Related Research Articles

The Chūbu region, Central region, or Central Japan is a region in the middle of Honshū, Japan's main island. In a wide, classical definition, it encompasses nine prefectures (ken): Aichi, Fukui, Gifu, Ishikawa, Nagano, Niigata, Shizuoka, Toyama, and Yamanashi.
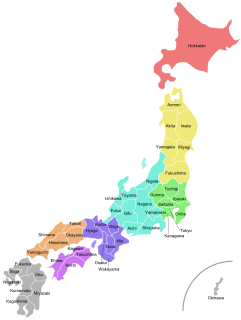
Japan is divided into 47 prefectures, which rank immediately below the national government and form the country's first level of jurisdiction and administrative division. They include 43 prefectures proper, two urban prefectures, one "circuit" or "territory" and one metropolis. In 1868, the Meiji Fuhanken sanchisei administration created the first prefectures to replace the urban and rural administrators in the parts of the country previously controlled directly by the shogunate and a few territories of rebels/shogunate loyalists who had not submitted to the new government such as Aizu/Wakamatsu. In 1871, all remaining feudal domains (han) were also transformed into prefectures, so that prefectures subdivided the whole country. In several waves of territorial consolidation, today's 47 prefectures were formed by the turn of the century. In many instances, these are contiguous with the ancient ritsuryō provinces of Japan.
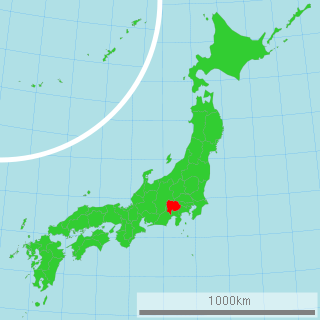
Yamanashi Prefecture is a prefecture of Japan located in the Chūbu region of Honshu. Yamanashi Prefecture has a population of 817,192 and has a geographic area of 4,465 km2. Yamanashi Prefecture borders Saitama Prefecture to the northeast, Nagano Prefecture to the northwest, Shizuoka Prefecture to the southwest, Kanagawa Prefecture to the southeast, and Tokyo to the east.

The Kanto region is a geographical area of Honshu, the largest island of Japan. In a common definition, the region includes the Greater Tokyo Area and encompasses seven prefectures: Gunma, Tochigi, Ibaraki, Saitama, Tokyo, Chiba and Kanagawa. Within its boundaries, slightly more than 45 percent of the land area is the Kanto Plain. The rest consists of the hills and mountains that form the land borders. According to the official census on October 1, 2010, by the Japan Statistics Bureau, the population was 42,607,376, amounting to approximately one third of the total population of Japan.

Yamanashi is a city located in Yamanashi Prefecture, Japan. As of 1 July 2019, the city had an estimated population of 34,738 in 14,679 households, and a population density of 120 persons per km2. The total area of the city is 289.80 square kilometres (111.89 sq mi).

Kai Province was a province of Japan in the area of Japan that is today Yamanashi Prefecture. Kai bordered on Sagami, Suruga, Shinano and Musashi Provinces. Its abbreviated form name was Kōshū (甲州). The origin of its name is uncertain. It lies in central Honshū, west of Tokyo, in a landlocked mountainous region that includes Mount Fuji along its border with modern Shizuoka Prefecture.
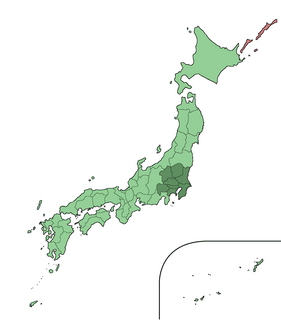
The Greater Tokyo Area is the most populous metropolitan area in the world, consisting of the Kantō region of Japan as well as the prefecture of Yamanashi of the neighboring Chūbu region. In Japanese, it is referred to by various terms, one of the most common being Capital Region.
The Japanese addressing system is used to identify a specific location in Japan. When written in Japanese characters, addresses start with the largest geographical entity and proceed to the most specific one. When written in Latin characters, addresses follow the convention used by most Western addresses and start with the smallest geographic entity and proceed to the largest. The Japanese system is complex and idiosyncratic, the product of the natural growth of urban areas, as opposed to the systems used in cities that are laid out as grids and divided into quadrants or districts.

Katsunuma was a town in Higashiyamanashi District, Yamanashi Prefecture, Japan.
Higashiyamanashi was a district located in Yamanashi Prefecture, Japan.

Fuefuki is a city in Yamanashi Prefecture, Japan. As of 31 March 2019, the city had an estimated population of 69,463 in 29,406 households, and a population density of 340 persons per km2. The total area of the city is 201.92 square kilometres (77.96 sq mi).

Chichibu-Tama-Kai National Park is a national park in Japan at the intersection of Saitama, Yamanashi, Nagano and Tokyo Prefectures.
Japanese place names include names for geographic features, present and former administrative divisions, transportation facilities such as railroad stations, and historic sites in Japan. The article Japanese addressing system contains related information on postal addresses.

Kōshū is a city located in Yamanashi Prefecture, Japan. As of 1 June 2019, the city had an estimated population of 31,526 in 13,147 households, and a population density of 120 persons per km². The total area of the city is 264.11 square kilometres (101.97 sq mi). The city is the home of the indigenous Koshu grape and is synonymous with viticulture and wine production in Japan.

Although viticulture and the cultivation of grapes for table consumption has a long history in Japan, domestic wine production using locally produced grapes only really began with the adoption of Western culture during the Meiji restoration in the second half of the 19th century.
Tourism Areas are areas or zones designated by the Japan Tourism Agency from 2008. As of April 2009, 30 Tourism Areas are located throughout Japan. The Japan Tourism Agency set the law in 2008 regarding this area to support and promote more synergistic activities among local governments, tourism associations, tourism industries and local hotels and other local organizations and individuals.

The Tōkai–Tōsan dialect is a group of the transitional Japanese dialects spoken in the southern and eastern Chūbu region. The dialects spoken in the northwest Chubu region are classified as the Hokuriku dialect of Western Japanese. The Tokai–Tosan dialect has three sub-groups: Gifu–Aichi, Echigo, and Nagano–Yamanashi–Shizuoka. These are transitional between Western and Eastern Japanese; which branch of the family they fall in depends on which isoglosses are taken as definitive.

Koshu is a white wine grape variety that has been grown primarily in the Koshu Valley in Yamanashi Prefecture, Japan. Though long thought to be of exclusively European origin, it is now known to be a hybrid of Europe's Vitis vinifera and one or more East Asian Vitis species. The name “Koshu” is a former name for Yamanashi and the present-day name of the main town in the valley where the majority of Koshu grapes are grown.

The Jōshin'etsu region is a region on the main Japanese island of Honshu, comprising parts of Gunma, Nagano, and Niigata Prefectures. It is a mountainous area with a large national park and numerous hot springs and ski resorts. It has long been a transportation corridor between the Kantō plain and coastal areas on the Japan Sea side of the island.

The Saruhashi Bridge (猿橋) is a historic arch bridge officially listed as a Place of Scenic Beauty of Japan in Ōtsuki, Yamanashi Prefecture. It is ranked as one of Japan's three unique bridges, along with the Kintai Bridge and the Shinkyo Bridge. It is also referred to as the monkey bridge, and is known as one of the "Japanese Sanky Bridges".
References
- ↑ "Koshu Valley Wine Country". Koshu Valley. Retrieved 2019-05-26.
- ↑ "Koshu Wine: A 1300-Year Journey" (PDF). Close to Mount Fuji. Retrieved 2019-05-26.
- ↑ "峡東地域とは (About the Kyōtō Region; Japanese only)". Yamanashi Prefecture. Retrieved 2019-05-26.
- ↑ "Yamanashi Wine Resort". Yamanashi Wine Resort. Retrieved 2019-05-26.
- ↑ "Kyoto Area in Yamanashi (Japanese only)". Yamanashi Wine Resort. Retrieved 2019-07-23.