
Security-Enhanced Linux (SELinux) is a Linux kernel security module that provides a mechanism for supporting access control security policies, including mandatory access controls (MAC).

OpenSSL is a software library for applications that provide secure communications over computer networks against eavesdropping, and identify the party at the other end. It is widely used by Internet servers, including the majority of HTTPS websites.

FileZilla is a free and open-source, cross-platform FTP application, consisting of FileZilla Client and FileZilla Server. Clients are available for Windows, Linux, and macOS. Both server and client support FTP and FTPS, while the client can in addition connect to SFTP servers. FileZilla's source code is hosted on SourceForge.

cPanel is web hosting control panel software developed by cPanel, L.L.C. It provides a graphical interface (GUI) and automation tools designed to simplify the process of hosting a web site to the website owner or the "end user". It enables administration through a standard web browser using a three-tier structure. While cPanel is limited to managing a single hosting account, cPanel & WHM allows the administration of the entire server.
A hypervisor, also known as a virtual machine monitor (VMM) or virtualizer, is a type of computer software, firmware or hardware that creates and runs virtual machines. A computer on which a hypervisor runs one or more virtual machines is called a host machine, and each virtual machine is called a guest machine. The hypervisor presents the guest operating systems with a virtual operating platform and manages the execution of the guest operating systems. Unlike an emulator, the guest executes most instructions on the native hardware. Multiple instances of a variety of operating systems may share the virtualized hardware resources: for example, Linux, Windows, and macOS instances can all run on a single physical x86 machine. This contrasts with operating-system–level virtualization, where all instances must share a single kernel, though the guest operating systems can differ in user space, such as different Linux distributions with the same kernel.
Platform virtualization software, specifically emulators and hypervisors, are software packages that emulate the whole physical computer machine, often providing multiple virtual machines on one physical platform. The table below compares basic information about platform virtualization hypervisors.
DreamHost is a Los Angeles-based web hosting provider and domain name registrar. It is owned by New Dream Network, LLC, founded in 1996 by Dallas Bethune, Josh Jones, Michael Rodriguez and Sage Weil, undergraduate students at Harvey Mudd College in Claremont, California, and registered in 1997 by Michael Rodriguez. DreamHost began hosting customers' sites in 1997. In May 2012, DreamHost spun off Inktank. Inktank is a professional services and support company for the open source Ceph file system. In November 2014, DreamHost spun off Akanda, an open source network virtualization project. As of February 2016, Dreamhost employs about 200 people and has close to 400,000 customers.

Jitsi is a collection of free and open-source multiplatform voice (VoIP), video conferencing and instant messaging applications for the Web platform, Windows, Linux, macOS, iOS and Android. The Jitsi project began with the Jitsi Desktop. With the growth of WebRTC, the project team focus shifted to the Jitsi Videobridge for allowing web-based multi-party video calling. Later the team added Jitsi Meet, a full video conferencing application that includes web, Android, and iOS clients. Jitsi also operates meet.jit.si, a version of Jitsi Meet hosted by Jitsi for free community use. Other projects include: Jigasi, lib-jitsi-meet, Jidesha, and Jitsi.
This is a comparison of notable free and open-source configuration management software, suitable for tasks like server configuration, orchestration and infrastructure as code typically performed by a system administrator.

DirectAdmin is a graphical web-based web hosting control panel allowing administration of websites through a web browser. The software is configurable to enable standalone, reseller, and shared web hosting from a single instance. DirectAdmin also permits management of server tasks and upgrades to package software from within the control panel - simplifying server and hosting configuration.
Heroku is a cloud platform as a service (PaaS) supporting several programming languages. As one of the first cloud platforms, Heroku has been in development since June 2007, when it supported only the Ruby programming language, but now also supports Java, Node.js, Scala, Clojure, Python, PHP, and Go. For this reason, Heroku is said to be a polyglot platform as it has features for a developer to build, run and scale applications in a similar manner across most of these languages. Heroku was acquired by Salesforce in 2010 for $212 million.

The TurnKey Linux Virtual Appliance Library is a free open-source software project which develops a range of Debian-based pre-packaged server software appliances. Turnkey appliances can be deployed as a virtual machine, in cloud computing services such as Amazon Web Services or installed in physical computers.
Hosting Controller is a multi-purpose cloud control panel and Active Directory synchronization solution that operates out of Canada and offers SaaS, Active Directory,Virtual Machine automation and Migration services to enterprises and service providers worldwide.
NehoX Game Panel was a web-based game server hosting control panel to help easily manage game servers. NehoX is designed to simplify the process to deploy, automate, and maintain game servers and remote servers. NehoX automates the installation process and the remote server installation process at the click of a button to enable administrators to add additional servers and fully control everything from the master server.

Google Authenticator is a software-based authenticator by Google. It implements multi-factor authentication services using the time-based one-time password and HMAC-based one-time password, for authenticating users of software applications.

Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) is a feature of Microsoft Windows that allows developers to run a Linux environment without the need for a separate virtual machine or dual booting. There are two versions of WSL: WSL 1 and WSL 2. WSL is not available to all Windows 10 users by default. It can be installed either by joining the Windows Insider program or manually via Microsoft Store or Winget.
Justin Cappos is a computer scientist and cybersecurity expert whose data-security software has been adopted by a number of widely used open-source projects. His research centers on software update systems, security, and virtualization, with a focus on real-world security problems.

Bitwarden is a freemium open-source password management service that is used to store sensitive information, such as website credentials, in an encrypted vault. The platform hosts multiple client applications, including a web interface, desktop applications, browser extensions, mobile apps, and a command-line interface. The platform offers a free US or European cloud-hosted service as well as the ability to self-host.

Rocky Linux is a Linux distribution developed by Rocky Enterprise Software Foundation, which is a privately owned benefit corporation that describes itself as a "self-imposed not-for-profit". It is intended to be a downstream, complete binary-compatible release using the Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) operating system source code. The project's aim is to provide a community-supported, production-grade enterprise operating system. Rocky Linux, along with RHEL and SUSE Linux Enterprise (SLE), has become popular for enterprise operating system use.
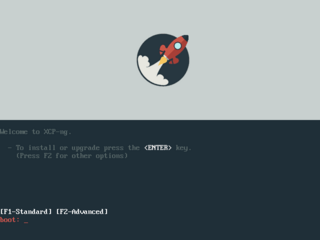
XCP-ng is a Linux distribution of the Xen Project, with pre-configured Xen Hypervisor and the Xen API project (XAPI) working out-of-the-box. The project was born in 2018, following the fork of Citrix XenServer. Since January 2020, it is also part of the Linux Foundation, via the Xen Project.











