Azerbaijan is a country in the Caucasus region, situated at the juncture of Eastern Europe and West Asia. Three physical features dominate Azerbaijan: the Caspian Sea, whose shoreline forms a natural boundary to the east; the Greater Caucasus mountain range to the north; and the extensive flatlands at the country's center. About the size of Portugal or the US state of Maine, Azerbaijan has a total land area of approximately 86,600 square kilometers, less than 1% of the land area of the former Soviet Union. Of the three Transcaucasian states, Azerbaijan has the greatest land area. Special administrative subdivisions are the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic, which is separated from the rest of Azerbaijan by a strip of Armenian territory, and the Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Region, entirely within Azerbaijan. The status of Nagorno-Karabakh is disputed by Armenia, but is internationally recognized as territory of Azerbaijan.

Ivory Coast is a sub-Saharan nation in southern West Africa located at 8 00°N, 5 00°W. The country is approximately square in shape. Its southern border is a 515 km (320 mi) coastline on the Gulf of Guinea on the north Atlantic Ocean. On the other three sides it borders five other African nations for a total of 3,458 km (2,149 mi): Liberia to the southwest for 778 km (483 mi), Guinea to the northwest for 816 km (507 mi), Mali to the north-northwest for 599 km (372 mi), Burkina Faso to the north-northeast for 545 km (339 mi), and Ghana to the east for 720 km (447 mi).

Cyprus is an island country in the Eastern Basin of the Mediterranean Sea. It is the third-largest island in the Mediterranean, after the Italian islands of Sicily and Sardinia, and the 80th-largest island in the world by area. It is located south of the Anatolian Peninsula, yet it belongs to the Cyprus Arc. Geographically, Cyprus is located in West Asia, but the country is considered a European country in political geography. Cyprus also had lengthy periods of mainly Greek and intermittent Anatolian, Levantine, Byzantine, Turkish, and Western European influence.

Denmark is a Nordic country located in Northern Europe. It consists of the Jutland Peninsula and several islands in the Baltic Sea, referred to as the Danish Archipelago. Denmark is located southwest of Sweden and due south of Norway and is bordered by the German state Schleswig-Holstein to the south, on Denmark's only land border, 68 kilometres long.
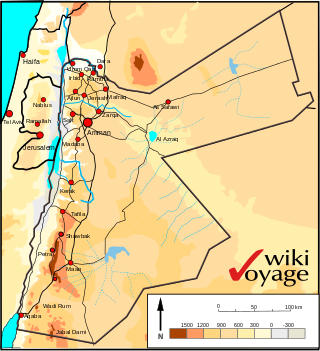
Jordan is situated geographically in West Asia, south of Syria, west of Iraq, northwest of Saudi Arabia, east of Israel. The area is also referred to as the Middle or Near East. The territory of Jordan now covers about 91,880 square kilometres (35,480 sq mi).
Kazakhstan is located in Central Asia. With an area of about 2,724,900 square kilometers (1,052,100 sq mi) Kazakhstan is more than twice the combined size of the other four Central Asian states and 60% larger than Alaska. The country borders Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, and Kyrgyzstan to the south; Russia to the north; Russia and the Caspian Sea to the west; and China's Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region to the east.
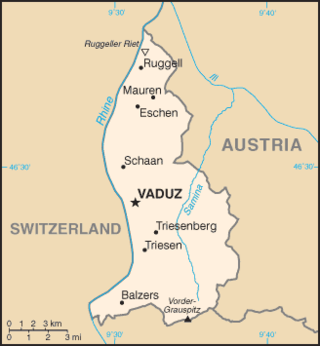
The principality of Liechtenstein encompasses most of the eastern half of the Rhine Valley, wedged between Austria and Switzerland. The majority of the country's population is found in the western half along the Rhine River. Along with Uzbekistan, Liechtenstein is one of only two doubly landlocked countries in the world.

China has great physical diversity. The eastern plains and southern coasts of the country consist of fertile lowlands and foothills. They are the location of most of China's agricultural output and human population. The southern areas of the country consist of hilly and mountainous terrain. The west and north of the country are dominated by sunken basins, rolling plateaus, and towering massifs. It contains part of the highest tableland on earth, the Tibetan Plateau, and has much lower agricultural potential and population.

The term "United States," when used in the geographical sense, refers to the contiguous United States, the state of Alaska, the island state of Hawaii, the five insular territories of Puerto Rico, Northern Mariana Islands, U.S. Virgin Islands, Guam, and American Samoa, and minor outlying possessions. The United States shares land borders with Canada and Mexico and maritime borders with Russia, Cuba, The Bahamas, and many other countries, mainly in the Caribbeanin addition to Canada and Mexico. The northern border of the United States with Canada is the world's longest bi-national land border.

Malawi is a landlocked country in southeast Africa. It is wholly within the tropics; from about 9°30S at its northernmost point to about 17°S at the southernmost tip. The country occupies a thin strip of land between Zambia and Mozambique, extending southwards into Mozambique along the valley of the Shire River. In the north and north east it also shares a border with Tanzania. Malawi is connected by rail to the Mozambican ports of Nacala and Beira. It lies between latitudes 9° and 18°S, and longitudes 32° and 36°E.

Iceland is an island country at the confluence of the North Atlantic and Arctic oceans, east of Greenland and immediately south of the Arctic Circle, atop the constructive boundary of the northern Mid-Atlantic Ridge. The island country is the world's 18th largest in area and one of the most sparsely populated. It is the westernmost European country when not including Greenland and has more land covered by glaciers than continental Europe. Its total size is 103,125 km2 (39,817 sq mi) and possesses an exclusive economic zone of 751,345 km2 (290,096 sq mi).

The geography of Chile is extremely diverse as the country extends from a latitude of 17° South to Cape Horn at 56° and from the ocean on the west to Andes on the east. Chile is situated in southern South America, bordering the South Pacific Ocean and a small part of the South Atlantic Ocean. Chile's territorial shape is among the world's most unusual. From north to south, Chile extends 4,270 km (2,653 mi), and yet it only averages 177 km (110 mi) east to west. Chile reaches from the middle of South America's west coast straight down to the southern tip of the continent, where it curves slightly eastward. Diego Ramírez Islands and Cape Horn, the southernmost points in the Americas, where the Pacific and Atlantic oceans meet, are Chilean territory. Chile's northern neighbors are Peru and Bolivia, and its border with Argentina to the east, at 5,150 km (3,200 mi), is the world's third-longest. The total land size is 756,102 km2 (291,933 sq mi). The very long coastline of 6,435 km (3,999 mi) gives it the 11th largest exclusive economic zone of 3,648,532 km2 (1,408,706 sq mi).

Anguilla is an island in the Leeward Islands. It has numerous bays, including Barnes, Little, Rendezvous, Shoal, and Road Bays.

Benin, a narrow, key-shaped, north–south strip of land in West Africa, lies between the Equator and the Tropic of Cancer. Its latitude ranges from 6°30′ N to 12°30′ N and its longitude from 1° E to 3°40′ E. It is bounded by Togo to the west, Burkina Faso and Niger to the north, Nigeria to the east, and the Bight of Benin to the south.

The Gambia is a very small and narrow African country with the border based on the Gambia River. The country is less than 48 kilometres (30 mi) wide at its greatest width. The country's present boundaries were defined in 1889 after an agreement between the United Kingdom and France. It is often claimed by Gambians that the distance of the borders from the Gambia River corresponds to the area that British naval cannon of the time could reach from the river's channel. However, there is no historical evidence to support the story, and the border was actually delineated using careful surveying methods by the Franco-British boundary commission. The Gambia is almost an enclave of Senegal and is the smallest country on mainland Africa.

Montenegro is a small, mountainous state in south-west Balkans. Montenegro borders Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbia, Albania, Kosovo and the Adriatic Sea. While being a small country at 13,812 km2, it is very diverse regarding the terrain configuration. Montenegro has 50 peaks of over 2,000m in altitude.

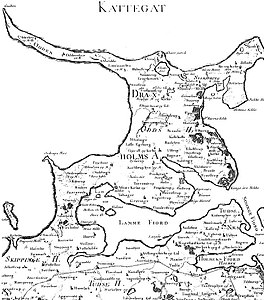
Odsherred is a peninsula in the north-western part of the island Zealand (Sjælland) in Denmark. Odsherred stretches from the Sjællands Odde in the north-west to the now drained Lammefjord in the south, covering an area with a wide range of the most typical Danish landscapes: long sandy beaches, small rolling hills and farming. The peninsula is served by the railway Odsherredsbanen, which runs through the most important towns, including Nykøbing Sjælland, Asnæs and Hørve.

Skjern River is the largest river in Denmark, in terms of volume. The river has its spring in Tinnet Krat in central Jutland, very close to Denmark's longest river, the Gudenå. It drains about one tenth of Denmark and flows into the Ringkøbing Fjord - a lagoon and former bay of the North Sea. The river has its name from town of Skjern, located at the river delta at Ringkøbing Fjord. In flood stage, it can discharge up to 200 m³/s.

The Zuidplaspolder is a polder in the western Netherlands, located northeast of Rotterdam, Zuid-Holland, neighbouring settlements such as Zuidplas, Zevenhuizen, Waddinxveen, Moerkapelle, Gouda, Moordrecht, and Nieuwerkerk aan den IJssel. It reaches a depth of 6.76 metres below average sea level. This makes it, along with Lammefjord in Denmark, the lowest point of the European Union.