Related Research Articles

In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about 12 centimetres in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the bladder.
Darbepoetin alfa (INN) is a re-engineered form of erythropoietin containing 5 amino acid changes resulting in the creation of 2 new sites for N-linked carbohydrate addition. It has a 3-fold longer serum half-life compared to epoetin alpha and epoetin beta. It stimulates erythropoiesis by the same mechanism as rHuEpo and is used to treat anemia, commonly associated with chronic kidney failure and cancer chemotherapy. Darbepoetin is marketed by Amgen under the trade name Aranesp.

Hemolysis or haemolysis, also known by several other names, is the rupturing (lysis) of red blood cells (erythrocytes) and the release of their contents (cytoplasm) into surrounding fluid. Hemolysis may occur in vivo or in vitro.

Anemia or anaemia is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen. This can be due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin available for oxygen transport, or abnormalities in hemoglobin that impair its function. The name is derived from Ancient Greek ἀν- (an-) 'not', and αἷμα (haima) 'blood'. When anemia comes on slowly, the symptoms are often vague, such as tiredness, weakness, shortness of breath, headaches, and a reduced ability to exercise. When anemia is acute, symptoms may include confusion, feeling like one is going to pass out, loss of consciousness, and increased thirst. Anemia must be significant before a person becomes noticeably pale. Additional symptoms may occur depending on the underlying cause. Anemia can be temporary or long term and can range from mild to severe.
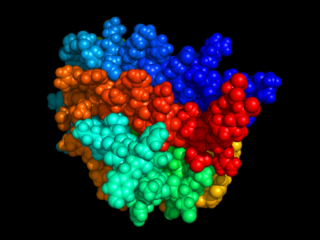
Erythropoietin, also known as erythropoetin, haematopoietin, or haemopoietin, is a glycoprotein cytokine secreted mainly by the kidneys in response to cellular hypoxia; it stimulates red blood cell production (erythropoiesis) in the bone marrow. Low levels of EPO are constantly secreted in sufficient quantities to compensate for normal red blood cell turnover. Common causes of cellular hypoxia resulting in elevated levels of EPO include any anemia, and hypoxemia due to chronic lung disease and mouth disease.
Mathematical and theoretical biology, or biomathematics, is a branch of biology which employs theoretical analysis, mathematical models and abstractions of living organisms to investigate the principles that govern the structure, development and behavior of the systems, as opposed to experimental biology which deals with the conduction of experiments to test scientific theories. The field is sometimes called mathematical biology or biomathematics to stress the mathematical side, or theoretical biology to stress the biological side. Theoretical biology focuses more on the development of theoretical principles for biology while mathematical biology focuses on the use of mathematical tools to study biological systems, even though the two terms are sometimes interchanged.

Erythropoiesis is the process which produces red blood cells (erythrocytes), which is the development from erythropoietic stem cell to mature red blood cell.

Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a type of kidney disease in which a gradual loss of kidney function occurs over a period of months to years. Initially generally no symptoms are seen, but later symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, vomiting, loss of appetite, and confusion. Complications can relate to hormonal dysfunction of the kidneys and include high blood pressure, bone disease, and anemia. Additionally CKD patients have markedly increased cardiovascular complications with increased risks of death and hospitalization.
Anemia of chronic disease (ACD) or anemia of chronic inflammation is a form of anemia seen in chronic infection, chronic immune activation, and malignancy. These conditions all produce elevation of interleukin-6, which stimulates hepcidin production and release from the liver. Hepcidin production and release shuts down ferroportin, a protein that controls export of iron from the gut and from iron storing cells. As a consequence, circulating iron levels are reduced. Other mechanisms may also play a role, such as reduced erythropoiesis. It is also known as anemia of inflammation, or anemia of inflammatory response.

A Cimino fistula, also Cimino-Brescia fistula, surgically created arteriovenous fistula and arteriovenous fistula, is a type of vascular access for hemodialysis. It is typically a surgically created connection between an artery and a vein in the arm, although there have been acquired arteriovenous fistulas which do not in fact demonstrate connection to an artery.

Hepcidin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HAMP gene. Hepcidin is a key regulator of the entry of iron into the circulation in mammals.
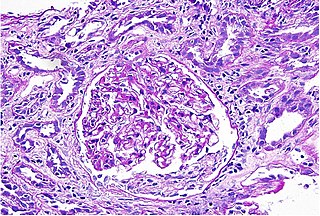
Interstitial nephritis, also known as tubulointerstitial nephritis, is inflammation of the area of the kidney known as the renal interstitium, which consists of a collection of cells, extracellular matrix, and fluid surrounding the renal tubules. It is also known as intestinal nephritis because the clinical picture may include mesenteric lymphadenitis in some cases of acute pyelonephritis. More specifically, in case of recurrent urinary tract infection, secondary infection can spread to adjacent intestine. In addition to providing a scaffolding support for the tubular architecture, the interstitium has been shown to participate in the fluid and electrolyte exchange as well as endocrine functions of the kidney.
Reticulocytopenia is the medical term for an abnormal decrease in circulating red blood cell precursors (reticulocytes) that can lead to anemia due to resulting low red blood cell (erythrocyte) production. Reticulocytopenia may be an isolated finding or it may not be associated with abnormalities in other hematopoietic cell lineages such as those that produce white blood cells (leukocytes) or platelets (thrombocytes), a decrease in all three of these lineages is referred to as pancytopenia.
Epoetin alfa is a human erythropoietin produced in cell culture using recombinant DNA technology. Authorised by the European Medicines Agency on 28 August 2007, it stimulates erythropoiesis and is used to treat anemia, commonly associated with chronic kidney failure and cancer chemotherapy.

Erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESA) are medications which stimulate the bone marrow to make red blood cells. They are used to treat anemia due to end stage kidney disease, chemotherapy, major surgery, or certain treatments in HIV/AIDS. In these situations they decrease the need for blood transfusions. The different agents are more or less equivalent. They are given by injection.
Cholestatic pruritus is the sensation of itch due to nearly any liver disease, but the most commonly associated entities are primary biliary cholangitis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, obstructive choledocholithiasis, carcinoma of the bile duct, cholestasis, and chronic hepatitis C viral infection and other forms of viral hepatitis.

Roxadustat, sold under the brand name Evrenzo, is an anti-anemia medication. Roxadustat is a HIF prolyl-hydroxylase inhibitor that increases endogenous production of erythropoietin and stimulates production of hemoglobin and red blood cells. It was investigated in clinical trials for the treatment of anemia caused by chronic kidney disease (CKD). It is taken by mouth. The drug was developed by FibroGen, in partnership with AstraZeneca.

Daprodustat, sold under the brand name Duvroq among others, is a medication that is used for the treatment of anemia due to chronic kidney disease. It is a hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor. It is taken by mouth.
Doron Levy is a mathematician, scientist, magician, and academic. He is a Professor and chair at the Department of Mathematics at the University of Maryland, College Park. He is also the Director of the Brin Mathematics Research Center.
References
- 1 2 Math Modeling: Getting Started and Getting Solutions, K. M. Bliss, K. R. Fowler, and B. J. Galluzzo, SIAM, Philadelphia, 2014.
- ↑ "Karen M. Bliss". Karen M. Bliss. Retrieved 2020-04-10.
- ↑ Bliss, Karen (2011-05-03). "Modeling of Red Blood Cell Dynamics in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ↑ "Teaching Experience". Karen M. Bliss. Retrieved 2020-04-10.
- ↑ "Faculty and Staff - Applied Mathematics - Virginia Military Institute". www.vmi.edu. Retrieved 2020-04-24.
- ↑ Math Modeling: Computing and Communicating, K. M. Bliss, K. F. Kavanagh, and B. J. Galluzzo, and R. Levy SIAM, Philadelphia, 2018.