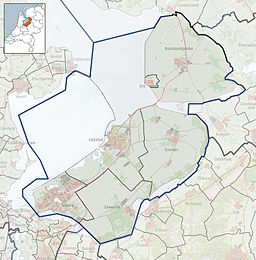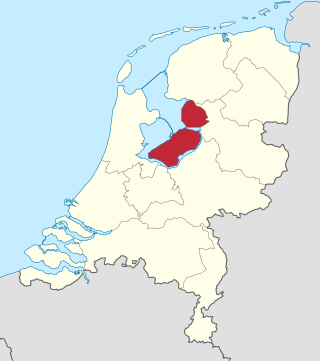
Flevoland is the twelfth and newest province of the Netherlands, established in 1986, when the southern and eastern Flevopolders, together with the Noordoostpolder, were merged into one provincial entity. It is in the centre of the country in the former Zuiderzee, which was turned into the freshwater IJsselmeer by the closure of the Afsluitdijk in 1932. Almost all of the land belonging to Flevoland was reclaimed in the 1950s and 1960s while splitting the Markermeer and Bordering lakes from the IJsselmeer. As to dry land, it is the smallest province of the Netherlands at 1,410 km2 (540 sq mi), but not gross land as that includes much of the waters of the fresh water lakes (meres) mentioned.

A polder is a low-lying tract of land that forms an artificial hydrological entity, enclosed by embankments known as dikes. The three types of polder are:
- Land reclaimed from a body of water, such as a lake or the seabed
- Flood plains separated from the sea or river by a dike
- Marshes separated from the surrounding water by a dike and subsequently drained; these are also known as koogs, especially in Germany

The IJsselmeer, also known as Lake IJssel in English, is a closed-off freshwater lake in the central Netherlands bordering the provinces of Flevoland, North Holland and Friesland. It covers an area of 1,100 km2 (420 sq mi) with an average depth of 4.5 m (15 ft). The river IJssel, after which the lake was named, flows into the IJsselmeer.

The Zuiderzee or Zuider Zee, historically called Lake Almere and Lake Flevo, was a shallow bay of the North Sea in the northwest of the Netherlands. It extended about 100 km inland and at most 50 km wide, with an overall depth of about 4 to 5 metres (13–16 feet) and a coastline of about 300 km. It covered 5,000 km2 (1,900 sq mi). Its name is Dutch for "southern sea", indicating that the name originates in Friesland, to the north of the Zuiderzee.

Overijssel is a province of the Netherlands located in the eastern part of the country. The province's name comes from the perspective of the Episcopal principality of Utrecht, which held the territory until 1528. The capital city of Overijssel is Zwolle and the largest city is Enschede. The province had a population of about 1,184,000 as of January 2023. The land mostly consists of grasslands and some forests ; it also borders a small part of the IJsselmeer to the west.

The IJssel is a Dutch distributary of the river Rhine that flows northward and ultimately discharges into the IJsselmeer, a North Sea natural harbour. It more immediately flows into the east-south channel around the Flevopolder, Flevoland which is kept at 3 metres below sea level. This body of water is then pumped up into the IJsselmeer.

The Zuiderzee Works is a system of dams and dikes, land reclamation and water drainage work, which was the largest hydraulic engineering project undertaken by the Netherlands during the twentieth century. The project involved the damming of the Zuiderzee, a large, shallow inlet of the North Sea, and the reclamation of land in the newly enclosed water using polders. Its main purposes are to improve flood protection and create additional land for agriculture.

Almere is a planned city and municipality in the province of Flevoland, Netherlands across the IJmeer from Amsterdam.

Urk is a municipality and a town in the Flevoland province in the central Netherlands.

Emmeloord is the administrative centre of the municipality of Noordoostpolder, Flevoland, Netherlands. In 2019, it had a population of 26,055.

Tollebeek is a village in the Dutch province of Flevoland. It is a part of the municipality of Noordoostpolder, and is approximately 90 kilometres north east of Amsterdam.

Creil is one of the ten so-called green villages (Dutch: groendorpen) in the Dutch province of Flevoland. It is a part of the municipality of Noordoostpolder, and lies about 6 km northwest of Emmeloord.

Salland is a historical dominion in the west and north of the present Dutch province of Overijssel. Nowadays Salland is usually used to indicate a region corresponding to the part of the former dominion more or less to the west of Twente.

The Flevopolder is an island polder forming the bulk of Flevoland, a province of the Netherlands. Created by land reclamation, its northeastern part was drained in 1955 and the remainder—the southwest—in 1968.

The Eemmeer is a lake situated in the middle of the Netherlands between the provinces of Flevoland, Utrecht, and North Holland. It measures 13.4 square kilometres (5.2 sq mi) and contains one small island, the Dode Hond. The Eemmeer is one in a series of peripheral lakes used to geohydrologically detach the low-lying polders of Flevoland from higher old mainland. The Eemmeer is connected to the peripheral lakes Gooimeer in the west, at the point where both lakes are crossed by the highway A27 bridge, and the Nijkerkernauw in the east. It is also connected to the lakes at the southern side of Markermeer near Amsterdam. The feeders of this lake system are the River IJssel and drains towards the North Sea.

The Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta is a river delta in the Netherlands formed by the confluence of the Rhine, the Meuse and the Scheldt rivers. In some cases, the Scheldt delta is considered a separate delta to the Rhine–Meuse delta. The result is a multitude of islands, branches and branch names, in which a waterway that appears to be one continuous stream may have numerous separate names for different sections, e.g. Rhine → Bijlands Kanaal → Pannerdens Kanaal → Nederrijn → Lek → Nieuwe Maas → Het Scheur → Nieuwe Waterweg. Since the Rhine contributes most of the water, the term "Rhine Delta" is commonly used, although this name is also used for the delta where the Alpine Rhine flows into Lake Constance. By some calculations, the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta covers 25,347 km2 (9,787 sq mi), making it the largest in Europe.

The IJsseloog is an artificial island in the Ketelmeer used as a depository to store polluted silt. Most of the polluted silt was deposited in the Ketelmeer by the IJssel river between 1950 and 1990. Removal of silt soil from the Ketelmeer lake also aims to deepen the channel leading to the mouth of the IJssel to at least a depth of 3.5 m (11.5 ft), thus aiming to improve access to the river for navigation.

In the Netherlands, the bordering lakes are a chain of lakes which separate the Flevopolder and Noordoostpolder from the ancient lands of the provinces of Gelderland, Utrecht, Overijssel and Friesland.

Windpark Noordoostpolder is an onshore and near-shore wind farm in Flevoland, the Netherlands. Upon completion in 2017, it was the largest wind farm in the Netherlands, and as of 2019 it is still one of the largest. Owner-operators are members of the Koepel Windenergie Noordoostpolder, a partnership of more than 100 agricultural entrepreneurs from the North East Polder (Noordoostpolder), and Innogy, a subsidiary of German energy company RWE.

Land reclamation in the Netherlands has a long history. As early as in the 14th century, the first reclaimed land had been settled. Much of the modern land reclamation has been done as a part of the Zuiderzee Works since 1919.