
Any planet is an extremely faint light source compared to its parent star. For example, a star like the Sun is about a billion times as bright as the reflected light from any of the planets orbiting it. In addition to the intrinsic difficulty of detecting such a faint light source, the light from the parent star causes a glare that washes it out. For those reasons, very few of the exoplanets reported as of April 2014 have been observed directly, with even fewer being resolved from their host star.

Transit-timing variation is a method for detecting exoplanets by observing variations in the timing of a transit. This provides an extremely sensitive method capable of detecting additional planets in the system with masses potentially as small as that of Earth. In tightly packed planetary systems, the gravitational pull of the planets among themselves causes one planet to accelerate and another planet to decelerate along its orbit. The acceleration causes the orbital period of each planet to change. Detecting this effect by measuring the change is known as transit-timing variations. "Timing variation" asks whether the transit occurs with strict periodicity or if there's a variation.

Kepler-9 is a sunlike star in the constellation Lyra. Its planetary system, discovered by the Kepler Mission in 2010 was the first detected with the transit method found to contain multiple planets.

Kepler-10, formerly known as KOI-72, is a Sun-like star in the constellation of Draco that lies 607 light-years from Earth. Kepler-10 was targeted by NASA's Kepler spacecraft, as it was seen as the first star identified by the Kepler mission that could be a possible host to a small, transiting exoplanet. The star is slightly less massive, slightly larger, and slightly cooler than the Sun; at an estimated 11.9 billion years in age, Kepler-10 is almost 2.6 times the age of the Sun. Kepler-10 is host to a planetary system made up of at least three planets. Kepler-10b, the first undeniably rocky planet, was discovered in its orbit after eight months of observation and announced on January 10, 2011. The planet orbits its star closely, completing an orbit every 0.8 days, and has a density similar to that of iron. The second planet, Kepler-10c, was confirmed on May 23, 2011, based on follow-up observations by the Spitzer Space Telescope. The data shows it has an orbital period of 42.3 days and has a radius more than double that of Earth, but it was initially thought to have a higher density, making it the largest and most massive rocky planet discovered as of June 2014. However, refined mass measurements have shown it to be a more typical volatile-rich planet. A third planet, Kepler-10d, was discovered in 2023 by radial velocity observations.
Kepler-19 is a G7V star that is host to three known planets - Kepler-19b, Kepler-19c, and Kepler-19d. It is located about 720 light-years away in the constellation Lyra, five arcminutes northwest of the much more distant open cluster NGC 6791.
Kepler-19b is a planet orbiting around the star Kepler-19. The planet has an orbital period of 9.3 days, with an estimated radius of roughly 2.2 times that of the Earth, with a mass around 8.4 times that of the Earth. It is one of three planets orbiting Kepler-19.

Kepler-42, formerly known as KOI-961, is a red dwarf located in the constellation Cygnus and approximately 131 light years from the Sun. It has three known extrasolar planets, all of which are smaller than Earth in radius, and likely also in mass.
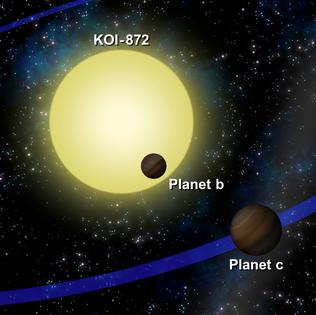
Kepler-46, previously designated KOI-872, is a star located in the constellation Lyra. Observed since 2009 by the Kepler space observatory, it has since been found to possess a planetary system consisting of at least three planets and while it has a similar mass to the Sun (90%) it is significantly older at ten billion years.
Kepler-36 is a star in the constellation of Cygnus with two known planets. It has an anomalously large radius, meaning that it is a subgiant.
Kepler-65 is a subgiant star slightly more massive than the Sun and has at least four planets.
Kepler-88 is a Sun-like star in the constellation of Lyra, with three confirmed planets. In April 2012, scientists discovered that a Kepler candidate known as KOI-142.01 (Kepler-88b) exhibited very significant transit-timing variations caused by a non-transiting planet. Timing variations were large enough to cause changes to transit durations to Kepler-88b as well. Large transit-timing variations helped to put tight constraints to masses of both planets. The non-transiting planet was further confirmed through the radial velocity method in November 2013.

Kepler-25 is a star in the northern constellation of Lyra. It is slightly larger and more massive than the sun with a luminosity 21⁄2 times that of the sun. With an apparent visual magnitude of 10.6, this star is too faint to be seen with the naked eye.

Kepler-90g is a super-puff exoplanet orbiting the early G-type main sequence star Kepler-90, one of eight planets around this star discovered using NASA's Kepler space telescope. It is located about 2,840 light-years (870 pc) from Earth, in the constellation Draco. The exoplanet was found by using the transit method, in which the dimming effect that a planet causes as it crosses in front of its star is measured. It orbits its parent star about every 210.5 days at a distance of 0.71 astronomical units.
Kepler-102 is a star 353 light-years away in the constellation of Lyra. Kepler-102 is less luminous than the Sun. The star system does not contain any observable amount of dust. Kepler-102 is suspected to be orbited by a binary consisting of two red dwarf stars, at projected separations of 591 and 627 AU.

Kepler-138, also known as KOI-314, is a red dwarf located in the constellation Lyra, 219 light years from Earth. It is located within the field of vision of the Kepler spacecraft, the satellite that NASA's Kepler Mission used to detect planets transiting their stars.
Kepler-30 is a star in the northern constellation of Lyra. It is located at the celestial coordinates: Right Ascension 19h 01m 08.0747s Declination +38° 56′ 50.219″. With an apparent visual magnitude of 15.5, this star is too faint to be seen with the naked eye. Kepler-30 is exhibiting a strong starspot activity.

Kepler-27 is a star in the northern constellation of Cygnus, the swan. It is located at the celestial coordinates: Right Ascension 19h 28m 56.81962s, Declination +41° 05′ 09.1405″. With an apparent visual magnitude of 15.855, this star is too faint to be seen with the naked eye.
Kepler-51 is a Sun-like star that is only about 500 million years old. It is orbited by three super-puff planets—Kepler-51b, c, and d—which have the lowest known densities of any exoplanet. The planets are all Jupiter-sized but with masses only a few times Earth's.
HD 175289 is a binary star system. Its primary star, also known as Kepler-410A, is a F-type subgiant star, orbited by the orange dwarf star Kepler-410B on a wide orbit. The companion star was discovered in 2012.
Kepler-167 is a K-type main-sequence star located about 1,119 light-years (343 pc) away from the Solar System in the constellation of Cygnus. The star has about 78% the mass and 75% the radius of the Sun, and a temperature of 4,884 K. It hosts a system of four known exoplanets. There is also a companion red dwarf star at a separation of about 700 AU, with an estimated orbital period of over 15,000 years.










