
An anti-ballistic missile (ABM) is a surface-to-air missile designed to counter ballistic missiles. Ballistic missiles are used to deliver nuclear, chemical, biological, or conventional warheads in a ballistic flight trajectory. The term "anti-ballistic missile" is a generic term conveying a system designed to intercept and destroy any type of ballistic threat; however, it is commonly used for systems specifically designed to counter intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs).

The People's Liberation Army (PLA) is the armed forces of the People's Republic of China (PRC) and the armed wing of the PRC's founding and ruling political party, the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). Besides the Central Military Commission (CMC) and several minor units directly under it, the PLA has five major service branches: the Ground Force (PLAGF), Navy (PLAN), Air Force (PLAAF), Rocket Force (PLARF), and the Strategic Support Force (PLASSF). A majority of military units around the country are assigned to one of five theater commands by geographical location. The PLA is the world's largest military force and constitutes the second largest defense budget in the world. It is also one of the fastest modernizing militaries in the world, and has been termed as a potential military superpower, with significant regional defense and rising global power projection capabilities.
Anti-satellite weapons (ASAT) are space weapons designed to incapacitate or destroy satellites for strategic or tactical purposes. Several nations possess operational ASAT systems. Although no ASAT system has yet been utilised in warfare, a few countries have successfully shot down their own satellites to demonstrate their ASAT capabilities in a show of force. ASATs have also been used to remove decommissioned satellites.

The HQ-16 is a medium range semi-active radar homing surface-to-air missile developed by the People's Republic of China.
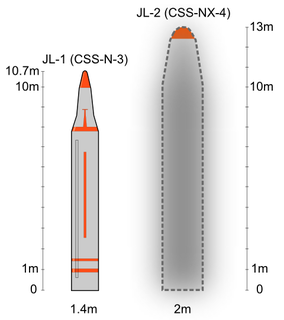
The JL-2 is a Chinese second-generation intercontinental-range submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) deployed on the People's Liberation Army Navy's (PLAN) Type 094 submarines. It succeeds the JL-1 SLBM deployed on the Type 092 submarine.

The People's Liberation Army Rocket Force, formerly the Second Artillery Corps, is the strategic and tactical missile force of the People's Republic of China. The PLARF is the 4th branch of the People's Liberation Army (PLA) and controls China's arsenal of land-based ballistic missiles—both nuclear and conventional. The armed service branch was established on 1 July 1966 and made its first public appearance on 1 October 1984. The headquarters for operations is located at Qinghe, Beijing. The PLARF is under the direct command of the Central Military Commission (CMC).

The HQ-9 is a long-range semi-active radar homing (SARH) surface-to-air missile (SAM) developed by the by the People's Republic of China. The naval variant is the HHQ-9.

The Weishi family of multiple rocket launcher systems were mainly developed by Sichuan Aerospace Industry Corporation in Chengdu, China. The systems include the 302 mm (11.9 in) WS-1, the improved 302 mm (11.9 in) WS-1B, the 122 mm (4.8 in) WS-1E, the 400 mm (16 in) WS-2, as well as many other models. The WS-1 series weapon system did not enter PLA service and has order from Thailand. The WS-2 may finally see PLA service in the future. It's worth noticing that although sharing the same name, there are other developers for different models of Weishi series multiple rocket launchers (MRL) other than the primary developer SCAIC.

The WS2400 is a 8x8 special heavy-duty truck developed and built by Wanshan Special Vehicle and used by the People's Liberation Army of the People's Republic of China as a transporter erector launcher (TEL) platform and is a reverse engineered version of the MAZ-543 missile Transporter erector launcher.
The Dongfeng-41 is a fourth-generation Chinese solid-fuelled road-mobile intercontinental ballistic missile operated by the People's Liberation Army Rocket Force. DF-41 is the fourth and the latest generation of the Dongfeng series strategic missiles developed by China. The missile was officially unveiled at the China National Day military parade on 1 October 2019.

The Korean People's Army Strategic Rocket Force, also known as Missile Guidance Bureau, is a military branch of the Korean People's Army that oversees North Korea's nuclear and conventional strategic missiles. It is mainly armed with surface-to-surface missiles of domestic design as well as older Soviet and Chinese models. The KPA-SRF was established in 1999 when several missile units under KPA Ground Force Artillery Command were re-organized into a single missile force reporting directly to the office of the Supreme Commander of the KPA via the General Staff.
An anti-ship ballistic missile (ASBM) is a military ballistic missile system designed to hit a warship at sea.

The CJ-10 is a second-generation Chinese ground-based land-attack missile. It is derived from the Kh-55 missile. It is reportedly manufactured by the China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation Third Academy and the China Haiying Electro-Mechanical Technology Academy.
The People's Republic of China carried out a land-based high-altitude anti-ballistic missile test on 11 January 2010. This reportedly made China the second country in the world after the United States of America to successfully destroy an incoming missile beyond the Earth's atmosphere.
China's anti-satellite (ASAT) program has been under development since 1964. The ASAT program has since been moved from Program 640 to Program 863, the General Armaments Department and the State Administration for Science, Technology and Industry for National Defense. Since its inception, the ASAT program has made progress on the development of three ASAT capable Systems: direct fire, directed-energy weapon, and microsatellites. Tests of these systems have either been directly acknowledged by the PRC, or reported on as ASAT capable. China is pursuing a broad and robust array of counterspace capabilities, which includes direct-ascent antisatellite missiles, co-orbital antisatellite systems, computer network operations, groundbased satellite jammers, and directed energy weapons.
This is a comparison list of intercontinental ballistic missiles developed by various countries.
Missile defense systems are a type of missile defense intended to shield a country against incoming missiles, such as intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBMs) or other ballistic missiles. The United States, Russia, India, France, Israel, Italy, United Kingdom and China have all developed missile defense systems.

The HQ-17 is an all-weather, low to medium altitude, short-range surface-to-air missile system cloned from the Tor-M1.
System A-235 PL-19 Nudol is a Russian anti-ballistic missile and anti-satellite weapon system in development. It is designed to deflect a nuclear attack on Moscow and important industrial regions. The main developer of the system is JSC Concern VKO Almaz-Antey. The new system should replace the current one — A-135. The two main differences will be that the A-235 will use conventional warheads and it will be mobile.
The Dong Neng-3 (DN-3/KO09) is a Chinese ballistic missile defense system.











