snRNPs, or small nuclear ribonucleoproteins, are RNA-protein complexes that combine with unmodified pre-mRNA and various other proteins to form a spliceosome, a large RNA-protein molecular complex upon which splicing of pre-mRNA occurs. The action of snRNPs is essential to the removal of introns from pre-mRNA, a critical aspect of post-transcriptional modification of RNA, occurring only in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. Additionally, U7 snRNP is not involved in splicing at all, as U7 snRNP is responsible for processing the 3′ stem-loop of histone pre-mRNA.
Small nuclear ribonucleic acid (snRNA) is a class of small RNA molecules that are found within the splicing speckles and Cajal bodies of the cell nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The length of an average snRNA is approximately 150 nucleotides. They are transcribed by either RNA polymerase II or RNA polymerase III. Their primary function is in the processing of pre-messenger RNA (hnRNA) in the nucleus. They have also been shown to aid in the regulation of transcription factors or RNA polymerase II, and maintaining the telomeres.

In molecular biology, LSm proteins are a family of RNA-binding proteins found in virtually every cellular organism. LSm is a contraction of 'like Sm', because the first identified members of the LSm protein family were the Sm proteins. LSm proteins are defined by a characteristic three-dimensional structure and their assembly into rings of six or seven individual LSm protein molecules, and play a large number of various roles in mRNA processing and regulation.
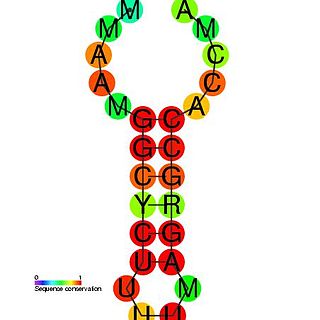
The histone 3' UTR stem-loop is an RNA element involved in nucleocytoplasmic transport of the histone mRNAs, and in the regulation of stability and of translation efficiency in the cytoplasm. The mRNAs of metazoan histone genes lack polyadenylation and a poly-A tail, instead 3' end processing occurs at a site between this highly conserved stem-loop and a purine rich region around 20 nucleotides downstream. The stem-loop is bound by a 31 kDa stem-loop binding protein. Together with U7 snRNA binding of the HDE, SLBP binding nucleates the formation of the processing complex.
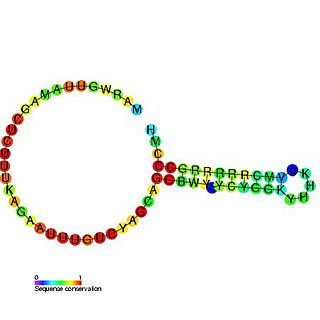
The U7 small nuclear RNA is an RNA molecule and a component of the small nuclear ribonucleoprotein complex. The U7 snRNA is required for histone pre-mRNA processing.

5'-3' Exoribonuclease 2 (XRN2) also known as Dhm1-like protein is an exoribonuclease enzyme that in humans is encoded by the XRN2 gene.

Histone RNA hairpin-binding protein or stem-loop binding protein (SLBP) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLBP gene.

Small nuclear ribonucleoprotein F is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNRPF gene.

Serine-threonine kinase receptor-associated protein is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the STRAP gene.

U6 snRNA-associated Sm-like protein LSm6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LSM6 gene.

U6 snRNA-associated Sm-like protein LSm5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LSM5 gene.

U6 snRNA-associated Sm-like protein LSm4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LSM4 gene.

U6 snRNA-associated Sm-like protein LSm1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LSM1 gene.

U6 snRNA-associated Sm-like protein LSm7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LSM7 gene.

U6 snRNA-associated Sm-like protein LSm2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LSM2 gene.

40S ribosomal protein S20 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RPS20 gene.

U6 snRNA-associated Sm-like protein LSm8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LSM8 gene.

Genetic suppressor element 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIAA0182 gene.

Zinc finger protein 473 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF473 gene.




















