
Physalis angulata is an erect herbaceous annual plant belonging to the nightshade family Solanaceae. Its leaves are dark green and roughly oval, often with tooth shapes around the edge. The flowers are five-sided and pale yellow; the yellow-orange fruits are borne inside a balloon-like calyx. The exact native range is uncertain. The species may be naturally endemic to Australia or the Americas or the native range may encompass both the Americas and Australia. It is now widely distributed and naturalized in tropical and subtropical regions worldwide.

Nicolás Bautista Monardes was a Spanish physician and botanist.

Real Jardín Botánico de Madrid is an 8 hectares botanical garden in Madrid (Spain). The public entrance is located at Plaza de Murillo, next to the Prado Museum.

Contrayerva, or contrajerva, is the medicinal rhizome of various tropical Central American and South American species of Dorstenia in the family Moraceae, mainly Dorstenia contrajerva and the closely related Dorstenia drakena but also Dorstenia brasiliensis. The word contrayerva means “counter herb” in Spanish. It was given this name since a 16th-century description claimed that the leaves of a herb were used by South American Indians to counter the deadly poisonous effect of the same herb when used as an arrow poison. Seventeenth century herbalists and botanists identified this herb as the aromatic root that had been brought from Peru to England by Francis Drake, and claimed that it was an antidote against all kinds of poison. By the late 18th century contrayerva had lost its reputation as an antidote, but it continued to be listed in European and American pharmacopoeias and herbals until the 1920s as a gentle stimulant, tonic and diaphoretic. It is still used in folk medicine in Central and South America.
The Redalyc project is a bibliographic database and a digital library of Open Access journals, supported by the Universidad Autónoma del Estado de México with the help of numerous other higher education institutions and information systems.
Latindex is a bibliographical information system available for free consultation. Established as a network in 1997, the project is based on the cooperation of 17 national resource centers that operate in a coordinated scheme for the gathering and dissemination of relevant information and data on the Iberoamerican journals.
ʿAlī ibn al-Ḥusayn ibn al-Wāfid al-Lakhmī, known in Latin Europe as Abenguefith, was an Andalusian Arab pharmacologist and physician from Toledo. He was the vizier of Al-Mamun of Toledo. His main work is Kitāb al-adwiya al-mufrada.

The Austrian Latin America Institute is an interdisciplinary orientated organisation, aiming at intensifying dialogue and exchange between Austria and Latin America. It was founded as an association in 1965 and receives subsidies for its work in development politics as well as scientific and cultural events and projects. About half of the annual budget originates from its own resources, mainly language courses as well as membership fees. In 1994 the institute moved to the historic Palais Schlick in Vienna's 9th district Alsergrund.
The Pan American Journal of Public Health is a peer-reviewed open-access public health journal covering research and case studies on issues of public health significance, mainly in areas related to national and local health systems, to improve the health of the peoples of the Americas. The journal is published monthly by the Pan American Health Organization, a regional office of the World Health Organization. Articles are published in English, Portuguese, and Spanish.

Browningia candelaris is a species of cactus from northern Chile and southern Peru. It has a distinctive growth habit, with a straight spiny trunk topped by more-or-less spineless thinner branches. In some places, the long-term survival of local populations may be threatened by grazing, which destroys seedlings.

The Open Access Journal of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants is a biannual peer-reviewed open-access medical journal published by the Medicinal and Aromatic Plants Association of India. The journal was established in 2010 and covers all aspects of medicinal and aromatic plants. The present editor-in-chief is Manivel Ponnuchamy, Director (Acting), Directorate of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants Research, Anand
Anton Julius (Ton) Butter was a Dutch economist, Associate Professor the Department of Economics of the University of Amsterdam and deputy director of SEO Economic Research.
Sonia Álvarez Leguizamón is an Argentine sociologist and anthropologist. She earned a bachelor's degree in social work from the Catholic University of Santa Maria, and a master's degree in Development Sociology from the National University of Cordoba. She earned her Ph.D. at the University of Seville in Social and Cultural Anthropology. Alvarez Leguizamón was the University of Salta as the Dean of the Faculty of Humanities and as the Director of the Masters programme in Social Policy. Alvarez Leguizamón has also worked extensively with Comparative Research Programme on Poverty (CROP) for the last fifteen years on issues relating to their organization and to El Consejo Latinoamericano de Ciencias Sociales (CLASCO). Along with writing her own research, Alvarez Leguizamón has also served as an editor for the second edition of CROP's Glossary of Poverty.

Martha Ellen Davis is an emeritus professor from the University of Florida, anthropologist and ethnomusicologist known for her multifarious work on African diasporic religion and music. Professor Davis' research has defied conventional tenets about Haitian and Dominican folk music, and her cultural preservation projects has raised awareness of the significance of the Samaná Americanos' enclave.
The Revista Mexicana de Astronomía y Astrofísica is a peer-reviewed scientific journal of astronomy founded in 1974. It is a successor to the Boletín de los Observatorios de Tonantzintla y Tacubaya which was published from 1952 to 1972.

Ádám Anderle was a Hungarian historian, hispanist, full (university) professor, professor emeritus of Faculty of Arts, University of Szeged (SZTE). He was active in research of the relationship between Latin America and Hungary for decades. He was fluent in Hungarian and Spanish.
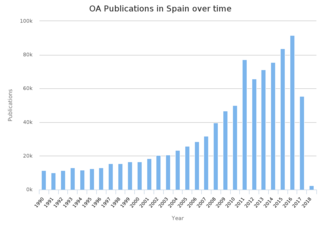
In Spain, the national 2011 "Ley de la Ciencia, la Tecnología y la Innovación" requires open access publishing for research that has been produced with public funding. The first peer-reviewed open access Spanish journal, Relieve, began in 1995. Publishers CSIC Press and Hipatia Press belong to the international Open Access Scholarly Publishers Association.

Vismia baccifera is a tropical plant used by indigenous peoples in South America, in Colombian Amazon as well as Brazil, infused as traditional medicine. It has been demonstrated to have great antitumor capability in kidney and liver by inducing massive oxidative stress in cancer cells, but not healthy cells, leading to rapid death of cancer cells. One of the phytochemicals it contains is lichexanthone.

María Fernanda Beigel is an Argentine sociologist and scientist who develops her research at the crossroads between Bourdieu's reflexivity and the Latin American historical-structural tradition.
The European Review of Latin American and Caribbean Studies(ERLACS) (Spanish: Revista Europea de Estudios Latinoamericanos y del Caribe) is a open access, peer-reviewed academic journal published semi-annually by the Centre for Latin American Research and Documentation in Amsterdam, which serves as a hub for Latin American research in Europe. Articles in English and Spanish present empirical research and theoretical innovation in social sciences and history. The journal also features book reviews, institutional news, and film reviews.











