
Fine Gael is a liberal-conservative political party in Ireland. Fine Gael is currently the governing and largest party in Ireland in terms of members of the Oireachtas and Irish members of European Parliament. The party has a membership of 21,000 and is the senior partner governing in a minority coalition with several independent politicians, with party leader Leo Varadkar serving as Taoiseach. Varadkar succeeded Enda Kenny as party leader on 2 June 2017 and as Taoiseach on 14 June; Kenny had been leader since 2002, and Taoiseach since 2011.

The politics of Latvia takes place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic republic, whereby the Prime Minister is the head of government, and of a multi-party system. The President holds a primarily ceremonial role as Head of State. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and parliament, the Saeima. The Judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature. The Economist Intelligence Unit has rated Latvia as "flawed democracy" in 2017.

The Scottish devolution referendum of 1997 was a pre-legislative referendum held in Scotland on 11 September 1997 over whether there was support for the creation of a Scottish Parliament with devolved powers, and whether the Parliament should have tax-varying powers. The result was "Yes–Yes": a majority voted in favour of both proposals, and the Parliament was established following an election in 1999. Turnout for the referendum was 60.4%.

The Scottish referendum of 1979 was a post-legislative referendum to decide whether there was sufficient support for a Scottish Assembly proposed in the Scotland Act 1978 among the Scottish electorate. This was an act to create a devolved deliberative assembly for Scotland. An amendment to the Act stipulated that it would be repealed if less than 40% of the total electorate voted "Yes" in the referendum. The result was that 51.6% supported the proposal, but with a turnout of 64%, this represented only 32.9% of the registered electorate. The Act was subsequently repealed.
The Fourth Amendment of the Constitution Act 1972 is an amendment to the Constitution of Ireland which lowered the voting age for all national elections and referendums in the state from twenty-one to eighteen years of age. It was approved by referendum on 7 December 1972 and signed into law on 5 January 1973.
There are three types of elections in Denmark: elections to the national parliament, local elections and elections to the European Parliament. Referendums may also be called to consult the Danish citizenry directly on an issue of national concern.

Referendums are held only occasionally by the Government of New Zealand. Referendums may be government-initiated or held in accordance with the Electoral Act 1993 or the Citizens Initiated Referenda Act 1993. Ten referendums have been held so far. Seven were government-led, and three were indicative citizen initiatives.

The Romanian presidential impeachment referendum of 2007 was conducted in order to determine whether the president of Romania Traian Băsescu should be forced to step down.

A referendum on two proposed security laws was held in Latvia on 7 July 2007; the referendum had been called after the president refused to sign the laws, claiming possible influence of oligarchs on Latvia's national security, and after 212,000 signatures had been collected, meeting the requirement of about 150,000 signatures. Although the referendum failed to reach the quorum of 453,730 votes, the results showed massive disapproval of the amendments.

A constitutional referendum to amend the constitution of Latvia in order to allow one-tenth of the total registered electorate to initiate a popular referendum to dissolve the Latvian parliament was held in Latvia on 2 August 2008.
Electoral reform is change in electoral systems to improve how public desires are expressed in election results. That can include reforms of:
The Alliance for European Integration was the centre-right anti-communist ruling coalition in Moldova from the July 2009 election until it lost a no confidence vote on February 13, 2013. It was succeeded by the anti-communist Pro-European Coalition.
Six referendums were held in Switzerland during 2010; three in March on pension funds, animal protection and a constitutional amendment, one in September on unemployment benefits, and two in November on deporting foreign criminals and introducing a canton tax.
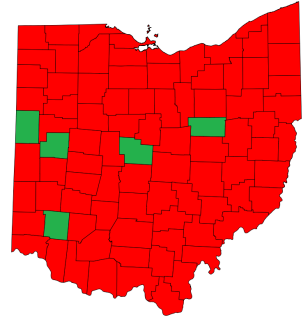
The Ohio Collective Bargaining Limit Repeal appeared on the November 8, 2011 general election ballot in the state of Ohio as a veto referendum. Senate Bill 5 (SB5) was repealed by Ohio voters after a campaign by firefighters, police officers and teachers against the measure, which would have limited collective bargaining for public employees in the state. The formal title of the proposal that this measure nullified is Senate Bill 5. Among other provisions, SB 5 would have prevented unions from charging fair share dues to employees who opt out. The process to place the referendum on the ballot for voters to decide was completed by supporters, as signatures were certified by the Ohio Secretary of State. The group behind the referendum effort was the political action committee We Are Ohio.

A constitutional referendum on the "Amendments to the Constitution of the Republic of Latvia" was held on 18 February 2012. Proposed amendments included Articles 4, 18, 21, 101 and 104 of the Constitution of Latvia by adding the condition about Russian as the second official language, as well as prescribing two working languages — Latvian and Russian — for self-government institutions. The referendum's question was "Do you support the adoption of the Draft Law "Amendments to the Constitution of the Republic of Latvia" that provides for the Russian language the status of the second official language?".
The Thirty-second Amendment of the Constitution Bill 2013 was a proposal to amend the Constitution of Ireland to abolish Seanad Éireann, the upper house of the Irish parliament, the Oireachtas. The proposal was rejected by the electorate in a referendum on 4 October 2013 by 51.7% voting against to 48.3% in favour.
A referendum is a direct vote in which an entire electorate is asked to either accept or reject a particular proposal. This article summarises referendum laws and practice in various countries.

Maine Question 4, formally An Act to Raise the Minimum Wage, is a citizen-initiated referendum question that appeared on the Maine November 8, 2016 statewide ballot. It sought to increase Maine's minimum wage from $7.50 per hour to $12 an hour by 2020, as well as increasing the minimum wage for tipped employees gradually to the same level by 2024. It would also index increases after 2024 to inflation. As the Maine Legislature and Governor Paul LePage declined to enact the proposal as written, it appeared on the ballot along with elections for President of the United States, Maine's two U.S. House seats, the Legislature, other statewide ballot questions, and various local elections. Efforts to place a competing, more moderate proposal alongside the citizen-initiated bill were unsuccessful.

The Thirty-sixth Amendment of the Constitution of Ireland is an amendment to the constitution of Ireland which permits the Oireachtas to legislate for abortion. The constitution had previously prohibited abortion unless there was a serious risk to the life of the mother.












