The 1910 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 8, 1910, while Maine and Vermont held theirs early in September, in the middle of President William Howard Taft's term. Elections were held for all 391 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 46 states, to the 62nd United States Congress.
The 1908 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 3, 1908, with Oregon, Maine, and Vermont holding theirs early in either June or September. They coincided with the 1908 United States presidential election, which William Howard Taft won. Elections were held for all 391 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 46 states, to serve in the 61st United States Congress.
The 1906 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 6, 1906, with Oregon, Maine, and Vermont holding theirs early in either June or September. They occurred in the middle of President Theodore Roosevelt's second term. Elections were held for 386 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 45 states, to serve in the 60th United States Congress.

The 1904 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 8, 1904, with Oregon, Maine, and Vermont holding theirs early in either June or September. They coincided with the election to a full term of President Theodore Roosevelt. Elections were held for 386 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 45 states, to serve in the 59th United States Congress.
The 1902 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 4, 1902, with Oregon, Maine, and Vermont holding theirs early in either June or September. They occurred in the middle of President Theodore Roosevelt's first term, about a year after the assassination of President William McKinley in September 1901. Elections were held for 386 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 45 states, to serve in the 58th United States Congress.
The 1900 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 6, 1900, with Oregon, Maine, and Vermont holding theirs early in either June or September. They coincided with the re-election of President William McKinley. Elections were held for 357 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 45 states, to serve in the 57th United States Congress. Special elections were also held throughout the year.

The 1896 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 3, 1896, with Oregon, Maine, and Vermont holding theirs early in either June or September. They coincided with the election of President William McKinley. Elections were held for 357 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 45 states, to serve in the 55th United States Congress. The size of the House increased by one seat after Utah gained statehood on January 4, 1896. Special elections were also held throughout the year.
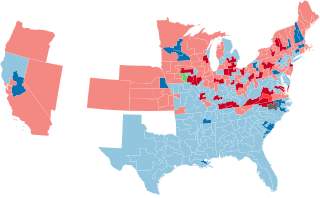
The 1886 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 2, 1886, with three states holding theirs early between June and September. They occurred in the middle of President Grover Cleveland's first term. Elections were held for 325 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 38 states, to serve in the 50th United States Congress. Special elections were also held throughout the year.

The 1884 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 4, 1884, with four states holding theirs early between June and October. They coincided with the election of President Grover Cleveland. Elections were held for 325 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 38 states, to serve in the 49th United States Congress. Special elections were also held throughout the year.

The 1882 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 7, 1882, with five states holding theirs early between June and October. They occurred during President Chester A. Arthur's term. Elections were held for 325 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 38 states, to serve in the 48th United States Congress. They were the first elections after reapportionment following the 1880 United States census, increasing the size of the House. Special elections were also held throughout the year.
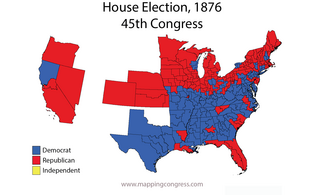
The 1876–77 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between June 5, 1876, and March 13, 1877. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 45th United States Congress convened on October 15, 1877. The size of the House increased to 293 seats with the addition of the new state of Colorado.

The 1868–69 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between June 1, 1868, and August 2, 1869. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before or after the first session of the 41st United States Congress convened on March 4, 1869. They coincided with the 1868 United States presidential election, which was won by Ulysses S. Grant. Elections were held for all 243 seats, representing 37 states. All of the former Confederate states were represented in Congress for the first time since they seceded from the Union.

The 1864–65 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between June 5, 1864, and November 7, 1865, in the midst of the American Civil War and President Abraham Lincoln's reelection. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives. Members were elected before the first session of the 39th United States Congress convened on December 4, 1865, including the at-large seat from the new state of Nevada, and the 8 from Tennessee, the first secessionist state to be readmitted. The other 10 secessionist states had not yet been readmitted, and therefore were not seated.

The 1846–47 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between August 2, 1846 and November 2, 1847. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives. 228 elected members representing 29 states took their seats when the first session of the 30th United States Congress convened December 6, 1847. The new states of Iowa and Texas elected their first representatives during this election cycle. These elections were held during President James K. Polk's term.
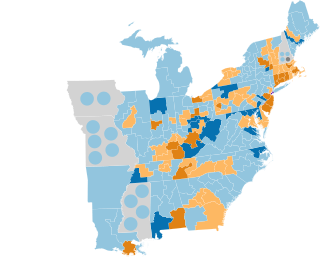
The 1844–45 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 1, 1844 and November 4, 1845. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives. 224 elected members representing 27 states took their seats when the first session of the 29th United States Congress convened on December 1, 1845. The new state of Florida elected its first representative during this election cycle, while one vacancy in New Hampshire's delegation remained unfilled for the duration of the 29th Congress.

The 1834–35 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 7, 1834, and November 5, 1835. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 24th United States Congress convened on December 7, 1835. They were held during President Andrew Jackson's second term. Elections were held for 240 seats that represented 24 states, as well as the at-large-district seat for the pending new state of Michigan.

In 1798, the Northwest Territory became eligible to send a non-voting delegate to the U.S. Congress. The Assembly elected this representative.
Alaska Territory's at-large congressional district was a congressional district created in 1906 to represent the District of Alaska, which was reorganized into the Alaska Territory in 1912. After Alaska's admission to the Union as the 49th state by act of Congress on January 3, 1959, this district evolved into Alaska's at-large congressional district.
The Oklahoma Territory's at-large congressional district is a defunct congressional district that was created by the Organic Act of 1890 and ended with Oklahoma statehood. One delegate was to be sent to the U.S. House of Representatives from Oklahoma Territory.
There were ten elections in 1907 to the United States House of Representatives. Five were special elections in the 60th United States Congress and the other five were new seats from the new state of Oklahoma. There were no special elections in 1907 during the 61st United States Congress.















