Biostatistics are the development and application of statistical methods to a wide range of topics in biology. It encompasses the design of biological experiments, the collection and analysis of data from those experiments and the interpretation of the results.
Computer vision is an interdisciplinary scientific field that deals with how computers can gain high-level understanding from digital images or videos. From the perspective of engineering, it seeks to understand and automate tasks that the human visual system can do.
A parameter, generally, is any characteristic that can help in defining or classifying a particular system. That is, a parameter is an element of a system that is useful, or critical, when identifying the system, or when evaluating its performance, status, condition, etc.
Pattern recognition is the automated recognition of patterns and regularities in data. It has applications in statistical data analysis, signal processing, image analysis, information retrieval, bioinformatics, data compression, computer graphics and machine learning. Pattern recognition has its origins in statistics and engineering; some modern approaches to pattern recognition include the use of machine learning, due to the increased availability of big data and a new abundance of processing power. These activities can be viewed as two facets of the same field of application, and they have undergone substantial development over the past few decades.

Image registration is the process of transforming different sets of data into one coordinate system. Data may be multiple photographs, data from different sensors, times, depths, or viewpoints. It is used in computer vision, medical imaging, military automatic target recognition, and compiling and analyzing images and data from satellites. Registration is necessary in order to be able to compare or integrate the data obtained from these different measurements.

Solid modeling is a consistent set of principles for mathematical and computer modeling of three-dimensional solids. Solid modeling is distinguished from related areas of geometric modeling and computer graphics, such as 3D modeling, by its emphasis on physical fidelity. Together, the principles of geometric and solid modeling form the foundation of 3D-computer-aided design and in general support the creation, exchange, visualization, animation, interrogation, and annotation of digital models of physical objects.

Cluster analysis or clustering is the task of grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group are more similar to each other than to those in other groups (clusters). It is a main task of exploratory data analysis, and a common technique for statistical data analysis, used in many fields, including pattern recognition, image analysis, information retrieval, bioinformatics, data compression, computer graphics and machine learning.

Morphometrics or morphometry refers to the quantitative analysis of form, a concept that encompasses size and shape. Morphometric analyses are commonly performed on organisms, and are useful in analyzing their fossil record, the impact of mutations on shape, developmental changes in form, covariances between ecological factors and shape, as well for estimating quantitative-genetic parameters of shape. Morphometrics can be used to quantify a trait of evolutionary significance, and by detecting changes in the shape, deduce something of their ontogeny, function or evolutionary relationships. A major objective of morphometrics is to statistically test hypotheses about the factors that affect shape.
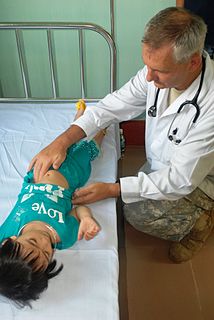
Palpation is the process of using one's hands to check the body, especially while perceiving/diagnosing a disease or illness. Usually performed by a health care practitioner, it is the process of feeling an object in or on the body to determine its size, shape, firmness, or location.
Spatial ecology studies the ultimate distributional or spatial unit occupied by a species. In a particular habitat shared by several species, each of the species is usually confined to its own microhabitat or spatial niche because two species in the same general territory cannot usually occupy the same ecological niche for any significant length of time.
In computer vision and image processing, a feature is a piece of information about the content of an image; typically about whether a certain region of the image has certain properties. Features may be specific structures in the image such as points, edges or objects. Features may also be the result of a general neighborhood operation or feature detection applied to the image. Other examples of features are related to motion in image sequences, or to shapes defined in terms of curves or boundaries between different image regions.

In statistics, Procrustes analysis is a form of statistical shape analysis used to analyse the distribution of a set of shapes. The name Procrustes refers to a bandit from Greek mythology who made his victims fit his bed either by stretching their limbs or cutting them off.
Statistical shape analysis is an analysis of the geometrical properties of some given set of shapes by statistical methods. For instance, it could be used to quantify differences between male and female gorilla skull shapes, normal and pathological bone shapes, leaf outlines with and without herbivory by insects, etc. Important aspects of shape analysis are to obtain a measure of distance between shapes, to estimate mean shapes from samples, to estimate shape variability within samples, to perform clustering and to test for differences between shapes. One of the main methods used is principal component analysis (PCA). Statistical shape analysis has applications in various fields, including medical imaging, computer vision, computational anatomy, sensor measurement, and geographical profiling.
The terms schema matching and mapping are often used interchangeably for a database process. For this article, we differentiate the two as follows: Schema matching is the process of identifying that two objects are semantically related while mapping refers to the transformations between the objects. For example, in the two schemas DB1.Student and DB2.Grad-Student ; possible matches would be: DB1.Student ≈ DB2.Grad-Student; DB1.SSN = DB2.ID etc. and possible transformations or mappings would be: DB1.Marks to DB2.Grades.
The point distribution model is a model for representing the mean geometry of a shape and some statistical modes of geometric variation inferred from a training set of shapes.
Object recognition – technology in the field of computer vision for finding and identifying objects in an image or video sequence. Humans recognize a multitude of objects in images with little effort, despite the fact that the image of the objects may vary somewhat in different view points, in many different sizes and scales or even when they are translated or rotated. Objects can even be recognized when they are partially obstructed from view. This task is still a challenge for computer vision systems. Many approaches to the task have been implemented over multiple decades.

3D reconstruction from multiple images is the creation of three-dimensional models from a set of images. It is the reverse process of obtaining 2D images from 3D scenes.
Medical image computing (MIC) is an interdisciplinary field at the intersection of computer science, information engineering, electrical engineering, physics, mathematics and medicine. This field develops computational and mathematical methods for solving problems pertaining to medical images and their use for biomedical research and clinical care.
Computational anatomy is an interdisciplinary field of biology focused on quantitative investigation and modelling of anatomical shapes variability. It involves the development and application of mathematical, statistical and data-analytical methods for modelling and simulation of biological structures.







