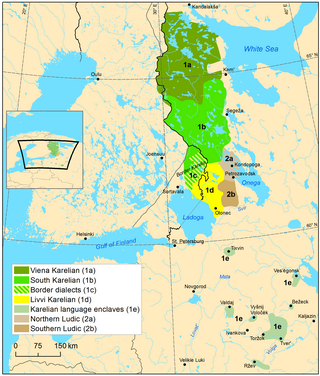
Karelian is a Finnic language spoken mainly in the Russian Republic of Karelia. Linguistically, Karelian is closely related to the Finnish dialects spoken in eastern Finland, and some Finnish linguists have even classified Karelian as a dialect of Finnish, though in the modern day it is widely considered a separate language. Karelian is not to be confused with the Southeastern dialects of Finnish, sometimes referred to as karjalaismurteet in Finland. In the Russian 2020–2021 census, around 9,000 people spoke Karelian natively, but around 14,000 said to be able to speak the language. There are around 11,000 speakers of Karelian in Finland.

Karelia is a historical province of Finland, consisting of the modern-day Finnish regions of South Karelia and North Karelia plus the historical regions of Ladoga Karelia and the Karelian isthmus, which are now in Russia. Historical Karelia also extends to the regions of Kymenlaakso, Northern Savonia and Southern Savonia (Mäntyharju).

Karelia is an area in Northern Europe of historical significance for Russia, Finland, and Sweden. It is currently divided between northwestern Russia and Finland.

Olonets Karelia is a historical and cultural region and the southern portion of East Karelia, which is part of Russia. Olonets Karelia is located between the other historical regions of Ladoga Karelia, to its west, White Karelia, to its north, the River Svir, to its south and Lake Onega on its eastern side. Olonets Karelia is home to its own dialect of the Karelian language, which is known as Livvi Karelian or sometimes as 'Olonets Karelian'.

White Karelia is a historical region in Northern Europe, comprising the northernmost part of Karelia, and of the Republic of Karelia in Russia. It is bordered by the White Sea to the east, Murmansk Oblast to the north, Finland to the west, and the Muyezersky and Segezhsky Districts of the Republic of Karelia to the south.
Forest Guerrillas were a East Karelian resistance movement that was created officially on 14 October 1921. There were around 3,000 Forest Guerillas in total during the East Karelian Uprising as a Karelian and Finnish resistance movement against Bolshevik Russia, aiming for an East Karelian state with independence from Russia, and in some occasions unification or cooperation with Finland. Most of the soldiers of the Forest Guerillas were from White Karelia, Repola & Porajärvi and Olonets Karelia. The heraldry of the East Karelian Forest Guerillas was created by Akseli Gallen-Kallela.

The Karelian question or Karelian issue is a dispute in Finnish politics over whether to try to regain control over eastern Karelia and other territories ceded to the Soviet Union in the Winter War and the Continuation War. Despite the name "Karelian question", the term may refer also to the return of Petsamo, ceded parts of Salla and Kuusamo, and four islands in the Gulf of Finland. Sometimes the phrase "debate on the return of the ceded territories" is used. The Karelian question remains a matter of public debate rather than a political issue.

Greater Finland, was an irredentist and nationalist idea that was a subset of Pan-Finnicism which emphasized the territorial expansion of Finland. The most common concept of Greater Finland saw the country as defined by natural borders encompassing the territories inhabited by Finns and Karelians, ranging from the White Sea to Lake Onega and along the Svir River and Neva River—or, more modestly, the Sestra River—to the Gulf of Finland. Some proponents also included the Torne Valley, Ingria, and Estonia.

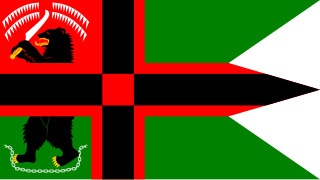
The flag of the Republic of Karelia is the official state symbol of the Republic of Karelia. Adopted by the Supreme Council of the Republic of Karelia on February 16, 1993. The flag was designed by Alexander Ivanovich Kinnear.

Ladoga Karelia is a historical region of Karelia, currently largely in Russia. Today, the term refers to the part of the Republic of Karelia in the Russian Federation comprising the south-west part of the Republic, specifically Lakhdenpokhsky District, Pitkyarantsky District and Sortavala District. This region is on the northern littoral of Lake Ladoga, which borders Olonets Karelia to the East, Leningrad Oblast to the south-west and the North Karelia region of Finland to the west.

The Karelian people's presence can be dated back to the 7th millennium BC–6th millennium BC. The region itself is rich with fish, lakes, and minerals, and because of that throughout history changed its holder, to this day divided between the Republic of Finland and the Russian Federation.

The East Karelian Uprising and the Soviet–Finnish conflict 1921–1922 were an attempt by a group of East Karelian separatists to gain independence from the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic. They were aided by a number of Finnish volunteers, starting from 6 November 1921. The conflict ended on 21 March 1922 with the Agreements between the governments of Soviet Russia and Finland about the measures of maintenance of the inviolability of the Soviet–Finnish border. The conflict is regarded in Finland as one of the heimosodat – "Kinship Wars".
Čičiliusku is a puppet theatre company from the Republic of Karelia in Russia. The company performs in the Karelian language. The company was founded in 2005 at the initiative of Pekka Zaikov, who at the time was the head of the Department of the Karelian and Veps languages. Amongst those who founded the company were teachers, students and alumni of the Faculty of Baltic Finnic languages of the Petrozavodsk State University. The Karelian folk theater was created in order to preserve the Karelian national intangible culture, popularize the Karelian language among children and youth language, introducing the younger generation to ethnocultural activities. A year later the company performed their first play, Kuin hukka vasikalla muamona oli.

The Karelian United Government was a short-lived state that existed from 1920 to 1923, as a merger of the Republic of Uhtua and the Olonets Government of Southern Karelia.
The Juminkeko Foundation, or simply Juminkeko, is a Finnish organization founded in 1991. It runs Juminkeko, an eponymous information centre of the national epic Kalevala and Karelian culture located in Kuhmo, Finland. The centre was designed by the Finnish architects Mikko Heikkinen and Markku Komonen and was completed in 1999.

The Republican Movement of Karelia or Karelian Republican Movement or RMK was a Karelian regionalist and separatist organization founded by a Russian philosopher and author Vadim Vladimirovich Shtepa and registered in January 2014.

The Karelian National Movement, officially KKL-Stop the Occupation of Karelia is an umbrella term for two organizations that split from each other in 2023. The organization led by the original creator, Dmitry Kuznetsov, who also goes by the name Miteri Panfilov, is called Stop the Occupation of Karelia ; it was previously known as the Karelian National Liberation Movement. The organization led by Vladislav Oleynik is called the Karelian National Movement.

Union of Karelian People or Regional Public Organization "Union of Karelian People" or RPO "UKP" is a regional Karelian public organization dedicated to the preservation and development of the Karelian culture and the Karelian language. It carries out its activities in the Republic of Karelia and other regions of the Russian Federation, Finland and other Karelian communities. It is one of the biggest and oldest Karelian culture organizations in Russia.

Karjalatalo is a red brick building in the Käpylä neighbourhood of Helsinki, Finland. It is owned by the Karelian Association, who built it as a meeting place for the Finnish Karelians who were displaced during World War II and their descendants. Designed by architect Into Pyykkö, construction of the building began in 1972 and completed in 1974. The interior design by Maisa Laaksonen features large amounts of pine, as well as the colours red, black and green.

Pan-Finnicism, also known as Pan-Fennicism or sometimes even referred to as Finno-Ugrism or even Heimoaate is a pan-nationalist idea which advocates for the political or economic unification of the Finno-Ugric peoples. The idea is broad in its meaning and oftentimes it simply refers to the Finno-Ugric peoples, however on rare occasion it can be limited to only the Baltic Finnic peoples or to the Finnic peoples.

















