Related Research Articles

The striatum or corpus striatum is a cluster of interconnected nuclei that make up the largest structure of the subcortical basal ganglia. The striatum is a critical component of the motor and reward systems; receives glutamatergic and dopaminergic inputs from different sources; and serves as the primary input to the rest of the basal ganglia.

The basal ganglia (BG) or basal nuclei are a group of subcortical nuclei found in the brains of vertebrates. In humans and other primates, differences exist, primarily in the division of the globus pallidus into external and internal regions, and in the division of the striatum. Positioned at the base of the forebrain and the top of the midbrain, they have strong connections with the cerebral cortex, thalamus, brainstem and other brain areas. The basal ganglia are associated with a variety of functions, including regulating voluntary motor movements, procedural learning, habit formation, conditional learning, eye movements, cognition, and emotion.
The mesolimbic pathway, sometimes referred to as the reward pathway, is a dopaminergic pathway in the brain. The pathway connects the ventral tegmental area in the midbrain to the ventral striatum of the basal ganglia in the forebrain. The ventral striatum includes the nucleus accumbens and the olfactory tubercle.
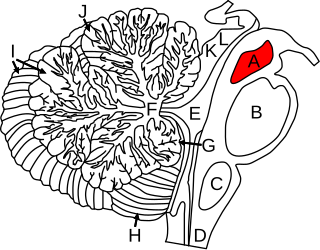
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the uppermost portion of the brainstem connecting the diencephalon and cerebrum with the pons. It consists of the cerebral peduncles, tegmentum, and tectum.

The nigrostriatal pathway is a bilateral dopaminergic pathway in the brain that connects the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) in the midbrain with the dorsal striatum in the forebrain. It is one of the four major dopamine pathways in the brain, and is critical in the production of movement as part of a system called the basal ganglia motor loop. Dopaminergic neurons of this pathway release dopamine from axon terminals that synapse onto GABAergic medium spiny neurons (MSNs), also known as spiny projection neurons (SPNs), located in the striatum.

The ventral tegmental area (VTA), also known as the ventral tegmental area of Tsai, or simply ventral tegmentum, is a group of neurons located close to the midline on the floor of the midbrain. The VTA is the origin of the dopaminergic cell bodies of the mesocorticolimbic dopamine system and other dopamine pathways; it is widely implicated in the drug and natural reward circuitry of the brain. The VTA plays an important role in a number of processes, including reward cognition and orgasm, among others, as well as several psychiatric disorders. Neurons in the VTA project to numerous areas of the brain, ranging from the prefrontal cortex to the caudal brainstem and several regions in between.

The reticular formation is a set of interconnected nuclei in the brainstem that spans from the lower end of the medulla oblongata to the upper end of the midbrain. The neurons of the reticular formation make up a complex set of neural networks in the core of the brainstem. The reticular formation is made up of a diffuse net-like formation of reticular nuclei which is not well-defined. It may be seen as being made up of all the interspersed cells in the brainstem between the more compact and named structures.

The pontine tegmentum, or dorsal pons, is the dorsal part of the pons located within the brainstem. The ventral part or ventral pons is known as the basilar part of the pons, or basilar pons. Along with the dorsal surface of the medulla oblongata, it forms part of the rhomboid fossa – the floor of the fourth ventricle.

The pedunculopontine nucleus (PPN) or pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus is a collection of neurons located in the upper pons in the brainstem. It is involved in voluntary movements, arousal, and provides sensory feedback to the cerebral cortex and one of the main components of the ascending reticular activating system. It is a potential target for deep brain stimulation treatment for Parkinson's disease. It was first described in 1909 by Louis Jacobsohn-Lask, a German neuroanatomist.

The tegmentum is a general area within the brainstem. The tegmentum is the ventral part of the midbrain and the tectum is the dorsal part of the midbrain. It is located between the ventricular system and distinctive basal or ventral structures at each level. It forms the floor of the midbrain (mesencephalon) whereas the tectum forms the ceiling. It is a multisynaptic network of neurons that is involved in many subconscious homeostatic and reflexive pathways. It is a motor center that relays inhibitory signals to the thalamus and basal nuclei preventing unwanted body movement.

The basal ganglia form a major brain system in all vertebrates, but in primates there are special differentiating features. The basal ganglia include the striatum, pallidus, substantia nigra and subthalamic nucleus. In primates the pallidus is divided into an external and internal globus pallidus, the external globus pallidus is present in other mammals but not the internal globus pallidus. Also in primates, the dorsal striatum is divided by a large nerve tract called the internal capsule into two masses named the caudate nucleus and the putamen. These differences contribute to a complex circuitry of connections between the striatum and cortex that is specific to primates, reflecting different functions in primate cortical areas.
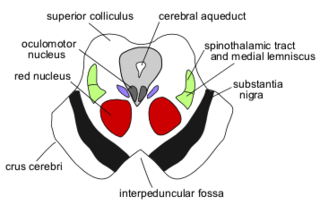
The central tegmental tract is a tract that carries ascending and descending fibers, situated in the midbrain tegmentum, and the pontine tegmentum. The tract is situated in the central portion of the reticular formation.
Sleep onset is the transition from wakefulness into sleep. Sleep onset usually transits into non-rapid eye movement sleep but under certain circumstances it is possible to transit from wakefulness directly into rapid eye movement sleep.
The interpeduncular nucleus (IPN) is an unpaired, ovoid group of neurons at the base of the midbrain tegmentum. In the midbrain it lies below the interpeduncular fossa. As the name suggests, the interpeduncular nucleus lies in between the cerebral peduncles.
Dopaminergic cell groups, DA cell groups, or dopaminergic nuclei are collections of neurons in the central nervous system that synthesize the neurotransmitter dopamine. In the 1960s, dopaminergic neurons or dopamine neurons were first identified and named by Annica Dahlström and Kjell Fuxe, who used histochemical fluorescence. The subsequent discovery of genes encoding enzymes that synthesize dopamine, and transporters that incorporate dopamine into synaptic vesicles or reclaim it after synaptic release, enabled scientists to identify dopaminergic neurons by labeling gene or protein expression that is specific to these neurons.

The parabrachial nuclei, also known as the parabrachial complex, are a group of nuclei in the dorsolateral pons that surrounds the superior cerebellar peduncle as it enters the brainstem from the cerebellum. They are named from the Latin term for the superior cerebellar peduncle, the brachium conjunctivum. In the human brain, the expansion of the superior cerebellar peduncle expands the parabrachial nuclei, which form a thin strip of grey matter over most of the peduncle. The parabrachial nuclei are typically divided along the lines suggested by Baxter and Olszewski in humans, into a medial parabrachial nucleus and lateral parabrachial nucleus. These have in turn been subdivided into a dozen subnuclei: the superior, dorsal, ventral, internal, external and extreme lateral subnuclei; the lateral crescent and subparabrachial nucleus along the ventrolateral margin of the lateral parabrachial complex; and the medial and external medial subnuclei
The rostromedial tegmental nucleus (RMTg), also known as the tail of the ventral tegmental area (tVTA), is a GABAergic nucleus which functions as a "master brake" for the midbrain dopamine system. This region was discovered by the researchers, M. Barrot, J.Kaufling and T. Jhou. It is poorly differentiated from the rest of the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and possesses robust functional and structural links to the dopamine pathways. Notably, both acute and chronic exposure to psychostimulants have been shown to induce FosB and ΔFosB expression in the RMTg; no other drug type has been shown to induce these proteins in the RMTg.
Tegmental nucleus may refer to:
The dorsal tegmental nucleus (DTN), also known as dorsal tegmental nucleus of Gudden, is a group of neurons located in the brainstem, which are involved in spatial navigation and orientation.
References
- ↑ Schröder, Hannsjörg; Moser, Natasha; Huggenberger, Stefan (2020-02-28). Neuroanatomy of the Mouse: An Introduction. Springer Nature. p. 134. ISBN 978-3-030-19898-5.