Glycomics is the comprehensive study of glycomes, including genetic, physiologic, pathologic, and other aspects. Glycomics "is the systematic study of all glycan structures of a given cell type or organism" and is a subset of glycobiology. The term glycomics is derived from the chemical prefix for sweetness or a sugar, "glyco-", and was formed to follow the omics naming convention established by genomics and proteomics.
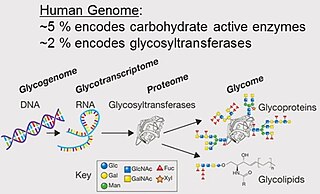
A glycome is the entire complement or complete set of all sugars, whether free or chemically bound in more complex molecules, of an organism. An alternative definition is the entirety of carbohydrates in a cell. The glycome may in fact be one of the most complex entities in nature. "Glycomics, analogous to genomics and proteomics, is the systematic study of all glycan structures of a given cell type or organism" and is a subset of glycobiology.

The Consortium for Functional Glycomics (CFG) is a large research initiative funded in 2001 by a glue grant from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS) to “define paradigms by which protein-carbohydrate interactions mediate cell communication”. To achieve this goal, the CFG studies the functions of:

Raymond Urgel Lemieux, CC, AOE, FRS was a Canadian organic chemist, who pioneered many discoveries in the field of chemistry, his first and most famous being the synthesis of sucrose. His contributions include the discovery of the anomeric effect and the development of general methodologies for the synthesis of saccharides still employed in the area of carbohydrate chemistry. He was a fellow of the Royal Society of Canada and the Royal Society (England), and a recipient of the prestigious Albert Einstein World Award of Science and Wolf Prize in Chemistry.

Robert G. Roeder is an American biochemist. He is known as a pioneer scientist in eukaryotic transcription. He discovered three distinct nuclear RNA polymerases in 1969 and characterized many proteins involved in the regulation of transcription, including basic transcription factors and the first mammalian gene-specific activator over five decades of research. He is the recipient of the Gairdner Foundation International Award in 2000, the Albert Lasker Award for Basic Medical Research in 2003, and the Kyoto Prize in 2021. He currently serves as Arnold and Mabel Beckman Professor and Head of the Laboratory of Biochemical and Molecular Biology at The Rockefeller University.
The terms glycans and polysaccharides are defined by IUPAC as synonyms meaning "compounds consisting of a large number of monosaccharides linked glycosidically". However, in practice the term glycan may also be used to refer to the carbohydrate portion of a glycoconjugate, such as a glycoprotein, glycolipid, or a proteoglycan, even if the carbohydrate is only an oligosaccharide. Glycans usually consist solely of O-glycosidic linkages of monosaccharides. For example, cellulose is a glycan composed of β-1,4-linked D-glucose, and chitin is a glycan composed of β-1,4-linked N-acetyl-D-glucosamine. Glycans can be homo- or heteropolymers of monosaccharide residues, and can be linear or branched.

Carolyn Ruth Bertozzi is an American chemist and Nobel laureate, known for her wide-ranging work spanning both chemistry and biology. She coined the term "bioorthogonal chemistry" for chemical reactions compatible with living systems. Her recent efforts include synthesis of chemical tools to study cell surface sugars called glycans and how they affect diseases such as cancer, inflammation, and viral infections like COVID-19. At Stanford University, she holds the Anne T. and Robert M. Bass Professorship in the School of Humanities and Sciences. Bertozzi is also an Investigator at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) and is the former director of the Molecular Foundry, a nanoscience research center at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.
Richard D. Cummings is an American biochemist who is the S. Daniel Abraham Professor of Surgery at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School in Boston, Massachusetts. He also the chief of the division of surgical sciences within the department of surgery. He is the director of the Harvard Medical School Center for Glycoscience, director of the National Center for Functional Glycomics, and also founder of the Glycomics Core at BIDMC. As of 2018 Cummings is also the scientific director of the Feihi Nutrition Laboratory at BIDMC. Before moving to BIDMC/HMS, Cummings was the William Patterson Timmie Professor and chair of the department of biochemistry at Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, Georgia from 2006 to 2015. At Emory, Cummings was a founder in 2007 of the Emory Glycomics Center.

Thomas Arthur Steitz was an American biochemist, a Sterling Professor of Molecular Biophysics and Biochemistry at Yale University, and investigator at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, best known for his pioneering work on the ribosome.
Eckard Wimmer is a German American virologist, organic chemist and distinguished professor of molecular genetics and microbiology at Stony Brook University. He is best known for his seminal work on the molecular biology of poliovirus and the first chemical synthesis of a viral genome capable of infection and subsequent production of live viruses.

A. Hari Reddi is a University of California Distinguished Professor and holder of the Lawrence J. Ellison Endowed Chair in Musculoskeletal Molecular Biology at the University of California, Davis. His research played an indispensable role in the identification, isolation and purification of bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) that are involved in bone formation and repair.
James C. Paulson is an American biochemist and biologist known for his work in glycobiology.

Margaret-Ann Armour was a Scottish-born Canadian chemist based at the University of Alberta. She is best known for her expertise in developing guidelines for hazardous lab waste disposal, and for being a vocal advocate for women in science. Armour founded the Women in Scholarship, Engineering, Science and Technology (WISEST) program, and served as the first and only Associate Dean of Science for Diversity at the University of Alberta. Among her many honors, she was named a member of the Order of Canada (2006), a 3M Teaching Fellow (1996) and a Canada 150 ambassador (2017).

Charles E. Warren was an assistant professor of biochemistry and molecular biology at the University of New Hampshire.
Ten Feizi is a Turkish Cypriot/British molecular biologist who is Professor and Director of the Glycosciences Laboratory at Imperial College London. Her research considers the structure and function of glycans. She was awarded the Society for Glycobiology Rosalind Kornfeld award in 2014. She was also awarded the Fellowship of the Academy of Medical Sciences in 2021.
Jessica R. Kramer is an American biomedical engineer working as an Assistant Professor of Bio-engineering and Adjunct Assistant Professor of Pharmaceutics and Pharmaceutical Chemistry at the University of Utah. Kramer’s research lab focuses on the synthesis and application of glycopolypeptides.
Toshifumi (Toshi) Yokota is a biomedical scientist and professor of medical genetics at the University of Alberta, also holding the titles of the Friends of Garrett Cumming Research & Muscular Dystrophy Canada Endowed Research Chair and the Henri M. Toupin Chair in Neurological Science. Known for pioneering research in antisense therapy for muscular dystrophy that led to the development of an FDA-approved drug viltolarsen, research interests encompass precision medicine for muscular dystrophy and genetic diseases. Publications exceed 100 refereed papers and patents, with contributions as co-editor to three books in the Methods in Molecular Biology series from Humana Press, Springer-Nature, Roles include fellow of the Canadian Academy of Health Sciences, a member of the editorial boards for numerous journals, a member of the Medical and Scientific Advisory Committee of Muscular Dystrophy Canada, chief scientific officer of OligomicsTx, and a co-founder of the Canadian Neuromuscular Network (CAN-NMD).
Todd Lambert Lowary is an American carbohydrate chemist. He is a professor of chemistry at the University of Alberta and a Fellow of the Royal Society of Canada.
GlycoRNAs are small non-coding RNAs with sialylated glycans.









