Related Research Articles

The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the pressure surrounding the liquid and the liquid changes into a vapor.

Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. A high concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evaporation, such as when humidity affects rate of evaporation of water. When the molecules of the liquid collide, they transfer energy to each other based on how they collide. When a molecule near the surface absorbs enough energy to overcome the vapor pressure, it will escape and enter the surrounding air as a gas. When evaporation occurs, the energy removed from the vaporized liquid will reduce the temperature of the liquid, resulting in evaporative cooling.
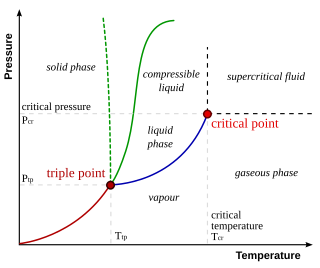
In thermodynamics, the triple point of a substance is the temperature and pressure at which the three phases of that substance coexist in thermodynamic equilibrium. It is that temperature and pressure at which the sublimation, fusion, and vaporisation curves meet. For example, the triple point of mercury occurs at a temperature of −38.8 °C (−37.8 °F) and a pressure of 0.165 mPa.

In thermodynamics, the enthalpy of vaporization, also known as the (latent) heat of vaporization or heat of evaporation, is the amount of energy (enthalpy) that must be added to a liquid substance to transform a quantity of that substance into a gas. The enthalpy of vaporization is a function of the pressure and temperature at which the transformation takes place.

Vapor pressure or equilibrium vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases at a given temperature in a closed system. The equilibrium vapor pressure is an indication of a liquid's thermodynamic tendency to evaporate. It relates to the balance of particles escaping from the liquid in equilibrium with those in a coexisting vapor phase. A substance with a high vapor pressure at normal temperatures is often referred to as volatile. The pressure exhibited by vapor present above a liquid surface is known as vapor pressure. As the temperature of a liquid increases, the attractive interactions between liquid molecules become less significant in comparison to the entropy of those molecules in the gas phase, increasing the vapor pressure. Thus, liquids with strong intermolecular interactions are likely to have smaller vapor pressures, with the reverse true for weaker interactions.

Condensation is the change of the state of matter from the gas phase into the liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization. The word most often refers to the water cycle. It can also be defined as the change in the state of water vapor to liquid water when in contact with a liquid or solid surface or cloud condensation nuclei within the atmosphere. When the transition happens from the gaseous phase into the solid phase directly, the change is called deposition.

Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.
Water vapor, water vapour or aqueous vapor is the gaseous phase of water. It is one state of water within the hydrosphere. Water vapor can be produced from the evaporation or boiling of liquid water or from the sublimation of ice. Water vapor is transparent, like most constituents of the atmosphere. Under typical atmospheric conditions, water vapor is continuously generated by evaporation and removed by condensation. It is less dense than most of the other constituents of air and triggers convection currents that can lead to clouds and fog.

Latent heat is energy released or absorbed, by a body or a thermodynamic system, during a constant-temperature process—usually a first-order phase transition, like melting or condensation.

Heat transfer is a discipline of thermal engineering that concerns the generation, use, conversion, and exchange of thermal energy (heat) between physical systems. Heat transfer is classified into various mechanisms, such as thermal conduction, thermal convection, thermal radiation, and transfer of energy by phase changes. Engineers also consider the transfer of mass of differing chemical species, either cold or hot, to achieve heat transfer. While these mechanisms have distinct characteristics, they often occur simultaneously in the same system.
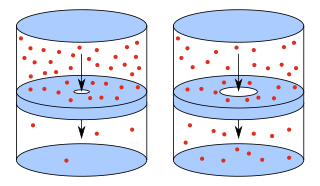
In physics and chemistry, effusion is the process in which a gas escapes from a container through a hole of diameter considerably smaller than the mean free path of the molecules. Such a hole is often described as a pinhole and the escape of the gas is due to the pressure difference between the container and the exterior.

Sublimation is the transition of a substance directly from the solid to the gas state, without passing through the liquid state. The verb form of sublimation is sublime, or less preferably, sublimate. Sublimate also refers to the product obtained by sublimation. The point at which sublimation occurs rapidly is called critical sublimation point, or simply sublimation point. Notable examples include sublimation of dry ice at room temperature and atmospheric pressure, and that of solid iodine with heating.

In chemistry, volatility is a material quality which describes how readily a substance vaporizes. At a given temperature and pressure, a substance with high volatility is more likely to exist as a vapour, while a substance with low volatility is more likely to be a liquid or solid. Volatility can also describe the tendency of a vapor to condense into a liquid or solid; less volatile substances will more readily condense from a vapor than highly volatile ones. Differences in volatility can be observed by comparing how fast substances within a group evaporate when exposed to the atmosphere. A highly volatile substance such as rubbing alcohol will quickly evaporate, while a substance with low volatility such as vegetable oil will remain condensed. In general, solids are much less volatile than liquids, but there are some exceptions. Solids that sublimate such as dry ice or iodine can vaporize at a similar rate as some liquids under standard conditions.
Chemical beam epitaxy (CBE) forms an important class of deposition techniques for semiconductor layer systems, especially III-V semiconductor systems. This form of epitaxial growth is performed in an ultrahigh vacuum system. The reactants are in the form of molecular beams of reactive gases, typically as the hydride or a metalorganic. The term CBE is often used interchangeably with metal-organic molecular beam epitaxy (MOMBE). The nomenclature does differentiate between the two processes, however. When used in the strictest sense, CBE refers to the technique in which both components are obtained from gaseous sources, while MOMBE refers to the technique in which the group III component is obtained from a gaseous source and the group V component from a solid source.

Deposition is the phase transition in which gas transforms into solid without passing through the liquid phase. Deposition is a thermodynamic process. The reverse of deposition is sublimation and hence sometimes deposition is called desublimation.
Electron-beam physical vapor deposition, or EBPVD, is a form of physical vapor deposition in which a target anode is bombarded with an electron beam given off by a charged tungsten filament under high vacuum. The electron beam causes atoms from the target to transform into the gaseous phase. These atoms then precipitate into solid form, coating everything in the vacuum chamber with a thin layer of the anode material.
Physical vapor deposition (PVD), sometimes called physical vapor transport (PVT), describes a variety of vacuum deposition methods which can be used to produce thin films and coatings on substrates including metals, ceramics, glass, and polymers. PVD is characterized by a process in which the material transitions from a condensed phase to a vapor phase and then back to a thin film condensed phase. The most common PVD processes are sputtering and evaporation. PVD is used in the manufacturing of items which require thin films for optical, mechanical, electrical, acoustic or chemical functions. Examples include semiconductor devices such as thin-film solar cells, microelectromechanical devices such as thin film bulk acoustic resonator, aluminized PET film for food packaging and balloons, and titanium nitride coated cutting tools for metalworking. Besides PVD tools for fabrication, special smaller tools used mainly for scientific purposes have been developed.
The Glossary of fuel cell terms lists the definitions of many terms used within the fuel cell industry. The terms in this fuel cell glossary may be used by fuel cell industry associations, in education material and fuel cell codes and standards to name but a few.

The vapor–liquid–solid method (VLS) is a mechanism for the growth of one-dimensional structures, such as nanowires, from chemical vapor deposition. The growth of a crystal through direct adsorption of a gas phase on to a solid surface is generally very slow. The VLS mechanism circumvents this by introducing a catalytic liquid alloy phase which can rapidly adsorb a vapor to supersaturation levels, and from which crystal growth can subsequently occur from nucleated seeds at the liquid–solid interface. The physical characteristics of nanowires grown in this manner depend, in a controllable way, upon the size and physical properties of the liquid alloy.

Thermal laser epitaxy (TLE) is a physical vapor deposition technique that utilizes irradiation from continuous-wave lasers to heat sources locally for growing films on a substrate. This technique can be performed under ultra-high vacuum pressure or in the presence of a background atmosphere, such as ozone, to deposit oxide films.
References
- ↑ Peter Atkins and Julio de Paula, Physical Chemistry (8th ed., W.H.Freeman 2006) p.756 ISBN 0-7167-8759-8
- ↑ Drago, R.S. Physical Methods in Chemistry (W.B.Saunders 1977) p.563 ISBN 0-7216-3184-3