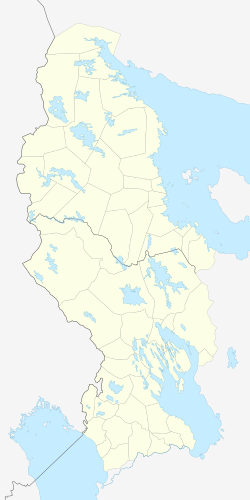
The Republic of Karelia, Karjala or Karelia is a republic of Russia situated in the northwest of the country. The republic is a part of the Northwestern Federal District, and covers an area of 172,400 square kilometres, with a population of 533,121 residents. Its capital is Petrozavodsk.
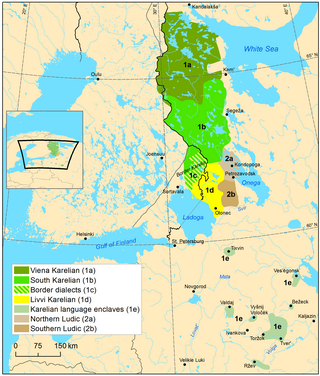
Karelian is a Finnic language spoken mainly in the Russian Republic of Karelia. Linguistically, Karelian is closely related to the Finnish dialects spoken in eastern Finland, and some Finnish linguists have even classified Karelian as a dialect of Finnish, though in the modern day it is widely considered a separate language. Karelian is not to be confused with the Southeastern dialects of Finnish, sometimes referred to as karjalaismurteet in Finland. In the Russian 2020–2021 census, around 9,000 people spoke Karelian natively, but around 14,000 said to be able to speak the language. There are around 11,000 speakers of Karelian in Finland. And around 30,000 have at least some knowledge of Karelian in Finland.
The Aunus expedition was an attempt by Finnish volunteers to occupy parts of East Karelia in 1919, during the Russian Civil War. Aunus is the Finnish name for Olonets Karelia. This expedition was one of many Finnic "kinship wars" (heimosodat) fought against forces of Soviet Russia after the Russian Revolution of 1917 and during the Russian Civil War.

Karelians are a Baltic Finnic ethnic group who are indigenous to the historical region of Karelia, which is today split between Finland and Russia. Karelians living in Russian Karelia are considered a distinct ethnic group closely related to Finnish Karelians, who are considered a subset of Finns. This distinction historically arose from Karelia having been fought over and eventually split between Sweden and Novgorod, resulting in Karelians being under different cultural spheres.

Karelia is an area in Northern Europe of historical significance for Russia, Finland, and Sweden. It is currently divided between northwestern Russia and Finland.

The Viena expedition was the military expedition in March 1918 by Finnish volunteer forces in order to annex White Karelia from Soviet Russia. It was one of the many "kinship wars" (Heimosodat) fought near the newly independent Finland during the Russian Civil War. Russian East Karelia was never part of the Swedish Empire or the Grand Duchy of Finland, and was at the time mostly inhabited by Karelians. However, many advocates of a Greater Finland considered these Karelians "kindred" to the Finnish nation, and therefore supported Finnish annexation of Russian East Karelia.

Olonets Karelia is a historical and cultural region and the southern portion of East Karelia, which is part of Russia. Olonets Karelia is located between the other historical regions of Ladoga Karelia, to its west, White Karelia, to its north, the River Svir, to its south and Lake Onega on its eastern side. Olonets Karelia is home to its own dialect of the Karelian language, which is known as Livvi Karelian or sometimes as 'Olonets Karelian'.
Forest Guerrillas were an East Karelian resistance movement that was created officially on 14 October 1921. There were around 3,000 Forest Guerillas in total during the East Karelian Uprising as a Karelian and Finnish resistance movement against Bolshevik Russia, aiming for an East Karelian state with independence from Russia, and in some occasions unification or cooperation with Finland. Most of the soldiers of the Forest Guerillas were from White Karelia, Repola & Porajärvi and Olonets Karelia. The heraldry of the East Karelian Forest Guerillas was created by Akseli Gallen-Kallela.

Greater Finland is an irredentist and nationalist idea which aims for the territorial expansion of Finland. It is associated with Pan-Finnicism. The most common concept saw the country as defined by natural borders encompassing the territories inhabited by Finns and Karelians, ranging from the White Sea to Lake Onega and along the Svir River and Neva River—or, more modestly, the Sestra River—to the Gulf of Finland. Some extremist proponents also included the Kola Peninsula, Finnmark, Swedish Meänmaa, Ingria, and Estonia.

The flag of the Republic of Karelia is the official state symbol of the Republic of Karelia. Adopted by the Supreme Council of the Republic of Karelia on February 16, 1993. The flag was designed by Alexander Ivanovich Kinnear.

The Karelian Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic, Karelian ASSR for short, sometimes referred to as Soviet Karelia or simply Karelia, was an autonomous republic of the Russian SFSR, Soviet Union, with the capital in Petrozavodsk.

The Karelian people's presence can be dated back to the 7th millennium BC–6th millennium BC. The region itself is rich with fish, lakes, and minerals, and because of that its holder has changed throughout history, and to this day it is divided between the Republic of Finland and the Russian Federation.

The East Karelian Uprising and the Soviet–Finnish conflict 1921–1922 were an attempt by a group of East Karelian separatists supported by Finland to gain independence from the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic. They were aided by a number of Finnish volunteers, starting from 6 November 1921. The conflict ended on 21 March 1922 with the Agreements between the governments of Soviet Russia and Finland about the measures of maintenance of the inviolability of the Soviet–Finnish border. The conflict is regarded in Finland as one of the heimosodat – "Kinship Wars".
Pro-independence movements in the Russian Civil War within the territory of the former Russian Empire sought the creation of independent nation states that were not aligned with the Bolsheviks after the October Revolution. Many pro-independence movements emerged after the dissolution of the Russian Empire and fought in the Russian Civil War.
Karjalan Sanomat is a weekly Finnish language newspaper from the Republic of Karelia, published in Petrozavodsk. The newspaper was founded in 1920 as 'Karjalan kommuuni'.

The Republic of Uhtua, also Provisional Government of Karelia, officially called the Republic of East Karelia was an unrecognized state that existed from 1919 to 1920, formed out of five volosts in the Kemsky Uyezd of the Arkhangelsk Governorate.
Lyudmila Fyodorovna Markianova is a Karelian linguist and a professor emerita. She has been called "karjalan kielen muamo", i.e. 'mother of the Karelian language'.

The Olonets Government, later called the Provisional Government of Olonets, was a short-lived unrecognized state originally created on May 15, 1918, as the Olonets Government of Southern Karelia, following Finland's declaration of war on Soviet Russia. Following the capture of Olonets on April 23, 1919, the country was renamed to the Provisional Caretaker Government of Olonets during the Olonets Expedition. The Olonets Government was cemented in May 1920, and found recognition and support from Finland, who was a keen supplier of money, in the form of loans and volunteers. On 27 June 1919 the Government went into exile in Finland, following the Soviet Russian capture of Vitele. In October 1920 the Olonets government merged with the Republic of Uhtua to form the Karelian United Government.

Kestenga is a rural village in the Loukhsky District of the Republic of Karelia in Russia on the northern shore of Lake Topozero.
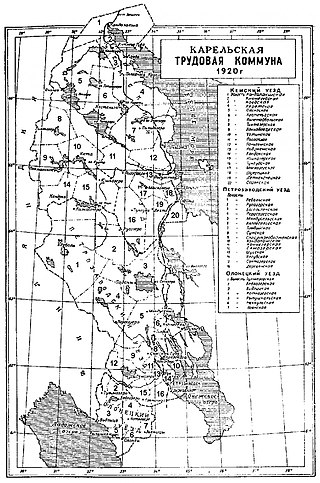
The Karelian Labor Commune was an autonomous region established in 1920 following the successes of the Red Army's incursion into the Republic of Uhtua, to undermine and discredit the separatist movements and to make Finland give up on attempting to liberate East Karelia shortly before the beginning of negotiations for the Treaty of Tartu and during the Heimosodat. Edvard Gylling and Yrjö Sirola, former members of the government of the Finnish Socialist Workers' Republic, met with Vladimir Lenin in the Kremlin to propose autonomy for Karelia within the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic. The Commune was founded on 8 June 1920 and was disestablished on 25 July 1923 and succeeded by the Karelian ASSR, following the end of the Heimosodat.