided by the heat of mixing of the Helium-3 and Helium-4 isotopes.

A superconducting magnet is an electromagnet made from coils of superconducting wire. They must be cooled to cryogenic temperatures during operation. In its superconducting state the wire has no electrical resistance and therefore can conduct much larger electric currents than ordinary wire, creating intense magnetic fields. Superconducting magnets can produce greater magnetic fields than all but the strongest non-superconducting electromagnets and can be cheaper to operate because no energy is dissipated as heat in the windings. They are used in MRI machines in hospitals, and in scientific equipment such as NMR spectrometers, mass spectrometers, fusion reactors and particle accelerators. They are also used for levitation, guidance and propulsion in a magnetic levitation (maglev) railway system being constructed in Japan.
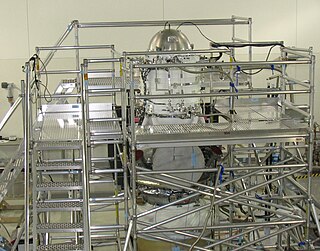
A cryostat is a device used to maintain low cryogenic temperatures of samples or devices mounted within the cryostat. Low temperatures may be maintained within a cryostat by using various refrigeration methods, most commonly using cryogenic fluid bath such as liquid helium. Hence it is usually assembled into a vessel, similar in construction to a vacuum flask or Dewar. Cryostats have numerous applications within science, engineering, and medicine.

Carl Paul Gottfried von Linde was a German scientist, engineer, and businessman. He discovered a refrigeration cycle and invented the first industrial-scale air separation and gas liquefaction processes, which led to the first reliable and efficient compressed-ammonia refrigerator in 1876. These breakthroughs laid the backbone for the 1913 Nobel Prize in Physics that was awarded to Heike Kamerlingh Onnes. Linde was a member of scientific and engineering associations, including being on the board of trustees of the Physikalisch-Technische Reichsanstalt and the Bavarian Academy of Sciences and Humanities. Linde was also the founder of what is now known as Linde plc, the world's largest industrial gases company, and ushered the creation of the supply chain of industrial gases as a profitable line of businesses. He was knighted in 1897 as Ritter von Linde.

Superconductivity is the phenomenon of certain materials exhibiting zero electrical resistance and the expulsion of magnetic fields below a characteristic temperature. The history of superconductivity began with Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes's discovery of superconductivity in mercury in 1911. Since then, many other superconducting materials have been discovered and the theory of superconductivity has been developed. These subjects remain active areas of study in the field of condensed matter physics.

Liquefaction of gases is physical conversion of a gas into a liquid state (condensation). The liquefaction of gases is a complicated process that uses various compressions and expansions to achieve high pressures and very low temperatures, using, for example, turboexpanders.

The pulse tube refrigerator (PTR) or pulse tube cryocooler is a developing technology that emerged largely in the early 1980s with a series of other innovations in the broader field of thermoacoustics. In contrast with other cryocoolers, this cryocooler can be made without moving parts in the low temperature part of the device, making the cooler suitable for a wide variety of applications.
Dr. Howard Oldford McMahon (1914-1990) was Science Director, Vice President, Head of the Research and Development Division, and then President of Arthur D. Little, Inc, of Cambridge, Massachusetts, retiring from the Company in 1977. He made important contributions to the field of cryogenics as inventor, research scientist and engineer during the 1940s through the 1960s, and subsequently as an executive and member of the Board of Directors of both ADL and the Helix Technology Corporation, of Waltham, Massachusetts. McMahon, born in Alberta, Canada, was a naturalized citizen of the United States.

The International Institute of Refrigeration (IIR), is an independent intergovernmental science and technology-based organization which promotes knowledge of refrigeration and associated technologies and applications on a global scale that improve quality of life in a cost-effective and environmentally sustainable manner, including:















