Related Research Articles

Gracilaria is a genus of red algae (Rhodophyta) notable for its economic importance as an agarophyte, as well as its use as a food for humans and various species of shellfish. Various species within the genus are cultivated among Asia, South America, Africa and Oceania.
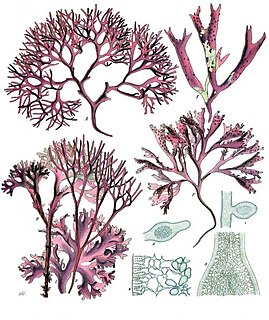
Red algae, or Rhodophyta, are one of the oldest groups of eukaryotic algae. The Rhodophyta also comprises one of the largest phyla of algae, containing over 7,000 currently recognized species with taxonomic revisions ongoing. The majority of species (6,793) are found in the Florideophyceae (class), and mostly consist of multicellular, marine algae, including many notable seaweeds. Red algae are abundant in marine habitats but are relatively rare in freshwaters. Approximately 5% of the red algae occur in freshwater environments with greater concentrations found in warmer areas. Except for two coastal cave dwelling species in the asexual class Cyanidiophyceae, there are no terrestrial species, which may be due to an evolutionary bottleneck where the last common ancestor lost about 25% of its core genes and much of its evolutionary plasticity.
Aquimarina agarilytica is a Gram-negative, aerobic, and rod-shaped bacterium from the genus of Aquimarina which has been isolated from the alga Porphyra haitanensis near the Nan'ao County from the China sea near China.
Phaeodactylibacter is a genus from the family Lewinellaceae.
Phaeodactylibacter luteus is a Gram-negative, aerobic and non-motile bacterium from the genus of Rubidimonas which has been isolated from the alga Picochlorum from the Indian Ocean.
Phaeodactylibacter xiamenensis is a Gram-negative, aerobic, rod-shaped, chemoheterotrophic and non-motile bacterium from the genus of Rubidimonas which has been isolated from the alga Phaeodactylum tricornutum from Xiamen in China.

Anicequol is a naturally occurring ergostane or lanostane steroid produced by Acremonium sp. TF-0356 which has nerve growth factor-like neurotrophic activity. It was under investigation by Taisho Pharmaceutical in Japan for the treatment of cognitive disorders in the 1990s, but development was discontinued and the drug was never marketed.
Catenovulum is a bacteria genus from the family of Alteromonadaceae.
Catenovulum maritimum is a Gram-negative, heterotrophic and facultatively anaerobic bacterium from the genus of Catenovulum which has been isolated from surface of the alga Porphyra yezoensis from Weihai in China.
Amylibacter is a genus of bacteria from the family of Rhodobacteraceae.
Kordia ulvae is a Gram-negative, aerobic and rod-shaped bacterium from the genus of Kordia which has been isolated from the alga Ulva.
Winogradskyella endarachnes is a Gram-negative, aerobic, rod-shaped and motile bacterium from the genus of Winogradskyella which has been isolated from the alga Endarachne binghamiae.
Reichenbachiella versicolor is a Gram-negative, strictly aerobic and rod-shaped bacterium from the genus of Reichenbachiella which has been isolated from the alga Gracilaria blodgettii from the coast of Lingshui County.
Lacinutrix algicola is a Gram-negative, aerobic and heterotrophic bacterium from the genus of Lacinutrix which has been isolated from a red alga.
Lacinutrix chionocetis is a Gram-negative, aerobic, rod-shaped and non-motile bacterium from the genus of Lacinutrix which has been isolated from the gut of a red snow crab.
Lacinutrix cladophorae is a Gram-negative, strictly aerobic, rod-shaped and motile bacterium from the genus of Lacinutrix which has been isolated from the alga Cladophora stimpsonii.
Lacinutrix himadriensis is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped, psychrophilic and non-motile bacterium from the genus of Lacinutrix.
Lacinutrix salivirga is a Gram-negative, strictly aerobic, rod-shaped and motile bacterium from the genus of Lacinutrix which has been isolated from seawater from Korea.
Lacinutrix venerupis is a Gram-negative, strictly aerobic and non-motile bacterium from the genus of Lacinutrix which has been isolated from clams from Galicia in Spain.
References
- 1 2 "Species: Lacinutrix gracilariae". lpsn.dsmz.de.
- 1 2 Huang, Zhaobin; Li, Guizhen; Lai, Qiliang; Gu, Li; Shao, Zongze (1 February 2016). "Lacinutrix gracilariae sp. nov., isolated from the surface of a marine red alga Gracilaria sp". International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology. 66 (2): 587–591. doi:10.1099/ijsem.0.000755.
- 1 2 "Lacinutrix gracilariae". www.uniprot.org.