The Kingdom of Asturias was a kingdom in the Iberian Peninsula founded by the Visigothic nobleman Pelagius. It was the first Christian political entity established after the Umayyad conquest of Visigothic Hispania in 711. In the Summer of 722, Pelagius defeated an Umayyad army at the Battle of Covadonga, in what is retroactively regarded as the beginning of the Reconquista.

Asturias officially the Principality of Asturias, is an autonomous community in northwest Spain.

Alfonso III, called the Great, was the king of León, Galicia and Asturias from 866 until his death. He was the son and successor of Ordoño I. In later sources, he is the earliest to be called "Emperor of Spain." He was also titled "Prince of all Galicia".

Oviedo or Uviéu is the capital city of the Principality of Asturias in northern Spain and the administrative and commercial centre of the region. It is also the name of the municipality that contains the city. Oviedo is located approximately 24 km (15 mi) southwest of Gijón and 23 km (14 mi) southeast of Avilés, both of which lie on the shoreline of the Bay of Biscay. Oviedo's proximity to the ocean of less than 30 kilometres (19 mi) in combination with its elevated position with areas of the city more than 300 metres above sea level causes the city to have a maritime climate, in spite of its not being located on the shoreline itself.

Ramiro I was king of Asturias from 842 until his death in 850. Son of King Bermudo I, he became king following a succession struggle after his predecessor, Alfonso II, died without children. During his turbulent reign, he fended off attacks from both Vikings and the forces of al-Andalus. Architecturally, his recreational palace Santa María del Naranco and other buildings used the ramirense style that prefigured Romanesque architecture. He was a contemporary of Abd ar-Rahman II, Umayyad Emir of Córdoba.

The Archaeological Museum of Asturias is housed in the 16th century Benedictine monastery of Saint Vicente in Oviedo, Asturias, Spain. Its findings include collections of the Asturian Neolithic, Megalithic, Bronze Age, Iron Age, Astur hill fort culture, Roman period, and of the Gothic, Pre-Romanesque and Romanesque periods of the Kingdom of Asturias. The museum also includes sections of Asturian Ethnography, Heraldry, Medieval and Modern Epigraphy, Spanish Numismatics, a European Medal Section, and Armor.

The Metropolitan Cathedral Basilica of the Holy Saviour or Cathedral of San Salvador is a Roman Catholic church and minor basilica in the centre of Oviedo, in the Asturias region of northern Spain.

Pre-Romanesque architecture in Asturias is framed between the years 711 and 910, the period of the creation and expansion of the kingdom of Asturias.

Asturians are a Romance ethnic group with Celtic roots, native to the autonomous community of Asturias, in the North-West of the Iberian Peninsula.

The church of Saint Mary at Mount Naranco is a pre-Romanesque Asturian building on the slope of Mount Naranco situated 3 kilometres (1.9 mi) from Oviedo, northern Spain. Ramiro I of Asturias ordered it to be built as a royal palace, part of a larger complex that also incorporated the nearby church of San Miguel de Lillo, 100 meters away. The palace was completed in 842 and had in part a religious function, being consecrated in 848. Its structural features, such as the barrel vault—with transverse ribs corresponding one-to-one with contraforts at the exterior, make it a clear precursor of the Romanesque construction. The exterior decorations, as well as the use of stilted arches, mark the intended verticality of the composition.

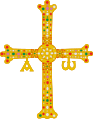
The Victory Cross is an early 10th-century Asturian jewelled cross gifted by King Alfonso III of Asturias, who reigned from 866 to 910, to the Cathedral of San Salvador in Oviedo. It was made in 908 in the Castle of Gauzón.

St Christine of Lena is a Roman Catholic Asturian pre-Romanesque church located in the Lena municipality, about 25 km south of Oviedo, Spain, on an old Roman road that joined the lands of the plateau with Asturias.

The Agate Casket of Oviedo is an elaborately decorated box, casket or small chest given by King Fruela II of Asturias and his wife Nunila to the Cathedral of San Salvador, Oviedo, Spain. This masterpiece of 10th century Asturian gold work is kept in the Cámara Santa treasury.

The Cross of the Angels is a pre-romanesque Asturian reliquary donated by Alfonso II of Asturias in the year 808 to the Church of San Salvador in Oviedo, Asturias (Spain). The Cross of the Angels is the symbol of the city of Oviedo.

The Church of Saint Thyrsus is a Roman Catholic Asturian Romanesque church situated in Oviedo, in Asturias, northern Spain. The church was established in the 790s. Dedicated to Saint Thyrsus, it was built by Tioda, the royal architect of Alfonso II of Asturias. The Great Fire of Oviedo in 1521 and rebuilding in the 18th century removed most of the original church, except for a three-light window.

St. Mary of Bendones is an Asturian Pre-Romanesque Roman Catholic church situated in Bendones, Spain, build between 792 and 842.

Saint Peter of Nora is a Roman Catholic Pre-Romanesque church, located in Las Regueras, Asturias, Spain, beside the Nora river, about 12 km from Oviedo. The church is recorded for the first time in a donation document of Alfonso III of Asturias in 905.

Saint James of Gobiendes is a Roman Catholic pre-romanesque church, located in Gobiendes, next to Colunga, Asturias, Spain. It was built during the reign of Alfonso II of Asturias, its structure is typical of pre-romanesque Asturian architecture.

The Holy chamber of Oviedo is a Roman Catholic pre-Romanesque church in Oviedo, Spain, built next to pre-romanesque Tower of San Miguel of the city's cathedral. Nowadays, the church occupies the angle between the south arm of the cathedral transept and a side of the cloister.

The Church of the Monastery of San Miguel de Bárcena is a church located in Bárcena del Monasterio, Tineo, Asturias, Spain.