
Pattadakal, also called Raktapura, is a complex of 7th and 8th century CE Hindu and Jain temples in northern Karnataka, India. Located on the west bank of the Malaprabha River in Bagalkot district, this UNESCO World Heritage Site is 23 kilometres (14 mi) from Badami and about 9.7 kilometres (6 mi) from Aihole, both of which are historically significant centres of Chalukya monuments. The monument is a protected site under Indian law and is managed by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI).

Aihole, also referred to as Aivalli, Ahivolal or Aryapura, is a historic site of ancient and medieval era Buddhist, Hindu and Jain monuments in Karnataka, India that dates from the sixth century through the twelfth century CE. Most of the surviving monuments at the site date from the 7th to 10th centuries. Located around an eponymous small village surrounded by farmlands and sandstone hills, Aihole is a major archaeological site featuring over one hundred and twenty stone and cave temples spread along the Malaprabha river valley, in Bagalakote district. Hunagunda Taluk Distance 35 km

Shikhara, a Sanskrit word translating literally to "mountain peak", refers to the rising tower in the Hindu temple architecture of North India, and also often used in Jain temples. A shikhara over the garbhagriha chamber where the presiding deity is enshrined is the most prominent and visible part of a Hindu temple of North India.

The Lakshmi Devi temple is an early 12th-century Hindu temples complex located in Doddagaddavalli village in Hassan District, Karnataka India. The main temple consists of four-shrines that share a common mandapa (hall), each sanctum being a square and aligned to a cardinal direction. The eastern shrine has Goddess Lakshmi, the northern shrine is dedicated to Kali-Durga, the western to Shiva, and the southern is empty and likely Vishnu. The complex has a separate Bhairava shrine to the northeast of the main temple, and four small shrines at the corners inside a nearly square prakara (compound). All nine temples are notable for its pyramidal north Indian style Nagara shikhara – likely an influence from Maharashtra and an evidence of active flow of ideas between the southern, central and northern India. The complex has additional smaller shrines.

Lakshmi Narasimha Temple, also referred to as Lakshminarasimha temple of Bhadravati, is a 13th-century Hindu temple dedicated to Vishnu, built by the Hoysala ruler Vira Someshwara. It is located in Bhadravati, Shimoga District of Karnataka state, India. The temple opens to the east and has three sanctums, one each dedicated to Venogopala, Lakshminarasimha and Vishnu-Puroshottama. It is notable for its Vesara architecture, with artwork that includes legends and deities of Vaishnavism, as well as those of Shaivism, Shaktism and Vedic deities. Important reliefs include those of Ganesha, Dakshinamurti, Bhairava, Sarasvati, Brahma, Surya, Harihara, and others. The temple's original shikaras were ruined, and have been restored with a conical structure. According to Adam Hardy – a scholar of Indian temple architecture, this temple has two "exceptional" stellate structures highlighting the architectural sophistication of the Hoysalas.
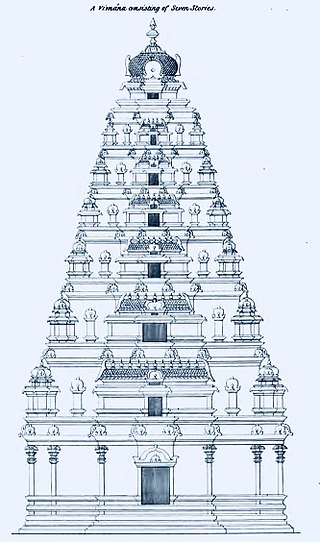
Vimana is the structure over the garbhagriha or inner sanctum in the Hindu temples of South India and Odisha in East India. In typical temples of Odisha using the Kalinga style of architecture, the vimana is the tallest structure of the temple, as it is in the shikhara towers of temples in West and North India. By contrast, in large South Indian temples, it is typically smaller than the great gatehouses or gopuram, which are the most immediately striking architectural elements in a temple complex. A vimana is usually shaped as a pyramid, consisting of several stories or tala. Vimana are divided in two groups: jati vimanas that have up to four tala and mukhya vimana that have five tala and more.

Thiru Anbil, or Sundararaja Perumal Temple, in Anbil, a village in the outskirts of Tiruchirappalli in the South Indian state of Tamil Nadu, is dedicated to the Hindu god Vishnu. Constructed in the Dravidian style of architecture, the temple is glorified in the Naalayira Divya Prabandham, the early medieval Tamil canon of the Alvar saints from the 6th–9th centuries CE. It is one of the 108 Divya Desams dedicated to Vishnu, who is worshipped as Sundararajan and his consort Lakshmi as Sundaravalli.

Brihadishvara Temple, called Rajarajesvaram by its builder, and known locally as Thanjai Periya Kovil and Peruvudaiyar Kovil, is a Shaivite Hindu temple built in a Chola architectural style located on the south bank of the Cauvery river in Thanjavur, Tamil Nadu, India. It is one of the largest Hindu temples and an exemplar of Tamil architecture. It is also called Dakshina Meru. Built by Chola emperor Rajaraja I between 1003 and 1010 CE, the temple is a part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site known as the "Great Living Chola Temples", along with the Chola-era Gangaikonda Cholapuram temple and Airavatesvara temple, which are about 70 kilometres (43 mi) and 40 kilometres (25 mi) to its northeast respectively.

Kote Venkataramana Temple is a Hindu temple in Krishnarajendra Road, Bangalore, India dedicated to the god Venkateshwara. The temple was built in 1689 in Dravidian and Vijayanagara style by King Chikka Devaraja Wodeyar, then ruler of Mysore.

The Loganatha Perumal Temple is a Hindu temple dedicated to Vishnu located 2 km away from Sikkal, Tamil Nadu, India on the Tiruvarur-Nagapatnam highway. Constructed in the Dravidian style of architecture, the temple is glorified in the Nalayira Divya Prabandham, the early medieval Tamil canon of the Alvar saints from the 6th–9th centuries CE. It is one of the 108 Divya Desams dedicated to Vishnu, who is worshiped as Loganatha Perumal and his consort Lakshmi as Loganayagi.

The Thripuliyoor Mahavishnu Temple is a Hindu temple dedicated to Vishnu and located in Puliyoor, Alappuzha District, Kerala, South India. Constructed in the Kerala style of architecture, the temple is glorified in the Nalayira Divya Prabandham, the early medieval Tamil canon of the Alvar saints from the 6th–9th centuries CE. It is one of the 108 Divya Desams dedicated to Vishnu, who is worshipped as Mayapiran/Thripuliyoorappan. The nearest railway station to the temple is located at Chengannur, while the nearest airport is Trivandrum International airport.

The Thiruvanvandoor Mahavishnu Temple is a Hindu temple dedicated to Vishnu and located in Thiruvanvandoor, Alappuzha District, Kerala, South India. Constructed in the Kerala style of architecture, the temple is glorified in the Nalayira Divya Prabandham, the early medieval Tamil canon of the Alvar saints from the 6th–9th centuries CE. It is one of the 108 Divya Desams dedicated to Vishnu, who is worshipped as Paambanaiappan. The nearest railway station to the temple is located in Chengannur, while the nearest airport is Trivandrum International Airport.

Bucesvara temple, also referred to as the Buceswara, Bucheshwara or Bhucheshvara temple, is a 12th-century Hindu temples in Koravangala village, Karnataka, India. The most sophisticated historical temple in the village, it is considered to be the flag-bearer of Hoysala architecture and was built by a wealthy patron named Buchi during the reign of king Ballala.

The Lakshminarasimha temple at Haranhalli, sometimes referred to as Lakshmi Narasimha temple of Haranhalli, is one of two major historic Hindu temples that have survived in Haranhalli, Karnataka, India. It is triple-shrine temple dedicated to Vishnu, while the other – Someshvara Temple, Haranhalli few hundred meters to the east – is dedicated to Shiva. Both temples reflect a Vesara-style Hoysala architecture, share similar design ideas and features, and were completed in the 1230s by three wealthy brothers – Peddanna Heggade, Sovanna and Kesanna.

The Kalleshvara temple is located in the town of Ambali in Bellary district of Karnataka state, India. According to an Old Kannada inscription placed in the sabhamantapa, the temple was constructed during the reign of the Western Chalukya Empire King Vikramaditya VI. This temple is protected as a monument of national importance by the Archaeological Survey of India.

The Kaitabheshvara temple is located in the town of Kubatur, near Anavatti in the Shimoga district of Karnataka state, India. The temple was constructed during the reign of Hoysala King Vinayaditya around 1100 AD. The Hoysala ruling family was during this time a powerful feudatory of the imperial Western Chalukya Empire ruled by King Vikramaditya VI. According to the Archaeological Survey of India, the architectural signature of the temple is mainly "Chalukyan". Art historian Adam Hardy classifies the style involved in the construction of the temple as "Later Chalukya, non mainstream, far end of spectrum". The building material used is soapstone The temple is protected as a monument of national importance by the Archaeological Survey of India.

The Nageshvara-Chennakeshava temple complex, sometimes referred to as the Nagesvara and Chennakesava temples of Mosale, are a pair of nearly identical Hindu temples in the village of Mosale near Hassan city, Karnataka, India. One for Shiva, other for Vishnu, this pair is a set of highly ornamented stone temples, illustrating the Hoysala architecture. These temples also include panels of artwork related to the goddess tradition of Hinduism (Shaktism) and Vedic deities. Another notable feature of these temples is the artwork in their ceilings, how the shilpins (artisans) integrated the historic pre-Hoysala architectural innovations from the Chalukya era. Further, the temples include north Indian Bhumija and south Indian Vesara aedicules on the outer walls above the panels. It is unclear when this temple pair was built, but given the style and architectural innovations embedded therein, it was likely complete before 1250 CE.

Thrikodithanam Mahavishnu Temple is a Hindu temple dedicated to Vishnu and located in Thrikkodithanam, Kottayam District, Kerala, South India. Constructed in the Kerala style of architecture, the temple is glorified in the Nalayira Divya Prabandham, the early medieval Tamil canon of the Alvar saints from the 6th–9th centuries CE. It is one of the 108 Divya Desam dedicated to Krishna, an avatar of Vishnu, who is worshipped as Mahavishnu. The nearest railway station to the temple is located in Changanassery, while the nearest airport is Cochin International Airport.

The Sadasiva temple at Nuggehalli is a 13th-century Shiva temple with Hoysala architecture in Nuggehalli village, Hassan district, Karnataka, India. The temple is one of the best illustrations of the Hoysala era Nagara temple with the stellate style, remarkable for its octagonal star configuration with clean, simple aesthetics. The brilliant synthesis of South Indian ideas with North Indian architectural plan makes it a special monument. It is also notable for its artwork that depicts legends of Shaivism, Vaishnavism, Shaktism and Vedic deities together.

Kunnakudi Shanmughanathar temple in Kundrakudi, a village in the outskirts of Karaikudi in Sivaganga district in the South Indian state of Tamil Nadu, is dedicated to the Hindu god Murugan. Constructed in the Hindu style of architecture, the temple is located in the Tirupattur - Karaikudi Road, around 14 km (14,000 m) from Karaikudi. There are three caves located on the western side of the lower rock, that has rock-cut shrines from the Pandyan Empire from the 8th century. The caves have the earliest sculptural representation of Dvarapalas, the guardian deities, for any South Indian temple.






















