Related Research Articles

The unified modeling language (UML) is a general-purpose visual modeling language that is intended to provide a standard way to visualize the design of a system.

The Z notation is a formal specification language used for describing and modelling computing systems. It is targeted at the clear specification of computer programs and computer-based systems in general.
In computer science, formal methods are mathematically rigorous techniques for the specification, development, analysis, and verification of software and hardware systems. The use of formal methods for software and hardware design is motivated by the expectation that, as in other engineering disciplines, performing appropriate mathematical analysis can contribute to the reliability and robustness of a design.

Bertrand Meyer is a French academic, author, and consultant in the field of computer languages. He created the Eiffel programming language and the idea of design by contract.
A modeling language is any artificial language that can be used to express data, information or knowledge or systems in a structure that is defined by a consistent set of rules. The rules are used for interpretation of the meaning of components in the structure Programing language.
Model Driven Architecture (MDA) is a software design approach for the development of software systems. It provides a set of guidelines for the structuring of specifications, which are expressed as models. Model Driven Architecture is a kind of domain engineering, and supports model-driven engineering of software systems. It was launched by the Object Management Group (OMG) in 2001.
The Object Constraint Language (OCL) is a declarative language describing rules applying to Unified Modeling Language (UML) models developed at IBM and is now part of the UML standard. Initially, OCL was merely a formal specification language extension for UML. OCL may now be used with any Meta-Object Facility (MOF) Object Management Group (OMG) meta-model, including UML. The Object Constraint Language is a precise text language that provides constraint and object query expressions on any MOF model or meta-model that cannot otherwise be expressed by diagrammatic notation. OCL is a key component of the new OMG standard recommendation for transforming models, the Queries/Views/Transformations (QVT) specification.

Business process modeling (BPM) in business process management and systems engineering is the activity of representing processes of an enterprise, so that the current business processes may be analyzed, improved, and automated. BPM is typically performed by business analysts, who provide expertise in the modeling discipline; by subject matter experts, who have specialized knowledge of the processes being modeled; or more commonly by a team comprising both. Alternatively, the process model can be derived directly from events' logs using process mining tools.
A UML tool is a software application that supports some or all of the notation and semantics associated with the Unified Modeling Language (UML), which is the industry standard general-purpose modeling language for software engineering.
Specification and Description Language (SDL) is a specification language targeted at the unambiguous specification and description of the behaviour of reactive and distributed systems.
The B method is a method of software development based on B, a tool-supported formal method based on an abstract machine notation, used in the development of computer software.
In computer science, an abstract state machine (ASM) is a state machine operating on states that are arbitrary data structures.
A model transformation language in systems and software engineering is a language intended specifically for model transformation.
The Toolkit for Conceptual Modeling (TCM) is a collection of software tools to present specifications of software systems in the form of diagrams, tables, trees, and the like. TCM offers editors for techniques used in Structured Analysis as well as editors for object-oriented (UML) techniques. For some of the behavior specification techniques, an interface to model checkers is offered. More in particular, TCM contains the following editors.
Enterprise engineering is the body of knowledge, principles, and practices used to design all or part of an enterprise. An enterprise is a complex socio-technical system that comprises people, information, and technology that interact with each other and their environment in support of a common mission. One definition is: "an enterprise life-cycle oriented discipline for the identification, design, and implementation of enterprises and their continuous evolution", supported by enterprise modelling. The discipline examines each aspect of the enterprise, including business processes, information flows, material flows, and organizational structure. Enterprise engineering may focus on the design of the enterprise as a whole, or on the design and integration of certain business components.
The Triune Continuum Paradigm is a paradigm for general system modeling published in 2002. The paradigm allows for building of rigorous conceptual frameworks employed for systems modeling in various application contexts.
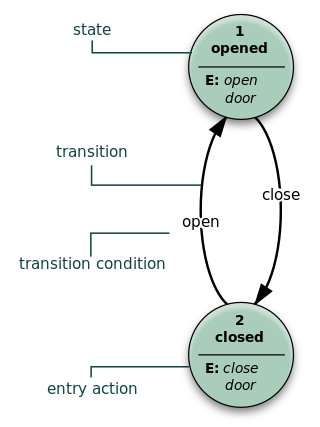
UML is a modeling language used by software developers. UML can be used to develop diagrams and provide users (programmers) with ready-to-use, expressive modeling examples. Some UML tools generate program language code from UML. UML can be used for modeling a system independent of a platform language. UML is a graphical language for visualizing, specifying, constructing, and documenting information about software-intensive systems. UML gives a standard way to write a system model, covering conceptual ideas. With an understanding of modeling, the use and application of UML can make the software development process more efficient.
Bernhard Rumpe is a German computer scientist, professor of computer science and head of the Software Engineering Department at the RWTH Aachen University. His research focusses on "technologies, methods, tools ... necessary to create software in the necessary quality that is as efficient and sustainable as possible."

Robert Bertrand France was a Jamaica-born American computer scientist.
UML-RSDS is a lightweight Model-driven engineering (MDE) and Model transformation tool supporting the UML 2.5 class diagram notation and OCL 2.4 Object Constraint Language. It supports code-generation in multiple 3GLs: Java, C#, C++, Python, Go, Swift and ANSI C.
References
- 1 2 France, Robert B. (March 2012). "Awards". Colorado State University . Retrieved 11 February 2020.
- 1 2 "Dr Kevin Lano". UK: King's College London. Archived from the original on 26 March 2012. Retrieved 3 July 2011.
- ↑ Taibi, Toufik (2007). Design patterns formalization techniques . IGI. p. 377. ISBN 978-1-59904-219-0.
- ↑ "Books : "Kevin Lano"". Amazon.co.uk . UK. Retrieved 10 May 2016.